核心处理层
Mybatis初始化
Mybatis中的配置文件主要有两个,分别是mybatis-config.xml配置文件和映射配置文件。
BaseBuilder
Mybatis初始化的主要工作是加载并解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件、映射配置文件以及相关的注解信息。Mybatis的初始化入口是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build()方法,其具体实现如下:
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
// 读取配置文件
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
// 解析配置文件得到Configuration对象,创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build()方法会创建XMLConfigurationBuilder对象来解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件,而XMLConfigBuilder继承自BaseBuilder抽象类,BaseBuilder的子类如图:
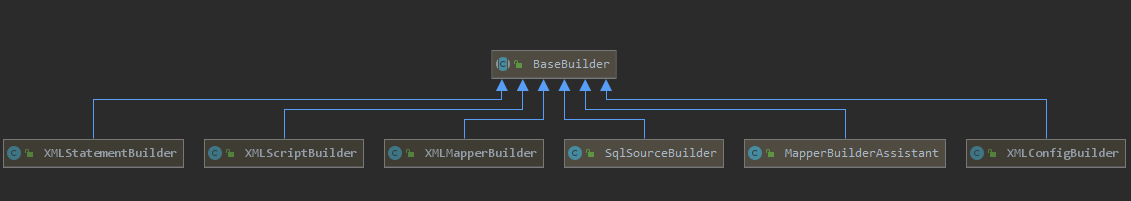
Mybatis的初始化过程使用了建造者模式,BaseBuilder中核心字段的含义如下:
// Configuration是Mybatis初始化过程的核心对象,Mybatis中几乎全部的配置信息会保存到
// Configuration对象中。Configuration对象是在Mybatis初始化过程中创建且是全局唯一的。
protected final Configuration configuration;
// 在mybatis-config.xml配置文件中可以使用<typeAliases>标签定义别名,这些定义的别名称都会记录在该
// typeAliasRegistry对象中。
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry;
// 在mybatis-config.xml配置文件中可以使用<typeHandlers>标签添加自定义TypeHandler,
// 完成指定数据库类型与Java类型的转换,这些TypeHandler都会记录在TypeHandlerRegistry中。
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry;
BaseBuilder中记录的TypeAliasRegistry对象和TypeHandlerRegistry对象,其实是全局唯一的,它们都是在Configuration对象初始化时创建的,代码如下:
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry();
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
在BaseBuilder构造函数中,通过相应的Configuration.get*()方法得到TypeAliasRegistry对象和TypeHandlerRegistry对象,并赋值给BaseBuilder相应字段。
Configuration中还包含很多配置项。
XMLConfigBuilder
XMLConfigBuilder是BaseBuilder的众多子类之一,它扮演的是具体建造者的角色。XMLConfigBuilder主要负责解析mybatis-config.xml,其核心字段如下:
private boolean parsed; // 标识是否已经解析过mybatis-config.xml配置文件
// 用于解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件的XPathParser对象。
private final XPathParser parser;
// 标识<enviroment>配置的名称,默认读取<enviroment>标签的default属性
private String environment;
// ReflectorFactory负责创建和缓存Reflector对象
private final ReflectorFactory localReflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory();
XMLConfigBuilder.parse()方法是解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件的入口,它通过调用XMLConfigBuilder.parseConfiguration()方法实现整个解析过程,具体实现如下:
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// 在mybatis-config.xml配置文件中查找<configuration>节点,并开始解析
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// 解析properties节点
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
// 解析settings节点
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
// 解析typeAliases节点
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
// 解析plugins节点
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
// 解析objectFactory节点
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
// 解析objectWrapperFactory节点
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
// 解析reflectorFactory节点
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
// 解析environments节点
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
// 解析databaseIdProvider节点
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
// 解析typeHandlers节点
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 解析mappers节点
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
- 解析properties节点
XMLConfigBuilder.propertiesElement()方法会解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件中的节点并形成java.util.Properties对象,之后将该Properties对象设置到XPathParser和Configuration的variable字段中。在后面的解析过程中,会使用该Properties对象中的信息替换占位符。propertiesElement()方法的具体实现如下:
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 解析<properties>的子节点<property>标签的name和value属性,并记录到Properties中
Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 解析<properties>的resource和url属性,这两个属性用于确定properties配置文件的位置
String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = context.getStringAttribute("url");
if (resource != null && url != null) {
throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other.");
}
// 加载resource属性或url属性指定的properties文件。
if (resource != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource));
} else if (url != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url));
}
Properties vars = configuration.getVariables();
if (vars != null) {
defaults.putAll(vars);
}
parser.setVariables(defaults);
configuration.setVariables(defaults);
}
}
- 解析settings节点
XMLConfigBuilder.settingsAsProperties()方法负责解析节点,在 节点吓得配置是Mybatis全局性的配置,他们会改变Mybatis的运行时行为,具体配置项的含义请参考Mybatis的官方文档。需要注意的是,在Mybatis初始化时,这些全局配置信息都会被记录到Configuration对象的对应属性中。
settingAsProperties方法与propertiesElement方法类似。
private Properties settingsAsProperties(XNode context) {
if (context == null) {
return new Properties();
}
// 解析<settings>的子节点<setting>标签的name和value属性,并返回Properties对象
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// Check that all settings are known to the configuration class
// 创建Configuration对应的MetaClass对象
MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class, localReflectorFactory);
// 检测Configuration中是否定义了key指定属性相应的setter方法
for (Object key : props.keySet()) {
if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) {
throw new BuilderException("The setting " + key + " is not known. Make sure you spelled it correctly (case sensitive).");
}
}
return props;
}
- 解析typeAliases,typeHandler节点
XMLConfigBuilder.typeAliasesElement()方法负责解析节点及其子节点,并通过TypeAliasRegistry完成别名的注册,具体实现如下:
private void typeAliasesElement(XNode parent) {
if (parent != null) {
// 处理全部子节点
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { // 处理package节点
// 获取指定的包名
String typeAliasPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
// 通过TypeAliasRegistry扫描指定包中所有的类,并解析@Alias注解,完成别名注册
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(typeAliasPackage);
} else { // 处理<typeAlias>节点
String alias = child.getStringAttribute("alias"); // 获取指定的别名
String type = child.getStringAttribute("type"); // 获取别名对应的类型
try {
