1、概述
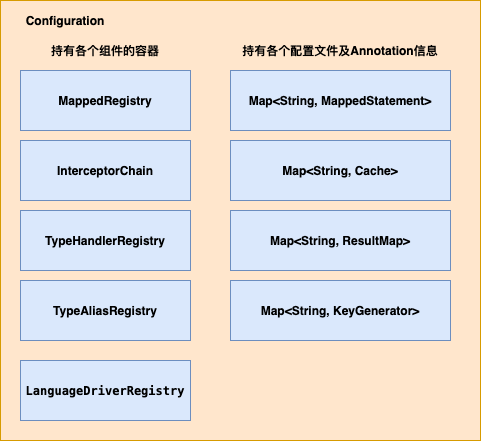
Configuration类的作用之前的文章中说明过,该类主要是用来存储Mybatis的运行时的数据。比如MappedStatement,本文主要是从Configuration的各个组件来入手从整体上说明Mybatis的运行时数据的构建等等。
Configuration类的主要功能大概分为以下两类:
(1)、持有或者构建各个Mybatis运行时的组件
(2)、存储相关配置文件及Annotation的运行时信息
2、MappedRegistry
MappedRegistry类的主要功能有两个:
(1)、负责根据类型或者名称空间来创建MappedStatement等映射器数据
(2)、负责为每个接口注册一个MapperProxyFactory
2.1、构建映射器数据
构建映射器数据分为两种方式一种是通过注解的方式,另一种是通过xml文件的方式。
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 通过package的方式来构建映射器数据,
// 这种方式会扫描包下的全部类,然后通过注解的方式构建映射器数据。
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
// 获取name属性
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
// 通过包名的方式来获取映射器数据
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
// 获取resource数据
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
// 获取url数据
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
// 获取class数据
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
// 通过resource的方式来构建映射器数据
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 通过XML的方式来构建映射器数据
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
// 通过url的方式来构建映射器数据
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
// 通过XML的方式来构建映射器数据
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
// 通过class的方式来构建映射器数据
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
// 获取接口类型
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
// 通过注解的方式来构建映射器数据
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
2.1.1、通过XML文件的方式来构建映射器数据
通过XML文件的方式来构建映射器数据是通过XMLMapperBuilder来实现的。代码如下:
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 解析mapper节点的映射器数据
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 标记该resource已经被解析过
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 生成对应的MapperProxyFactory,内部会调用Configuration的addMapper()
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
// 解析未完成的相关数据
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
configurationElement()方法的代码如下:
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// 获取namespace的属性
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
// 设置当前的namespace属性
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
// 解析cache-ref属性
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
// 解析cache属性
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
// 解析parameter属性
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
// 解析resultMap属性
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
// 解析sql属性
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 解析select|insert|update|delete标签的属性
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
具体分部的详细解析代码不再列出。
2.1.2、通过注解的方式来构建映射器数据
通过注解的方式来构建映射器数据入口是Configuration通过MapperRegistry来进行的。
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 首先类型必须是接口。
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 将mapper注册到Configuration中供SqlSession使用。
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
// 通过MapperAnnotationBuilder来解析接口中映射器数据。
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
// 最后需要判断下是否成功解析,如果没有解析完成,那么还需要移除该类型。
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
具体的解析操作则是依赖MapperAnnotationBuilder。
这里具体分析下MappedStatement及SqlSource的整体设计结构。
MappedStatement对象通过XML及Annotation中构建代码如下所示:
XML中构建MappedStatement代码如下:
public void parseStatementNode() {
// 获取标签的id属性
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
// 获取标签的databaseId属性
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
// 获取标签的名称
