1、动态SQL的使用
例如
<select id="getUserById"
resultType="com.matrix.dao.User"
resultMap="user"
flushCache="false"
useCache="true"
timeout="10000"
fetchSize="256"
statementType="PREPARED"
resultSetType="FORWARD_ONLY">
SELECT <include refid="userAllColumn"/> FROM user
<where>
<if test="id != null">
AND id = #{id}
</if>
</where>
</select>
其他例子这里不多介绍了。
2、SqlSource与BoundSql详解
Mybatis中的SqlSource用于描述SQL资源。Mybatis可以通过两种方式配置SQL信息,一种是通过@Select、@Insert、@Delete、@Update或者@SelectProvider、@InsertProvider、@DeleteProvider、@UpdateProvider等注解;另一种是通过XML配置文件。SqlSource就代表Java注解或者XML文件配置的SQL资源。
public interface SqlSource {
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}
getBoundSql()方法:该方法返回一个BoundSql实例,BoundSql是对SQL语句及参数信息的封装,它是SqlSource解析后的结果。SqlSource接口有4个不同的实现,分别为StaticSqlSource、DynamicSqlSource、RawSqlSource和ProviderSqlSource。
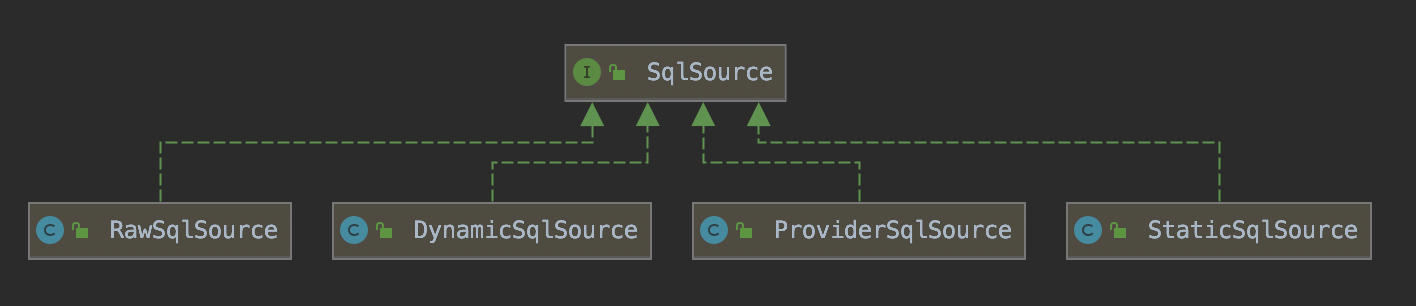
这四种SqlSource实现类的作用如下:
(1)、ProviderSqlSource:用于描述通过@Select、@SelectProvider等注解配置的SQL资源信息。
(2)、DynamicSqlSource:用于描述Mapper XML文件中配置的SQL资源信息,这些SQL通常包含动态SQL配置或者${}参数占位符,需要在Mapper调用时才能确定具体的SQL语句。
(3)、RawSqlSource:用于描述Mapper XML文件中配置的SQL资源信息,与DynamicSqlSource不同的是,这些SQL语句在解析XML配置的时候就能确定,即不包含SQL相关配置。
(4)、StaticSqlSource:用于描述ProviderSqlSource、DynamicSqlSource及RawSqlSource解析后得到的静态SQL资源。
3、LanguageDriver详解
SQL配置信息到SqlSource对象的转换是由LanguageDriver组件来完成的。
public interface LanguageDriver {
/**
* Creates a {@link ParameterHandler} that passes the actual parameters to the the JDBC statement.
*
* @param mappedStatement The mapped statement that is being executed
* @param parameterObject The input parameter object (can be null)
* @param boundSql The resulting SQL once the dynamic language has been executed.
* @return
* @author Frank D. Martinez [mnesarco]
* @see DefaultParameterHandler
*/
ParameterHandler createParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql);
/**
* Creates an {@link SqlSource} that will hold the statement read from a mapper xml file.
* It is called during startup, when the mapped statement is read from a class or an xml file.
*
* @param configuration The MyBatis configuration
* @param script XNode parsed from a XML file
* @param parameterType input parameter type got from a mapper method or specified in the parameterType xml attribute. Can be null.
* @return
*/
SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType);
/**
* Creates an {@link SqlSource} that will hold the statement read from an annotation.
* It is called during startup, when the mapped statement is read from a class or an xml file.