Class<?> clazz = Resources.classForName(type);
if (alias == null) {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(clazz); // 扫描@Alias注解,完成注册
} else {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(alias, clazz); // 注册别名
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error registering typeAlias for '" + alias + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
XMLConfigBuilder.typeHandlerElement()方法负责解析
4. 解析plugins节点
插件是Mybatis提供的扩展机制之一,用户可以通过添加自定义插件在SQL语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截。Mybatis中的自定义插件只需实现Interceptor接口,并通过注解指定想要拦截的方法签名即可。
XMLConfigBuilder.pluginElement()方法负责解析
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { // 遍历全部子节点即<plugin>节点
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor"); // 获取<plugin>节点的interceptor属性的值
// 获取<plugin>节点下<properties>配置的信息,并形成Properties对象
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 实例化Interceptor对象
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance();
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties); // 设置Interceptor的属性
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance); // 记录Interceptor对象
}
}
}
所有配置的Interceptor对象都是通过Configuration.interceptorChain字段管理的,InterceptorChain底层使用ArrayList
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<Interceptor>();
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
- 解析objectFactory节点
XMLConfigBuilder.objectFactoryElement()方法负责解析并实例化节点指定的ObjectFactory实现类,之后将自定义的ObjectFactory对象记录到Configuration.objectFactory字段中,实现如下:
private void objectFactoryElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 获取<objectFactory>节点的type属性
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
// 获取<objectFactory>节点下配置的信息,并形成Properties对象
Properties properties = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 进行别名解析后,实例化自定义ObjectFactory实现
ObjectFactory factory = (ObjectFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
// 设置自定义ObjectFactory的属性,完成初始化的相关操作
factory.setProperties(properties);
// 将自定义ObjectFactory对象记录到Configuration对象的objectFactory字段中,待后续使用
configuration.setObjectFactory(factory);
}
}
- 解析enviroments节点
Mybatis可以配置多个节点,每个 节点对应一种环境的配置,但需要注意的是,尽管可以配置多个环境,每个SqlSessionFactory实例只能选择其一。
XMLConfigBuilder.enviromentsElement()方法负责解析的相关配置,它会根据XMLConfigBuilder.environment字段值确定要使用的 配置,之后创建对应的TransactionFactory和DataSource对象,并封装进Environment对象中。实现如下:
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 未指定XMLConfigBuilder.enviroment字段,则使用default属性指定的<enviroment>
if (environment == null) {
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) { // 遍历子节点<enviroment>节点
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) { // 与XMLConfigBuilder.enviroment字段匹配
// 创建TransactionManager
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
// 创建DataSourceFactory和DataSource
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
- 解析databaseIdProvider节点
- 解析mappers节点
在Mybatis初始化时,除了加载mybatis-config.xml配置文件,还会加载全部的映射配置文件,mybatis-config.xml配置文件中的节点会告诉Mybatis去哪些位置查找映射配置文件以及使用了配置注解标识的接口。
XMLConfigBuilder.mapperElement()方法负责解析节点,它会创建XMLMapperBuilder对象加载映射文件,如果映射文件存在相应的Mapper接口,也会加载相应的Mapper接口,解析其中的注解并完成向MapperRegistry的注册。
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { // 处理<mappers>节点
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { // <package>节点
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
// 加载指定的包,并向MapperRegistry注册Mapper接口
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
// 获取mapper中的三个属性,互斥的
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
// 如果<mapper>节点指定resource和url属性,则常见XMLMapperBuilder对象,
// 并通过该对象解析resource和url属性指定的Mapper配置文件
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 创建XMLMapperBuilder对象,解析映射配置文件
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
// 如果<mapper>节点指定了class属性,则向MapperRegistry注册该Mapper接口
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
Mybatis初始化过程中对mybatis-config.xml配置文件的解析过程到此结束了。
XMLMapperBuilder
通过对XMLConfigBuilder.mapperElement()方法的介绍我们知道,XMLMapperBuilder负责解析映射配置文件,它继承了BaseBuilder抽象类,也是具体建造者角色。XMLMapperBuilder.parse()方法是解析映射文件的入口,具体代码如下:
public void parse() {
// 判断是否已经加载过该映射文件
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper")); // 处理mapper节点
// 将resource添加到Configuration.loadedResources集合中保存,它是HashSet类型的集合,
// 其中记录了已经加载过的映射文件
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace(); // 注册Mapper接口
}
// 处理configurationElement()方法中解析失败的resultMap节点
parsePendingResultMaps();
// 处理configurationElement()方法中解析失败的cache-ref节点
parsePendingCacheRefs();
// 处理configurationElement()方法中解析失败的SQL语句节点
parsePendingStatements();
}
XMLMapperBuilder也是将每个节点的解析过程封装成了一个方法,而且这些方法在XMLMapperBuilder.configurationElement()方法调用。
configurationElement()方法实现如下:
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// 获取mapper节点的namespace属性
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
// 如果namespace属性为空,则抛出异常
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
// 设置MapperBuilderAssistant的currentNamespace字段,记录当前的命名空间。
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
// 解析cache-ref节点
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
// 解析cache节点
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
// 解析parameterMap节点
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
// 解析resultMap节点
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
// 解析sql节点
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 解析select、insert、update、delete等SQL节点
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
- 解析cache节点
Mybatis拥有非常强大的二级缓存功能,该功能可以非常方便地进行配置,Mybatis默认情况下没有开启二级缓存,如果要为某命名空间开启二级缓存功能,则需要相应映射配置文件中添加cache节点,还可以通过配置cache节点的相关属性,为二级缓存配置相应的特性。实际上就是添加相应的装饰器。
XMLMapperBuilder.cacheElement()方法主要负责解析cache节点,其具体实现如下:
private void cacheElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 获取cache节点的type属性,默认值是PERPETUAL
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