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// 解析SQL类型
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
// 判断是否是查询语句
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// 获取flushCache属性,如果不是select语句,则为true
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
// 获取useCache属性,如果是select语句,则为true
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
// 获取resultOrdered,默认情况下为false
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
// 解析include标签
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
// LanguageDriver的作用是生成SqlSource
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
// 生成SqlSource
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
// 获取其他的属性
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
if (resultSetTypeEnum == null) {
resultSetTypeEnum = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
}
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
// 通过MapperBuilderAssistant来创建和注册MappedStatement
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
Annotation中构建MappedStatement代码如下所示:
void parseStatement(Method method) {
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
SqlSource sqlSource = getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(method, parameterTypeClass, languageDriver);
if (sqlSource != null) {
Options options = method.getAnnotation(Options.class);
final String mappedStatementId = type.getName() + "." + method.getName();
Integer fetchSize = null;
Integer timeout = null;
StatementType statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
ResultSetType resultSetType = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = getSqlCommandType(method);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = !isSelect;
boolean useCache = isSelect;
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyProperty = null;
String keyColumn = null;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) || SqlCommandType.UPDATE.equals(sqlCommandType)) {
// first check for SelectKey annotation - that overrides everything else
SelectKey selectKey = method.getAnnotation(SelectKey.class);
if (selectKey != null) {
keyGenerator = handleSelectKeyAnnotation(selectKey, mappedStatementId, getParameterType(method), languageDriver);
keyProperty = selectKey.keyProperty();
} else if (options == null) {
keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
} else {
keyGenerator = options.useGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
keyProperty = options.keyProperty();
keyColumn = options.keyColumn();
}
} else {
keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
if (options != null) {
if (FlushCachePolicy.TRUE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = true;
} else if (FlushCachePolicy.FALSE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = false;
}
useCache = options.useCache();
fetchSize = options.fetchSize() > -1 || options.fetchSize() == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? options.fetchSize() : null; //issue #348
timeout = options.timeout() > -1 ? options.timeout() : null;
statementType = options.statementType();
if (options.resultSetType() != ResultSetType.DEFAULT) {
resultSetType = options.resultSetType();
}
}
String resultMapId = null;
if (isSelect) {
ResultMap resultMapAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class);
if (resultMapAnnotation != null) {
resultMapId = String.join(",", resultMapAnnotation.value());
} else {
resultMapId = generateResultMapName(method);
}