*
* @param configuration The MyBatis configuration
* @param script The content of the annotation
* @param parameterType input parameter type got from a mapper method or specified in the parameterType xml attribute. Can be null.
* @return
*/
SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType);
}
LanguageDriver接口中一共有3个方法,其中createParameterHandler()方法用于创建ParameterHandler对象,另外还有两个重载的createSqlSource()方法,这两个重载的方法用于创建SqlSource对象。
Mybatis中为LanguageDriver接口提供了两个实现类,分别为XMLLanguageDriver和RawLanguageDriver。XMLLanguageDriver为XML语言驱动,为Mybatis提供了通过XML标签结合OGNL表达式语法实现动态SQL的功能。而RawLanguageDriver表示仅支持静态SQL配置,不支持动态SQL功能。
XMLLanguageDriver的createSqlSource()方法如下所示:
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
// 该方法用于解析XML文件中配置SQL信息
// 创建XMLScriptBuilder对象
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
// 调用XMLScriptBuilder对象的parseScriptNode()方法啊解析SQL资源
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType) {
// issue #3
// 该方法用于解析Java注解中配置的SQL信息
// 若字符串以script标签开头,则以XML方式解析
if (script.startsWith("<script>")) {
XPathParser parser = new XPathParser(script, false, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver());
return createSqlSource(configuration, parser.evalNode("/script"), parameterType);
} else {
// issue #127
// 解析SQL配置中的全局变量
script = PropertyParser.parse(script, configuration.getVariables());
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(script);
// 如果SQL中仍包含${}参数占位符,则返回DynamicSqlSource实例,否则返回RawSqlSource
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
return new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, textSqlNode);
} else {
return new RawSqlSource(configuration, script, parameterType);
}
}
}
从XMLLanguageDriver类的createSqlSource()方法实现来看,除了可以通过XML配置文件结合OGNL表达式配置动态SQL外,还可以通过Java注解的方式配置,只需要注解中的内容加上script标签。
4、SqlNode详解
SqlNode用于描述Mapper SQL配置中的SQL节点,它是Mybatis框架实现动态SQL的基石。接口内容如下:
public interface SqlNode {
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}
apply()方法:该方法用于解析SQL节点,根据参数信息生成静态SQL内容。apply()方法需要接收一个DynamicContext对象作为参数,DynamicContext对象中封装了Mapper调用时传入的参数信息及Mybatis内置的_parameter和_databaseId参数。
在使用动态SQL时,可以使用if、where、trim等标签,这些标签都对应一种具体的SqlNode实现类。
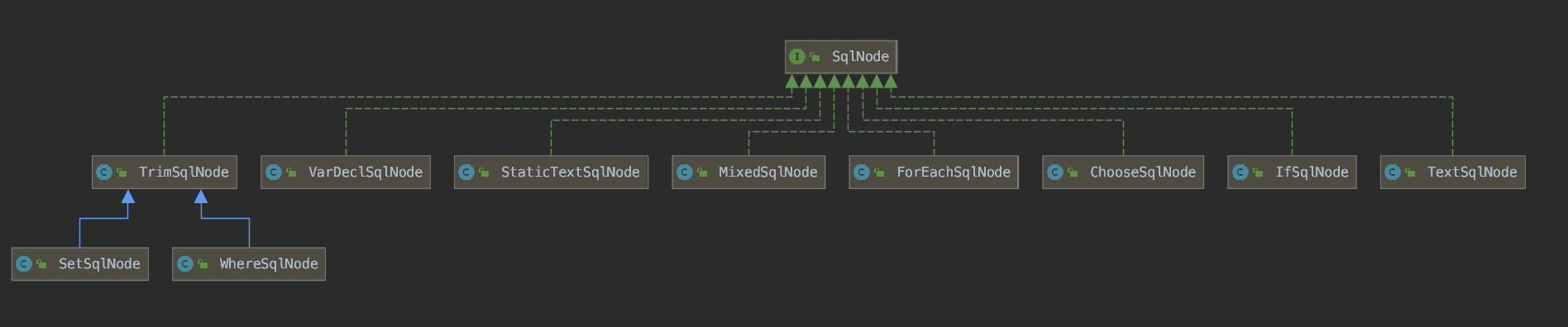
这些SqlNode实现类的作用如下:
(1)、IfSqlNode:用于描述动态SQL中if标签的内容,XMLLanguageDriver在解析Mapper SQL配置生成SqlSource时,会对动态SQL中if标签转换为IfSqlNode对象。
(2)、ChooseSqlNode:用于描述动态SQL配置中的choose标签内容,Mapper解析时会把choose标签内容转换为ChooseSqlNode对象。
(3)、ForEachSqlNode:用于描述动态SQL配置中的foreach标签,foreach标签配置信息在Mapper解析时会转换为ForEachSqlNode对象。
(4)、MixedSqlNode;用于描述一组SqlNode对象,通常一个Mapper配置是由多个SqlNode对象组成的,这些SqlNode对象通过MixedSqlNode进行关联,组成一个完整的动态SQL配置。
(5)、SetSqlNode:用于描述动态SQL配置中的set标签,Mapper解析时会把set标签配置信息转换为SetSqlNode对象。
(6)、WhereSqlNode:用于描述动态SQL配置中的where标签,动态SQL解析时,会把where标签内容转换为WhereSqlNode对象。
(7)、TrimSqlNode:用于描述动态SQL中的trim标签,动态解析SQL时,会把trim标签内容转化为TrimSqlNode对象。
(8)、StaticTextSqlNode:用于描述动态SQL中的静态文本内容。
(9)、TextSqlNode:该类与StaticTextSqlNode类不同的是,当静态文本中包含${}占位符时,说明${}需要在Mapper调用时将${}替换为具体的参数值。因此使用TextSqlNode类来描述。
(10)、VarDeclSqlNode:用于描述动态SQL中的bind标签,动态解析SQL时,会把bind标签配置信息转换为VarDeclSqlNode。
举个例子:
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
SqlNode staticNode = new StaticTextSqlNode("select * from user where");
SqlNode ifNode1 = new IfSqlNode(new StaticTextSqlNode(" id = #{id}"), "id != null");
SqlNode ifNode2 = new IfSqlNode(new StaticTextSqlNode(" AND name = #{name}"), "name != null");
SqlNode ifNode3 = new IfSqlNode(new StaticTextSqlNode(" AND phone = #{phone}"), "phone != null");
SqlNode mixedSqlNode = new MixedSqlNode(Arrays.asList(staticNode, ifNode1, ifNode2, ifNode3));
Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
paramMap.put("id", "1");
paramMap.put("name", "gaoming");
paramMap.put("phone", "111");
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), paramMap);
mixedSqlNode.apply(context);
System.out.println(context.getSql());
SQL如下:
select * from user where id = #{id} AND name = #{name} AND phone = #{phone}
了解下SqlNode解析生成SQL语句的过程。首先来看MixedSqlNode的实现,代码如下:
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
for (SqlNode sqlNode : contents) {
sqlNode.apply(context);
}
return true;
}
通过一个List对象维护所有的SqlNode对象,apply()方法对所有的SqlNode对象进行遍历,以当前DynamicContext对象作为参数,调用所有的SqlNode对象的apply()方法。
StaticTextSqlNode类的实现如下:
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
context.appendSql(text);
return true;
}
IfSqlNode的实现如下:
public class IfSqlNode implements SqlNode {
// evaluator属性用于解析OGNL表达式
private final ExpressionEvaluator evaluator;
// 保存if标签test属性内容
private final String test;
// if标签内的SQL内容
private final SqlNode contents;
public IfSqlNode(SqlNode contents, String test) {
this.test = test;
this.contents = contents;
this.evaluator = new ExpressionEvaluator();
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 如果OGNL表达式值为true,则调用if标签内容对应的SqlNode的apply()方法
if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {
contents.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
5、动态SQL解析过程
Mybatis动态SQL相关的一些组件。其中SqlSource用于描述通过XML文件或者Java注解配置的SQL资源信息;SqlNode用于描述动态SQL中if、where等标签信息;LanguageDriver用于对Mapper SQL配置进行解析,将SQL配置转换为SqlSource对象。
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
// 该方法用于解析XML文件中配置的SQL信息
// 创建XMLScriptBuilder对象
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
// 调用XMLScriptBuilder对象parseScriptNode()方法解析SQL资源
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}
XMLScriptBuilder类的parseScriptNode()方法的代码如下:
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
// 调用parseDynamicTags()方法将SQL配置转化为SqlNode对象
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource = null;
// 判断Mapper SQL配置中是否包含动态SQL元素,如果是,就创建DynamicSqlSource对象,否则就创建RawSqlSource对象
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}
需要注意的是,Mybatis中判断SQL配置是否属于动态SQL的标准是SQL配置是否包含if、where、trim等元素或者${}参数占位符。
XMLScriptBuilder类的parseDynamicTags()方法实现,代码如下:
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<SqlNode>();
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
// 对XML子元素进行遍历
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
// 如果子元素为SQL文本内容,则使用TextSqlNode描述该节点
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
String data = child.getStringBody("");
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
// 若SQL文本中包含${}参数占位符,则为动态SQL
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
// 如果SQL文本中不包含${}参数占位符,则不是动态SQL
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // issue #628
// 如果子元素为if、where等标签,则使用对应的NodeHandler处理
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
isDynamic = true;
}
}
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}
XMLScriptBuilder类中定义了一个私有的NodeHandler接口提供的8个实现类,每个类用于处理对应的动态SQL标签。接口定义如下:
private interface NodeHandler {
void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents);
}
handleNode()方法接收一个动态SQL标签对应的XNode对象和一个存放SqlNode对象的List对象,handleNode()方法中对XML标签进行解析后,把生成的SqlNode对象添加到List对象中。
参考下IfHandler类的实现
private class IfHandler implements NodeHandler {
public IfHandler() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
// 继续调用parseDynamicTags方法解析if标签中的子节点
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
// 获取if标签test属性
String test = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("test");