// 查找type属性对应的Cache接口实现
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
// 获取cache节点的eviction属性,默认是LRU
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
// 解析eviction属性指定的Cache装饰器类型
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
// 获取cache节点的flushInterval属性,默认值是null
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
// 获取cache节点的size属性,默认值是null
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
// 获取cache节点的readOnly属性,默认值是false
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
// 获取cache节点的blocking属性,默认值是false
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
// 获取cache节点下的子节点,将用于初始化二级缓存
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 通过MapperBuilderAssistant创建Cache对象,并添加到Configuration.caches集合中保存
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}
MapperBuilderAssistant是一个辅助类,其useNewCache()方法负责创建Cache对象,并将其添加到Configuration.caches集合中保存。Configuration中的caches字段是StrictMap类型的字段,它记录的Cache的id(默认是映射文件的namespace)与Cache对象(二级缓存)之间的对应关系。StrictMap继承了HashMap,并在其基础上进行了少许的修改,如果检测到重复的key则抛出异常,如果没有重复的key则添加到key以及value,同时会根据key产生shortKey,具体实现如下:
public V put(String key, V value) {
// 如果已经包含了该Key,则直接返回异常
if (containsKey(key)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " already contains value for " + key);
}
// 按照.将key切分成数组,并将数组的最后一项作为shortKey
if (key.contains(".")) {
final String shortKey = getShortName(key);
if (super.get(shortKey) == null) {
super.put(shortKey, value); // 如果不包含指定shortKey,则添加该键值对
} else {
super.put(shortKey, (V) new Ambiguity(shortKey)); // 如果该键值对已经存在,则将value修改成Ambiguity对象
}
}
return super.put(key, value); // 如果不包含该key,则添加该键值对
}
Ambiguity是StrictMap中定义的静态内部类,它表示的是存在二义性的键值对,Ambiguity中使用subject字段记录了存在二义性的key,并提供了相应的getter方法。
StrictMap.put()方法会检测value是否存在以及value是否为Ambiguity类型对象,如果满足这两个条件中的任意一个,则抛出异常。
public V get(Object key) {
V value = super.get(key);
if (value == null) { // 如果该key没有对应的value,则报错
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " does not contain value for " + key);
}
if (value instanceof Ambiguity) { // 如果value是Ambiguity类型,则报错
throw new IllegalArgumentException(((Ambiguity) value).getSubject() + " is ambiguous in " + name
+ " (try using the full name including the namespace, or rename one of the entries)");
}
return value;
}
MapperBuilderAssistant.useNewCache()方法的实现:
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass,
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
// 创建Cache对象,这里使用了建造者模式,CacheBuilder是建造者的角色,而Cache是生成的产品
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
// 将Cache对象添加到Configuration.caches集合中会将Cache的id作为key.Cache
// 对象本身作为value
configuration.addCache(cache);
currentCache = cache; // 记录当前命名空间使用的cache对象
return cache;
}
CacheBuilder是Cache的建造者,CacheBuilder中各个字段的含义如下:
private final String id; // Cache对象的唯一标识,一般情况下对应映射文件中的配置namespace
// Cache接口的真正实现类,默认值是前面的PerpetualCache
private Class<? extends Cache> implementation;
// 装饰器集合,默认只包含LruCache.class
private final List<Class<? extends Cache>> decorators;
// Cache大小
private Integer size;
// 清理时间周期
private Long clearInterval;
// 是否可读写
private boolean readWrite;
// 其他配置信息
private Properties properties;
// 是否阻塞
private boolean blocking;
CacheBuilder中提供了很多设置属性的方法(对应于建造者模式中的建造方法),这些方法比较简单。重点分析下build()方法:
public Cache build() {
// 如果implement字段和decorators集合为空,则为其设置默认值,implementation默认值是PrepetualCache.class,
// decoratos集合默认只包含LruCache.class
setDefaultImplementations();
// 根据implement指定的类型,通过反射获取参数为String类型的构造方法,并通过该构造方法创建Cache对象
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
// 根据cache节点下的properties对象,初始化为Cache对象
setCacheProperties(cache);
// 检测cache对象的类型,如果是PerpetualCache类型,则为其添加decorators集合中
// 的装饰器;如果是自定义类型的Cache接口实现,则不添加decorators集合中的装饰器
// issue #352, do not apply decorators to custom caches
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {
for (Class<? extends Cache> decorator : decorators) {
// 通过反射获取参数为Cache类型的构造方法,并通过构造方法创建装饰器
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
setCacheProperties(cache); // 配置cache对象的属性
}
// 添加Mybatis中提供的标准装饰器
cache = setStandardDecorators(cache);
} else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
// 如果不是LoggingCache的子类,则添加LoggingCache装饰器
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
}
CacheBuilder.setCacheProperties()方法会根据cache节点下配置的property信息,初始化Cache对象,具体实现如下:
private void setCacheProperties(Cache cache) {
if (properties != null) {
// cache相应的创建MetaObject对象
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String name = (String) entry.getKey(); // 配置项的名称。即Cache对应的属性名称
String value = (String) entry.getValue(); // 配置项的值,即Cache对应的属性值
if (metaCache.hasSetter(name)) { // 检测cache是否有该属性对应的setter方法
Class<?> type = metaCache.getSetterType(name); // 获取该属性的类型
if (String.class == type) { // 进行类型转换,并设置该属性值
metaCache.setValue(name, value);
} else if (int.class == type
|| Integer.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Integer.valueOf(value));
} else if (long.class == type
|| Long.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Long.valueOf(value));
} else if (short.class == type
|| Short.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Short.valueOf(value));
} else if (byte.class == type
|| Byte.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Byte.valueOf(value));
} else if (float.class == type
|| Float.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Float.valueOf(value));
} else if (boolean.class == type
|| Boolean.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Boolean.valueOf(value));
} else if (double.class == type
|| Double.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Double.valueOf(value));
} else {
throw new CacheException("Unsupported property type for cache: '" + name + "' of type " + type);
}
}
}
}
// 如果Cache继承了InitializingObject接口,则调用其initialize()方法继续自定义的初始化操作
if (InitializingObject.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())){