}
assistant.addMappedStatement(
mappedStatementId,
sqlSource,
statementType,
sqlCommandType,
fetchSize,
timeout,
// ParameterMapID
null,
parameterTypeClass,
resultMapId,
getReturnType(method),
resultSetType,
flushCache,
useCache,
// TODO gcode issue #577
false,
keyGenerator,
keyProperty,
keyColumn,
// DatabaseID
null,
languageDriver,
// ResultSets
options != null ? nullOrEmpty(options.resultSets()) : null);
}
}
这里重点说明下通过LanguageDriver构建SqlSource。
LanguageDriver该类的功能主要是创建SqlSource。mybatis允许用户自定义LanguageDriver实现类。
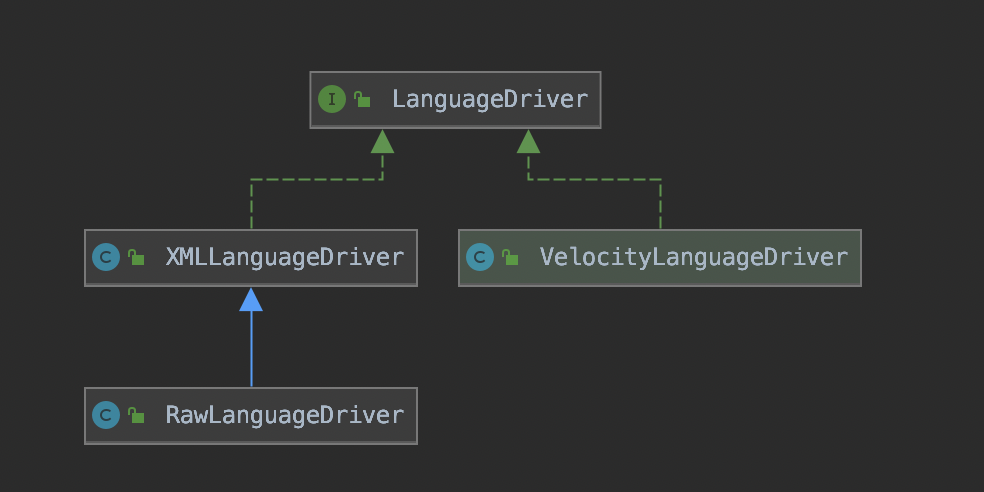
在mybatis中如果用户不指定lang属性的话,默认的LanguageDriver是XMLLanguageDriver,这个对象是在Configuration的构造函数中注册的。
mybatis这里将XML及Annotation解析统一放到XMLLanguageDriver中了。
看下XMLLanguageDriver的代码:
// XML标签解析SqlSource
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
// 使用XMLScriptBuilder来解析并生成SqlSource
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}
// Annotation属性解析成SqlSource
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType) {
// issue #3
if (script.startsWith("<script>")) {
XPathParser parser = new XPathParser(script, false, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver());
return createSqlSource(configuration, parser.evalNode("/script"), parameterType);
} else {
// issue #127
// 将SQL中的${}代表的内容进行替换
script = PropertyParser.parse(script, configuration.getVariables());
// 封装成TextSqlNode
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(script);
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
return new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, textSqlNode);
} else {
return new RawSqlSource(configuration, script, parameterType);
}
}
}
判断是否是Dynamic具体代码如下:
public boolean isDynamic() {
DynamicCheckerTokenParser checker = new DynamicCheckerTokenParser();
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(checker);
parser.parse(text);
return checker.isDynamic();
}
private GenericTokenParser createParser(TokenHandler handler) {
// 字符串中存在"${", "}",则使用DynamicSqlSource
return new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
}
否则使用RawSqlSource
两个类的相关代码如下所示:
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<>());
}
// RowSqlSource
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
return sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
// DynamicSqlSource
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : context.getBindings().entrySet()) {
boundSql.setAdditionalParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
return boundSql;
}
DynamicSqlSource和RawSqlSource
1、DynamicSqlSource解析含有${}的sql语句,而RawSqlSource解析含有#{}的sql语句。
2、DynamicSqlSource涵盖的操作比RawSqlSource多了一步,便是优先处理${}字符,其本身也会调用去解析#{}字符。
3、${}语句的解析是最终转换为Statement直接执行,其中的参数赋值是直接赋值,不做字符串引号拼装;而#{}语句的解析是最终转换为PrepareStatement预表达式来进行sql执行,安全性很高。
所以这里单独使用SqlSource来封装SQL,是用来实现不同的SQL风格的,比如#和$。
在说明下这里遇到的构建MappedStatement类的Builder模式
public final class MappedStatement {
private String resource;
private Configuration configuration;
private String id;
private Integer fetchSize;
private Integer timeout;
private StatementType statementType;
private ResultSetType resultSetType;
private SqlSource sqlSource;
private Cache cache;
private ParameterMap parameterMap;
private List<ResultMap> resultMaps;
private boolean flushCacheRequired;
private boolean useCache;
private boolean resultOrdered;
private SqlCommandType sqlCommandType;
private KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
private String[] keyProperties;