// 创建IfSqlNode对象
IfSqlNode ifSqlNode = new IfSqlNode(mixedSqlNode, test);
// 将IfSqlNode对象添加到List中
targetContents.add(ifSqlNode);
}
}
需要注意的是,XMLScriptBuilder类的构造方法中,会调用initNodeHandlerMap()方法将所有的NodeHandler的实例注册到Map中。
private void initNodeHandlerMap() {
nodeHandlerMap.put("trim", new TrimHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("where", new WhereHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("set", new SetHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("foreach", new ForEachHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("if", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("choose", new ChooseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("when", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("otherwise", new OtherwiseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("bind", new BindHandler());
}
需要解析动态SQL标签时,只需要根据标签名获取对应的NodeHandler对象进行处理即可,而不用每次都创建对应的NodeHandler实例,这也是享元思想的应用。
动态SQL标签解析完成后,将解析后生成的SqlNode对象封装在SqlSource对象中。Mybatis中的MappedStatement用于描述Mapper中的SQL配置,SqlSource创建完毕后,最终会存放在MappedStatement对象的sqlSource属性中,Executor组件操作数据库时,会调用MappedStatement对象的getBoundSql()方法获取BoundSql对象。
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 调用SqlSource对象的getBoundSql()方法获取BoundSql对象
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}
SqlSource对象的getBoundSql()方法,这个方法就完成了SqlNode对象解析成SQL语句的过程。
DynamicSqlSource的getBoundSql方法如下:
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : context.getBindings().entrySet()) {
boundSql.setAdditionalParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
return boundSql;
}
parse方法如下所示:
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
// ParameterMappingTokenHandler为Mybatis参数映射器,用于处理SQL中的#{}参数占位符
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters);
// Token解析器,用于解析#{}参数
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
String sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}
6、从源码角度分析#{}和${}的区别
首先来看下${}参数占位符的解析过程。当动态SQL配置中存在${}占位符时,Mybatis会使用TextSQLNode对象描述对应的SQL节点,在调用TextSqlNode对象的apply()方法时会完成动态SQL解析。也就是说,${}参数占位符的解析是在TextSqlNode类的apply()方法中完成的。
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 通过GenericTokenParser对象解析${}参数占位符,使用BindingTokenParser对象处理参数占位符内容
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(new BindingTokenParser(context, injectionFilter));
context.appendSql(parser.parse(text));
return true;
}
createParser方法如下:
private GenericTokenParser createParser(TokenHandler handler) {
return new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
}
parse方法如下
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
int start = text.indexOf(openToken, 0);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
// 调用TokenHandler的handleToken方法替换参数占位符
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
handleToken方法如下:
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
Object parameter = context.getBindings().get("_parameter");
if (parameter == null) {
context.getBindings().put("value", null);
} else if (SimpleTypeRegistry.isSimpleType(parameter.getClass())) {
context.getBindings().put("value", parameter);
}
Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(content, context.getBindings());
String srtValue = (value == null ? "" : String.valueOf(value)); // issue #274 return "" instead of "null"
checkInjection(srtValue);
return srtValue;
}
总结下#{}和${}参数占位符的区别,使用#{}参数占位符时,占位符内容会被替换成?,然后通过PreparedStatement对象的setXxx()方法为参数占位符设置值;而${}参数占位符会被直接替换为参数值。使用#{}参数占位符能够有效避免SQL注入问题,所以可以优先使用#{}占位符,当#{}占位符无法满足要求时,才考虑使用${}参数占位符。