try {
((InitializingObject) cache).initialize();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Failed cache initialization for '" +
cache.getId() + "' on '" + cache.getClass().getName() + "'", e);
}
}
}
CacheBuilder.setStandardDecorators()方法会根据CacheBuilder中各个字段的值,为cache对象添加对应的装饰器,具体实现如下:
private Cache setStandardDecorators(Cache cache) {
try {
// 创建Cache对象对应的MetaObject对象
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
if (size != null && metaCache.hasSetter("size")) {
metaCache.setValue("size", size);
}
if (clearInterval != null) {
cache = new ScheduledCache(cache);
((ScheduledCache) cache).setClearInterval(clearInterval);
}
if (readWrite) { // 是否只读,对象添加SerializedCache
cache = new SerializedCache(cache);
}
// 默认添加LoggingCache和Synchronized两个装饰器
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
cache = new SynchronizedCache(cache);
if (blocking) { // 是否阻塞,对应添加BlockingCache装饰器
cache = new BlockingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Error building standard cache decorators. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
- 解析cache-ref节点
XMLMapperBuilder.cacheElement()方法会为每个namespace创建一个对应的Cache对象,并在Configuration.caches集合中记录namesapce与Cache对象之间的对应关系。如果我们希望多个namespace共用同一个二级缓存,即同一个Cache对象,则可以是使用cache-ref节点进行配置。
XMLMapperBuilder.cacheRefElement()方法负责解析cache-ref节点。这里首先需要读者了解的是Configuration.cacheRefMap集合,该集合是HashMap类型,其中key是cache-ref节点所在的namespace,value是cache-ref节点的namespace属性所指定的namespace,也就是说,前者共用后者的Cache对象,XMLMapperBuilder.cacheRefElement()方法如下:
private void cacheRefElement(XNode context) {
if (context != null) {
// 将当前Mapper配置文件的namespace与被引用的Cache所在的namespace之间的对应关系,
// 记录到Configuration.cacheRefMap集合中
configuration.addCacheRef(builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(), context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
// 创建CacheRefResolver对象
CacheRefResolver cacheRefResolver = new CacheRefResolver(builderAssistant, context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
try {
// 解析Cache引用,该过程主要是设置MapperBuilderAssistant中的
// currentCache和unresolvedCacheRef字段
cacheRefResolver.resolveCacheRef();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// 如果解析过程出现异常,则添加到Confiration.incompleteCacheRefs集合
configuration.addIncompleteCacheRef(cacheRefResolver);
}
}
}
CacheRefResolve是一个简单的Cache引用解析器,其中封装了被引用的namespace以及当前XMLMapperBuilder对应的MapperBuilderAssistant对象。CacheRefResolve.resolveCacheRef()方法会调用MapperBuilderAssistant.useCacheRef()方法。在MapperBuilderAssistant.useCacheRef()方法中会通过namespace查找被引用的Cache对象,具体实现如下:
public Cache useCacheRef(String namespace) {
if (namespace == null) { // 如果namespace为空,则抛出异常
throw new BuilderException("cache-ref element requires a namespace attribute.");
}
try {
unresolvedCacheRef = true; 标识未成功解析Cache引用
Cache cache = configuration.getCache(namespace); // 获取namespace对应的Cache对象
if (cache == null) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '" + namespace + "' could be found.");
}
currentCache = cache; // 记录当前命名空间使用的Cache引用
unresolvedCacheRef = false; // 标识已成功解析Cache引用
return cache;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '" + namespace + "' could be found.", e);
}
}
另一个需要了解的是Configuration字段是incompleteCacheRefs集合,它是LinkedList类型,其中记录了当前解析出现异常的CacheRefResolver对象。
3. 解析parameterMap节点
已经废弃,不再详细介绍。
4. 解析resultMap节点
select语句查询到的结果集是一张二维表,水平方向看是一个个字段,垂直方向上看是一条条记录,而Java是面向对象的程序设计语言,对象是根据类定义创建的,类之间引用关系可以认为是嵌套结构。在JDBC编程中,为了将结果集中的数据映射成对象,我们需要自己写代码从结果集中获取数据,然后封装成对应的对象并设置对象之间的关系,而这些都是大量的重复性代码。为了减少这些重复代码,Mybatis使用resultMap节点定义了结果集与结果对象之间的映射规则,resultMap节点可以满足大部分的映射需求,从而减少开发人员的重复性工作,提高开发效率。
每个ResultMapping对象记录了结果集中一列与JavaBean中一个属性之间的映射关系。resultMap节点下都会被解析成对应的ResultMapping对象,ResultMapping中的核心字段含义如下:
private Configuration configuration; // Configuration对象
private String property; // 对应节点的property属性,表示的是与该列映射的属性
private String column; // 对应节点的column属性,表示的是从数据库中得到的列名或是列明的别名
private Class<?> javaType; // 对应节点的javaType属性,表示的是一个JavaBean的完全限定名,或是一个类型名
private JdbcType jdbcType; // 对应节点的jdbcType属性,表示的是进行映射的列的JDBC类型
private TypeHandler<?> typeHandler; // 对应节点的typeHandler属性,表示的是类型处理器
// 对应节点的nestedResultMapId属性,该属性通过另一个resultId进行引用,它负责将结果集中的一部分列映射成其他关联的结果对象
// 这样我们可以通过join方式进行关联查询,然后直接映射成多个对象,并同时设置这些对象之间的组合关系
private String nestedResultMapId;
// 对应节点的nestedQueryId属性,该属性通过id引用另一个select节点定义,它会把指定的列的值传入
// select属性指定的select语句中作为参数进行查询,使用select属性可能会导致N+1问题,请注意
private String nestedQueryId;
// 对应节点的notNullColumns属性拆分后的结果
private Set<String> notNullColumns;
// 对应节点的columnPrefix属性
private String columnPrefix;
private List<ResultFlag> flags; // 处理后的标志,标志共两个:id和constructor
// 对应节点的column属性拆分后生成的结果,composites.size()>0会使column为null
private List<ResultMapping> composites;
// 对应节点的resultSet属性
private String resultSet;
// 对应节点的foreignColumn属性
private String foreignColumn;
// 是否延迟加载,对应节点的fetchType属性
private boolean lazy;
ResultMapping中定义了一个内部Builder类,也应用了建造者模式,该Builder类主要用于数据整理和数据校验。
另一个比较重要的类是ResultMap,每个resultMap节点都会被解析成一个ResultMap对象,其中每个节点所定义的映射关系,则使用ResultMapping对象表示。
ResultMap中各个字段的含义如下:
// Configuration 对象的引用
private Configuration configuration;
private String id; // resultMap节点的id属性
private Class<?> type; // resultMap节点的type属性
// 记录了除discriminator节点之外的其他映射关系(即resultMapping对象集合)
private List<ResultMapping> resultMappings;
// 记录了映射关系中带有id标志的映射关系
private List<ResultMapping> idResultMappings;
// 记录了映射关系中带有Constructor标志的映射关系
private List<ResultMapping> constructorResultMappings;
// 记录了映射关系中不带有Constructor标志的映射关系
private List<ResultMapping> propertyResultMappings;
private Set<String> mappedColumns; // 记录了所有映射关系中涉及的column属性的集合
private Set<String> mappedProperties;
// 鉴别器,对应discriminator节点
private Discriminator discriminator;
// 是否有嵌套查询,如果某个映射关系中存在resultMap属性,且不存在resultSet属性,则为true
private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;
// 是否有嵌套查询,如果某个属性映射存在select属性,则为true