private String[] keyColumns;
private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;
private String databaseId;
private Log statementLog;
private LanguageDriver lang;
private String[] resultSets;
MappedStatement() {
// constructor disabled
}
public static class Builder {
private MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement();
public Builder(Configuration configuration, String id, SqlSource sqlSource, SqlCommandType sqlCommandType) {
mappedStatement.configuration = configuration;
mappedStatement.id = id;
mappedStatement.sqlSource = sqlSource;
mappedStatement.statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
mappedStatement.resultSetType = ResultSetType.DEFAULT;
mappedStatement.parameterMap = new ParameterMap.Builder(configuration, "defaultParameterMap", null, new ArrayList<>()).build();
mappedStatement.resultMaps = new ArrayList<>();
mappedStatement.sqlCommandType = sqlCommandType;
mappedStatement.keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
String logId = id;
if (configuration.getLogPrefix() != null) {
logId = configuration.getLogPrefix() + id;
}
mappedStatement.statementLog = LogFactory.getLog(logId);
mappedStatement.lang = configuration.getDefaultScriptingLanguageInstance();
}
public Builder resource(String resource) {
mappedStatement.resource = resource;
return this;
}
public String id() {
return mappedStatement.id;
}
public Builder parameterMap(ParameterMap parameterMap) {
mappedStatement.parameterMap = parameterMap;
return this;
}
public Builder resultMaps(List<ResultMap> resultMaps) {
mappedStatement.resultMaps = resultMaps;
for (ResultMap resultMap : resultMaps) {
mappedStatement.hasNestedResultMaps = mappedStatement.hasNestedResultMaps || resultMap.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
return this;
}
public Builder fetchSize(Integer fetchSize) {
mappedStatement.fetchSize = fetchSize;
return this;
}
public Builder timeout(Integer timeout) {
mappedStatement.timeout = timeout;
return this;
}
public Builder statementType(StatementType statementType) {
mappedStatement.statementType = statementType;
return this;
}
public Builder resultSetType(ResultSetType resultSetType) {
mappedStatement.resultSetType = resultSetType == null ? ResultSetType.DEFAULT : resultSetType;
return this;
}
public Builder cache(Cache cache) {
mappedStatement.cache = cache;
return this;
}
public Builder flushCacheRequired(boolean flushCacheRequired) {
mappedStatement.flushCacheRequired = flushCacheRequired;
return this;
}
public Builder useCache(boolean useCache) {
mappedStatement.useCache = useCache;
return this;
}
public Builder resultOrdered(boolean resultOrdered) {
mappedStatement.resultOrdered = resultOrdered;
return this;
}
public Builder keyGenerator(KeyGenerator keyGenerator) {
mappedStatement.keyGenerator = keyGenerator;
return this;
}
public Builder keyProperty(String keyProperty) {
mappedStatement.keyProperties = delimitedStringToArray(keyProperty);
return this;
}
public Builder keyColumn(String keyColumn) {
mappedStatement.keyColumns = delimitedStringToArray(keyColumn);
return this;
}
public Builder databaseId(String databaseId) {
mappedStatement.databaseId = databaseId;
return this;
}
public Builder lang(LanguageDriver driver) {
mappedStatement.lang = driver;
return this;
}
public Builder resultSets(String resultSet) {
mappedStatement.resultSets = delimitedStringToArray(resultSet);
return this;
}
/**