private boolean hasNestedQueries;
private Boolean autoMapping;// 是否开启自动映射
ResultMap中也定义了一个内部Builder类,该Builder类主要用于创建ResultMap对象,也应用了建造者模式。
在XMLMapperBuilder中通过resultMapElements()方法解析映射配置文件中的全部resultMap节点,该方法会循环调用resultMapElement()方法处理每个resultMap节点。实现如下:
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List<ResultMapping> additionalResultMappings) throws Exception {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
// 获取resultMap的id属性,默认值会拼装所有父节点的id或value或property属性值
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id",
resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
// 获取resultMap的type属性,表示结果集将被映射成type指定类型的对象,
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
// 获取resultMap节点的extends属性,该属性值指定了resultMap节点的继承关系
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
// 读取resultMap节点的autoMapping属性,将该属性设置为true,则启动自动映射功能
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
// 解析type类型
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);
Discriminator discriminator = null;
// 该集合用于记录解析的结果
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<ResultMapping>();
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
// 处理resultMap的子节点
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) { // 处理constructor节点
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) { // 处理discriminator节点
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else {
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<ResultFlag>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) { // 处理id、result、association、collection等节点
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
// 创建ResultMapping对象,并添加到resultMappings集合中保存
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend, discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
return resultMapResolver.resolve();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
}
ResultMapping解析过程如下:
private ResultMapping buildResultMappingFromContext(XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultFlag> flags) throws Exception {
String property;
// 获取该节点的property的属性值
if (flags.contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
property = context.getStringAttribute("name");
} else {
property = context.getStringAttribute("property");
}
// 获取column属性
String column = context.getStringAttribute("column");
// 获取javaType属性
String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType");
// 获取jdbcType属性
String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String nestedSelect = context.getStringAttribute("select");
String nestedResultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap",
processNestedResultMappings(context, Collections.<ResultMapping> emptyList()));
String notNullColumn = context.getStringAttribute("notNullColumn");
String columnPrefix = context.getStringAttribute("columnPrefix");
// 获取typeHandler属性
String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler");
String resultSet = context.getStringAttribute("resultSet");
String foreignColumn = context.getStringAttribute("foreignColumn");
// 获取lazy属性
boolean lazy = "lazy".equals(context.getStringAttribute("fetchType", configuration.isLazyLoadingEnabled() ? "lazy" : "eager"));
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerClass = (Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>>) resolveClass(typeHandler);
JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType);
// 构建ResultMapping属性
return builderAssistant.buildResultMapping(resultType, property, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, nestedSelect, nestedResultMap, notNullColumn, columnPrefix, typeHandlerClass, flags, resultSet, foreignColumn, lazy);
}
buildResultMapping方法实现如下:
public ResultMapping buildResultMapping(
Class<?> resultType,
String property,
String column,
Class<?> javaType,
JdbcType jdbcType,
String nestedSelect,
String nestedResultMap,
String notNullColumn,
String columnPrefix,
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandler,
List<ResultFlag> flags,
String resultSet,
String foreignColumn,
boolean lazy) {
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveResultJavaType(resultType, property, javaType);
TypeHandler<?> typeHandlerInstance = resolveTypeHandler(javaTypeClass, typeHandler);
List<ResultMapping> composites = parseCompositeColumnName(column);
return new ResultMapping.Builder(configuration, property, column, javaTypeClass)
.jdbcType(jdbcType)
.nestedQueryId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedSelect, true))
.nestedResultMapId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedResultMap, true))
.resultSet(resultSet)
.typeHandler(typeHandlerInstance)
.flags(flags == null ? new ArrayList<ResultFlag>() : flags)
.composites(composites)
.notNullColumns(parseMultipleColumnNames(notNullColumn))
.columnPrefix(columnPrefix)
.foreignColumn(foreignColumn)
.lazy(lazy)
.build();
}
得到ResultMapping对象集合之后,会调用ResultMapResolver.resolve()方法,该方法会调用MappingBuilderAssistant.addResultMap()方法创建ResultMap对象,并将ResultMap对象添加到Configuration.resultMap()集合中保存。
public ResultMap addResultMap(
String id,
Class<?> type,
String extend,
Discriminator discriminator,
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings,
Boolean autoMapping) {
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
extend = applyCurrentNamespace(extend, true);
if (extend != null) {
if (!configuration.hasResultMap(extend)) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Could not find a parent resultmap with id '" + extend + "'");
}
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(extend);
List<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappings = new ArrayList<ResultMapping>(resultMap.getResultMappings());
extendedResultMappings.removeAll(resultMappings);
// Remove parent constructor if this resultMap declares a constructor.
boolean declaresConstructor = false;
for (ResultMapping resultMapping : resultMappings) {
if (resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
declaresConstructor = true;
break;
}
}
if (declaresConstructor) {
Iterator<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappingsIter = extendedResultMappings.iterator();
while (extendedResultMappingsIter.hasNext()) {
if (extendedResultMappingsIter.next().getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
extendedResultMappingsIter.remove();
}
}
}
resultMappings.addAll(extendedResultMappings);
}
// 创建ResultMap对象,并添加到Configuration.resultMaps集合中保存
ResultMap resultMap = new ResultMap.Builder(configuration, id, type, resultMappings, autoMapping)
.discriminator(discriminator)
.build();
configuration.addResultMap(resultMap);
return resultMap;
}
- 解析sql节点
在映射配置文件中,可以使用sql节点定义可重用的SQL语句片段。当需要重用sql节点中定义的SQL语句片段时,只需要使用include节点引入相应的片段即可,这样,在编写SQL语句可以及维护这些SQL语句时,都会比较方便。
XMLMapperBuilder.sqlElement()方法负责解析映射配置文件中定义的全部sql节点,具体实现代码如下:
private void sqlElement(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) throws Exception {
for (XNode context : list) { // 遍历sql节点
// 获取databaseId属性
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
// 获取id属性
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
// 为id添加命名空间
id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
// 检测sql的databaseid与当前Configuration中记录的databaseId是否一致
if (databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, requiredDatabaseId)) {
// 记录到XMLMapperBuilder.sqlElements中保存,在XMLMapperBuilder的构造函数中,
// 可以看到该字段指向了Configuration.sqlFragments集合
sqlFragments.put(id, context);
}
}
}
XMLStatementBuilder
SQL节点主要用于定义SQL语句,它们不再由XMLMapperBuilder进行解析,而是由XMLStatementBuilder负责进行解析。
Mybatis使用SqlSource接口表示映射文件或注解中定义的SQL语句,但它表示的SQL语句是不能直接被数据库指定的,因为其中可能含有动态SQL语句相关的节点或者占位符等需要解析的元素。SqlSource接口的定义如下:
public interface SqlSource {
// getBoundSql()方法会根据映射文件或注解描述的SQL语句,以及传入的参数,返回可执行的SQL
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}
Mybatis使用MappedStatement表示映射配置文件中定义的SQL节点,MappedStatement包含了这些节点的很多属性,其中比较重要的字段如下:
private String resource; //节点中的id属性(包含命名空间前缀)
private Configuration configuration;
private String id;
private Integer fetchSize;
private Integer timeout;
private StatementType statementType;
private ResultSetType resultSetType;
private SqlSource sqlSource; // SqlSource对象,对应一条SQL语句
private Cache cache;
private ParameterMap parameterMap;
private List<ResultMap> resultMaps;
private boolean flushCacheRequired;
private boolean useCache;
private boolean resultOrdered;
private SqlCommandType sqlCommandType; // SQL的类型,INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE、SELECT或FLUSH
private KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
private String[] keyProperties;
private String[] keyColumns;
private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;
private String databaseId;
private Log statementLog;
private LanguageDriver lang;
private String[] resultSets;
XMLStatementBuilder.parseStatementNode()方法是解析SQL节点的入口函数,其具体的实现如下:
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// 根据SQL节点的名称决定其SqlCommandType
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
// 在解析SQL语句之前,先处理其中的include节点
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver); // 处理selectKey节点
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
- 解析include节点
在解析SQL节点之前,首先通过XMLIncludeTransformer解析SQL语句中的include节点,该过程会将include节点替换成sql节点中定义的SQL片段,并将其中的"$"占位符替换成真实的参数,该解析过程是在XMLIncludeTransformer.applyIncludes()方法中实现的。
private void applyIncludes(Node source, final Properties variablesContext, boolean included) {
if (source.getNodeName().equals("include")) { // 处理include子节点
// 查找refid属性指向的sql节点,返回的是其深克隆的Node对象
Node toInclude = findSqlFragment(getStringAttribute(source, "refid"), variablesContext);
// 解析include节点下的property节点,将得到的键值对添加到variablesContext中,并
// 形成新的properties对象返回,用于替换占位符
Properties toIncludeContext = getVariablesContext(source, variablesContext);
// 递归处理include节点,在sql节点中可能会使用include引用了其他SQL片段
applyIncludes(toInclude, toIncludeContext, true);
if (toInclude.getOwnerDocument() != source.getOwnerDocument()) {
toInclude = source.getOwnerDocument().importNode(toInclude, true);
}
// 将include节点替换成sql节点
source.getParentNode().replaceChild(toInclude, source);
while (toInclude.hasChildNodes()) { // 将sql节点的子节点添加到sql节点前面
toInclude.getParentNode().insertBefore(toInclude.getFirstChild(), toInclude);
}
toInclude.getParentNode().removeChild(toInclude); // 删除sql节点
} else if (source.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
if (included && !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {
// replace variables in attribute values
NamedNodeMap attributes = source.getAttributes();
for (int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) {