* Resul sets.
*
* @param resultSet
* the result set
* @return the builder
* @deprecated Use {@link #resultSets}
*/
@Deprecated
public Builder resulSets(String resultSet) {
mappedStatement.resultSets = delimitedStringToArray(resultSet);
return this;
}
public MappedStatement build() {
assert mappedStatement.configuration != null;
assert mappedStatement.id != null;
assert mappedStatement.sqlSource != null;
assert mappedStatement.lang != null;
mappedStatement.resultMaps = Collections.unmodifiableList(mappedStatement.resultMaps);
return mappedStatement;
}
}
}
mybatis中所有的类似的数据全部都是采用这种构造器模式。
2.2、注册MapperProxyFactory
在Mybatis中每个用户定义的接口实际上都使用动态代理技术来创建具体的实现类,这个实现类里面通过封装SqlSession来完成数据库的相关操作。
MapperProxyFactory是一个MapperProxy的工厂类,用来创建MapperProxy对象。
相关代码如下:
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
// mapper的接口类型
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// 接口中的方法及MapperMethodInvoker的缓存
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
// 通过动态代理来创建一个关于mapperInterface的实现类
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
// 创建代理对象
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
Mybatis中使用了MapperProxy来执行具体的代理逻辑。
具体的字段如下所示:
// 用于执行真正的数据库操作
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
// mapper的接口
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// 缓存接口中的方法
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache;
MapperProxy实现了InvocationHandler,同时实现了对应的invoke方法,代码如下:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, m -> {
// 兼容了接口的默认方法
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
// 如果不是默认方法则使用PlainMethodInvoke
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
MapperProxy的invoke方法中调用了PlainMethodInvoker的invoke方法。
MapperMethodInvoker的实现类PlainMethodInvoker的实现如下所示:
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
// 调用mapperMethod的execute方法。
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
MapperMethod的类结构如下:
// 封装了SQL语句的类型及MappedStatement的ID
private final SqlCommand command;
// 封装了method的返回值及参数解析等的相关信息
private final MethodSignature method;
(1)、SqlCommand字段主要是封装SQL语句类型及MappedStatement的ID
(2)、MethodSignature字段主要是用来封装method的相关属性及参数解析
execute()方法如下:
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
// 判断本次执行的SQL语句的类型
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
// 将用户传入的参数解析成一个Map类型数据
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 通过调用SqlSession来实现插入操作,command.name是MappedStatement的ID,
// SqlSession根据这个ID来查找MappedStatement,进而获取SQL的信息。
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
// 同上
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
// 同上
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
// 执行查询类型数据库操作
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 将用户传入的数据存入Map中供后续使用
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 通过SqlSession执行查询语句,这里之后其实使用的是ibatis框架的内容了
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
// 执行flush
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
在封装执行参数时使用了MethodSignature的convertArgsToSqlCommandParam方法。
convertArgsToSqlCommandParam方法中使用了ParamNameResolver来封装用户传参。
// 默认的输入类型
public static final String GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX = "param";
// 是否在用户不使用@Param注解时,继续解析方法参数名作为默认的参数值使用
private final boolean useActualParamName;
/**
* <p>
* The key is the index and the value is the name of the parameter.<br />
* The name is obtained from {@link Param} if specified. When {@link Param} is not specified,