Node attr = attributes.item(i);
attr.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(attr.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
}
NodeList children = source.getChildNodes(); // 遍历当前SQL语句的子节点
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
applyIncludes(children.item(i), variablesContext, included);
}
} else if (included && source.getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE
&& !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {
// replace variables in text node
// 使用之前解析得到的Properties对象替换对应的占位符
source.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(source.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
}
绑定Mapper接口
每个映射配置文件的命名空间可以绑定一个Mapper接口,并注册到MapperRegistry中。在XMLMapperBuilder.bindMapperForNamespace()方法中,完成了映射配置文件与对应Mapper接口的绑定,具体实现如下:
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
// 注册Mapper
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}
MapperAnnotationBuilder.parse()方法解析Mapper接口中的注解信息,具体实现如下:
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) { // 检测是否已经加载过该接口
// 检测是否加载过对应的映射配置文件,如果未加载,则创建XMLMapperBuilder对象解析对应的
// 映射文件,该过程就是前面介绍的映射配置文件解析过程
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache(); // 解析@CacheNamespace注解
parseCacheRef(); // 解析@CacheNamespaceRef注解
Method[] methods = type.getMethods(); // 获取接口中定义的全部方法
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge()) {
// 解析方法上的注解,并创建MappedStatement对象
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// 如果解析过程出现IncompleteException异常,可能是引用了为解析的注解
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
处理incomplete*集合
XMLMapperBuilder.configurationElement()方法解析映射配置文件时,是按照从文件头到文件尾的顺序解析的,但是有时候在解析一个节点时,会引用定义在该节点之后的,还为解析的节点,这就会导致解析失败并抛出IncompleteElementException。
根据抛出的异常的节点不同,Mybatis会创建不同的Resolver对象,并添加到Configuration的不同的incomplete集合中。
SqlNode&SqlSource
对Mybatis初始化过程的分析可知,映射配置文件中定义的SQL节点会被解析成MappedStatement对象,其中的SQL语句会被解析成SqlSource对象,SQL语句中定义的动态SQL节点,文本节点等,则由SqlNode接口的相应实现表示。
SqlSource接口的定义如下所示:
public interface SqlSource {
// 通过解析得到BoundSql对象,BoundSql对象会在后面具体介绍,其中封装了包含?占位符的SQL语句,以及绑定的实参
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}
DynamicSqlSource负责处理动态SQL语句,RawSqlSource负责处理静态语句,两者最终都会将处理后的SQL语句封装成StaticSqlSource返回。DynamicSqlSource与StaticSqlSource的主要区别是:StaticSqlSource中记录的SQL语句中可能含有?占位符,但是可以直接提交给数据库执行;DynamicSqlSource中封装的SQL语句还需要进行一系列的解析,才会最终形成数据库可执行的SQL语句。
OGNL表达式简介
OGNL(Object Graph Navigation Language,对象图导航语言)表达式在struts,Mybatis等开源项目中有广泛的应用,其中Struts框架更是将OGNL作为默认的表达式语言。在Mybatis中涉及的OGNL表达式的功能主要是,存取Java对象数中的属性,调用Java对象数中的方法等。
首先需要读者了解OGNL表达式中比较重要的三个概念:
- 表达式
OGNL表达式执行的所有操作都是根据表达式解析得到的。例如对象名.方法名表示调用指定对象的指定方法。@[类的完全限定名]@[静态方法或静态字段]表示调用指定类的静态方法或访问静态字段;OGNL表达式还可以完成变量的赋值,操作集合等操作。 - root对象
OGNL表达式指定了具体的操作,而root对象指定了需要操作的对象。 - OgnlContext(上下文对象)
OgnlContext类继承了Map接口,OgnlContext对象说白了也就是一个Map对象,既然如此,OgnlContext对象中就可以存放除root对象之外的其他对象。在使用OGNL表达式操作非root对象时,需要使用#前缀,而操作root对象则不需要使用#前缀。
在Mybatis中,使用OgnlCache对原生的OGNL进行了封装。OGNL表达式的解析过程是比较耗时的,为了提高效率,OgnlCache中使用expressionCache字段对解析后的OGNL表达式进行缓存。
DynamicContext
DynamicContext主要用于记录解析动态SQL语句之后产生的SQL语句片段,可以认为它是一个用于记录动态SQL语句解析结果的容器。
DynamicContext中核心字段的含义如下:
private final ContextMap bindings; // 参数上下文
// 在SqlNode解析动态SQL时,会将解析后的SQL语句片段添加到该属性中保存,最终拼凑出一条完整的SQL语句
private final StringBuilder sqlBuilder = new StringBuilder();
ContextMap是DynamicContext中定义的内部类,它实现了HashMap并重写了get()方法具体实现如下:
public Object get(Object key) {
String strKey = (String)key;
if (super.containsKey(strKey)) { // 如果ContextMap中已经包含了该key,则直接返回
return super.get(strKey);
} else {
// 从运行时参数中查找对应的属性
return this.parameterMetaObject != null ? this.parameterMetaObject.getValue(strKey) : null;
}
}
DynamicContext的构造方法会初始化,bindings集合,注意构造方法的第二个参数parameterObject,它是运行时传入的参数,其中包含了后续用于替换#{}占位符的实参,DynamicContext构造方法的具体实现如下:
public DynamicContext(Configuration configuration, Object parameterObject) {
if (parameterObject != null && !(parameterObject instanceof Map)) {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
this.bindings = new DynamicContext.ContextMap(metaObject);
} else {
this.bindings = new DynamicContext.ContextMap((MetaObject)null);
}
this.bindings.put("_parameter", parameterObject);
this.bindings.put("_databaseId", configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
SqlNode
SqlNode接口的定义如下:
public interface SqlNode {
// apply()是SqlNode接口中定义的唯一方法,该方法会根据用户传入的实参,参数解析该SqlNode所记录的动态SQL节点,并调用
// DynamicContext.appendSql()方法将解析后的SQL片段追加到DynamicContext.sqlBuilder中保存
// 当SQL节点下的所有SqlNode完成解析后,我们就可以从DynamicContext中获取一条动态生成的完整SQL语句
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}
SqlNode接口中有很多实现类,每个实现类对应一个动态的SQL节点。
- StaticTextSqlNode&MixedSqlNode
StaticTextSqlNode中使用text字段(String类型)记录了对应的非动态SQL语句节点,其apply()方法直接将text字段追加到DynamicContext.sqlBuilder字段中。