* the parameter index is used. Note that this index could be different from the actual index
* when the method has special parameters (i.e. {@link RowBounds} or {@link ResultHandler}).
* </p>
* <ul>
* <li>aMethod(@Param("M") int a, @Param("N") int b) -> {{0, "M"}, {1, "N"}}</li>
* <li>aMethod(int a, int b) -> {{0, "0"}, {1, "1"}}</li>
* <li>aMethod(int a, RowBounds rb, int b) -> {{0, "0"}, {2, "1"}}</li>
* </ul>
*/
// 具体的存储格式参考注释
private final SortedMap<Integer, String> names;
// 是否有参数注解
private boolean hasParamAnnotation;
ParamNameResolve的构造函数如下:
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
// 获取useActualParamName,该属性是用户在config文件的setting标签下指定的,默认true,
// 即如果用户没有使用@Param注解标记形参时,会使用方法参数名。
this.useActualParamName = config.isUseActualParamName();
// 获取方法参数类型
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// 获取方法参数的注解,因为参数注解允许存在多个,所以此处使用二维数组
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
// get names from @Param annotations
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {
// skip special parameters
continue;
}
String name = null;
// 遍历全部的参数注解
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
// 判断参数注解是否使用@Param
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
hasParamAnnotation = true;
// 获取注解的值
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
if (name == null) {
// @Param was not specified.
// 如果方法参数的注解的值为空,则判断是否需要继续使用方法参数名作为值,
// 否则直接写成"0","1"这种类型的数据
if (useActualParamName) {
// 获取参数名称
name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);
}
if (name == null) {
// 如果参数名称为null,证明此时javac在编译class文件的时候没有使用了-parameters参数,使用"0"等作为值
// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)
// gcode issue #71
name = String.valueOf(map.size());
}
}
map.put(paramIndex, name);
}
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}
注意:mybatis中的获取参数名称并没有Spring那样深入,它仅仅是使用反射来进行获取参数名,而这个参数名如果在javac不指定-parameter参数时,是不存在的,值会变成args0、args1等值。Spring并不仅仅使用反射,如果反射获取不到,还是会使用asm来获取LocalVariableTable的class文件中关于方法的描述来获取。如下所示:
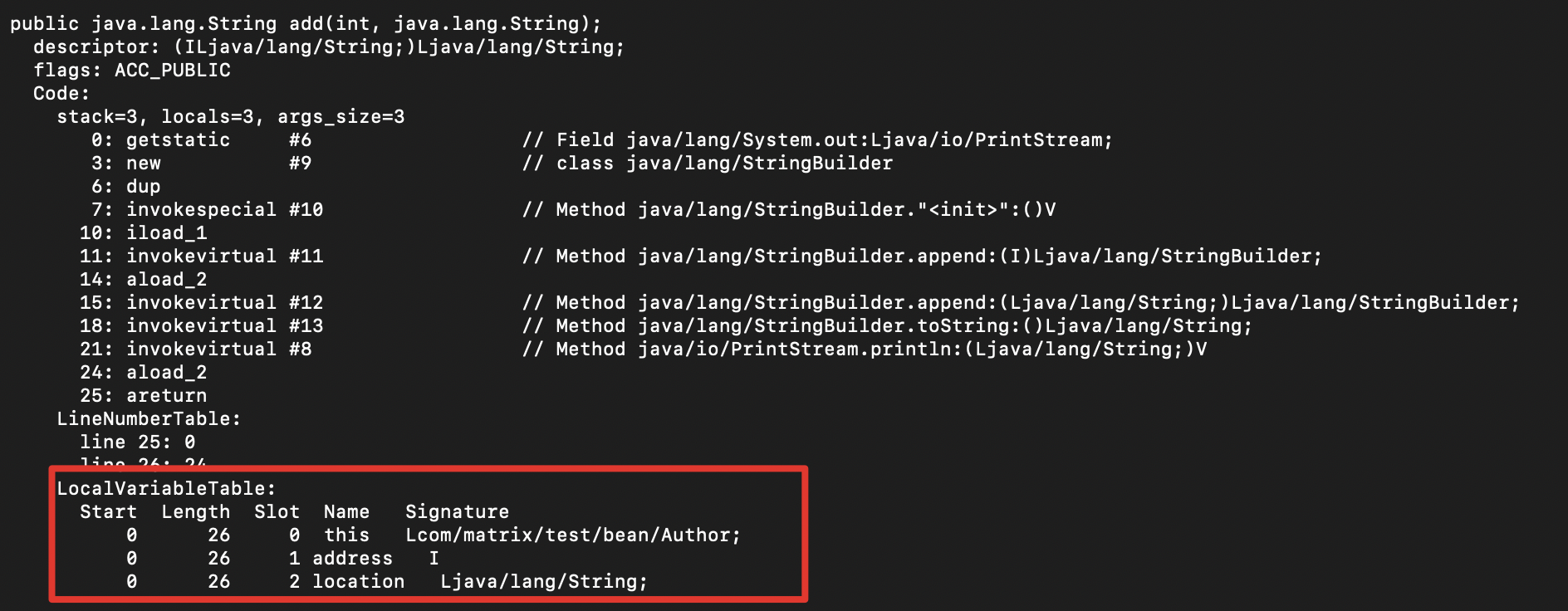
红框表示LocalVariableTable的内容,如果是实例方法,那么取从数组的索引1开始之后的内容。如果是类方法,则由于不存在this属性,直接从0开始取即可。
getNamedParams()方法如下所示:
/**
* <p>
* A single non-special parameter is returned without a name.
* Multiple parameters are named using the naming rule.
* In addition to the default names, this method also adds the generic names (param1, param2,
* ...).
* </p>
*
* @param args
* the args
* @return the named params
*/
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
// 获取方法中的参数数量
final int paramCount = names.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
Object value = args[names.firstKey()];
return wrapToMapIfCollection(value, useActualParamName ? names.get(0) : null);
} else {
// 将用户传递的数据封装成map
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();
int i = 0;
// 遍历封装方法参数名和用户的数据
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
// 形如参数名:数据
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// add generic param names (param1, param2, ...)
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + (i + 1);
// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param
if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
// 形如param1:数据
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
封装好用户的数据及方法参数名之后,传递给SqlSession来执行数据库相关操作。
至此mybatis通过动态代理实现对SqlSession的数据库操作的封装调用。后续的SqlSession的执行逻辑及结构在之前的文章中已经进行了分析。
其实此处通过动态代理只是实现了用户通过SqlSession来过去通过动态代理生成的实体类。并执行相应的代理操作。技术关键点是动态代理。