MixedSqlNode中使用contexts字段记录其子节点对应的SqlNode对象集合,其apply()方法会循环调用contents集合中所有的SqlNode对象的apply()方法。 - TextSqlNode
TextSqlNode表示的是包含"${}"占位符的动态SQL节点。TextSqlNode.apply()方法会使用GenericTokenParser解析“${}”占位符,并直接替换成用户给定的实际参数值,具体实现如下:
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 创建GenericTokenParser解析器,GenericTokenParser前面介绍过了,这里重点来看BindingTokenParser的功能
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(new BindingTokenParser(context, injectionFilter));
// 将解析后的SQL片段添加到DynamicContext中
context.appendSql(parser.parse(text));
return true;
}
private GenericTokenParser createParser(TokenHandler handler) {
return new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
}
BindingTokenParser是TextSqlNode中定义的内部类,继承了TokenHandler接口,它的主要功能是根据DynamicContext.bindings集合中的信息解析SQL语句节点中的"$"占位符。BindingTokenParser.context字段指向了对应的DynamicContext对象,BindingTokenParser.handleToken()方法的实现如下:
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
// 获取用户提供的实参
Object parameter = context.getBindings().get("_parameter");
if (parameter == null) {
context.getBindings().put("value", null);
} else if (SimpleTypeRegistry.isSimpleType(parameter.getClass())) {
context.getBindings().put("value", parameter);
}
// 通过OGNL解析context的值
Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(content, context.getBindings());
String srtValue = (value == null ? "" : String.valueOf(value)); // issue #274 return "" instead of "null"
checkInjection(srtValue); // 检测合法性
return srtValue;
}
- IfSqlNode
IfSqlNode对应的动态SQL节点是节点,其中定义的字段的含义如下:
// evaluator对象用于解析<if>节点的test表达式的值
private final ExpressionEvaluator evaluator;
private final String test;// 记录了<if>节点中的test表达式
private final SqlNode contents; // 记录了<if>节点的子节点
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 检测test属性中记录的表达式
if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {
contents.apply(context); // test表达式为true,则执行子节点的apply()方法
return true;
}
return false; // 注意返回值,表示的是test表达式是否为true
}
public boolean evaluateBoolean(String expression, Object parameterObject) {
// 首先通过OGNL解析表达式的值
Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(expression, parameterObject);
if (value instanceof Boolean) { // 处理Boolean类型
return (Boolean) value;
}
if (value instanceof Number) { // 处理数字类型
return new BigDecimal(String.valueOf(value)).compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) != 0;
}
return value != null;
}
- TrimSqlNode$WhereSqlNode$SetSqlNode
TrimSqlNode会根据子节点的解析结果,添加或删除相应的前缀或后缀。TrimSqlNode中字段的含义如下:
private final SqlNode contents; // 该<trim>节点的子节点
private final String prefix; // 记录了前缀字符串
private final String suffix; // 记录了后缀字符串
// 如果trim节点包裹了SQL语句是空语句,删除指定的前缀
private final List<String> prefixesToOverride;
// 如果trim节点包裹了SQL语句是空语句,删除指定的后缀
private final List<String> suffixesToOverride;
private final Configuration configuration;
WhereSqlNode和SetSqlNode都继承了TrimSqlNode,其中WhereSqlNode指定了prefix字段为"WHERE",prefixesToOverride集合中的项为“AND”和"OR",suffix字段和suffixesToOverride集合为null。也就是说,
SetSqlNode指定了prefix字段为SET,suffixesToOverride集合中的项只有.,suffix字段和prefixesToOverride集合为null。也就是说,set节点解析后的SQL语句片段如果以,结尾,则将结尾处的,删除掉,之后再将SET关键字添加到SQL片段的开始位置,从而得到该set节点最终生成的SQL片段。WhereSqlNode和SetSqlNode的实现比较简单。
- ForeachSqlNode
在动态SQL语句中构建IN条件语句的时候,通常需要对一个集合进行迭代,Mybatis提供了foreach标签实现该功能。在使用foreach标签迭代集合时,不仅可以使用集合的元素和索引值,还可以在循环开始之前或结束之后添加指定的字符串,也允许在迭代过程中添加指定的分隔符。
foreach标签对应的SqlNode实现是ForeachSqlNode,ForeachSqlNode中各个字段含义和功能如下所示:
// 用于判断循环的终止条件,ForeachSqlNode构造方法中创建该对象
private final ExpressionEvaluator evaluator; // 迭代的集合表达式
private final String collectionExpression; // 记录了该ForeachSqlNode节点的子节点
private final SqlNode contents; // 记录了该ForeachSqlNode节点的子节点
private final String open; // 在循环开始前要添加字符串
private final String close; // 在循环结束后要添加的字符串
private final String separator; // 循环过程中,每项之间的分隔符
// index是当前的迭代的次数,item的值是本次迭代的元素。若迭代集合是Map,则index是键,item是值
private final String item;
private final String index;
private final Configuration configuration; // 配置对象
SqlSourceBuilder
在经过SqlNode.apply()方法解析之后,SQL语句会被传递到SqlSourceBuilder中进行进一步解析。SqlSourceBuilder主要完成了两方面的操作,一方面是解析SQL语句中的#{}占位符中定义的属性,另一方面是将SQL语句中的#{}占位符替换成?占位符。
ResultSetHandler
Mybatis会将结果集按照映射配置文件中定义的映射规则,这种机制是Mybatis的核心功能之一,可以避免重复的JDBC代码。
在StatementHandler接口在执行完指定的select语句之后,会将查询得到的结果集交给ResultSetHandler完成映射处理。ResultSetHandler处理负责映射select语句查询得到的结果集,还会处理存储过程执行后的输出参数。
ResultSetHandler是一个接口,其定义如下:
public interface ResultSetHandler {
// 处理结果集,生成相应的结果对象集合
<E> List<E> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException;
// 处理结果集,返回相应的游标对象
<E> Cursor<E> handleCursorResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException;
// 处理存储过程的输出参数
void handleOutputParameters(CallableStatement cs) throws SQLException;
}
DefaultResultSetHandler是Mybatis提供的ResultSetHandler接口的唯一实现。DefaultResultSetHandler中的核心字段的含义如下,这些字段是在DefaultResultSetHandler中多个方法中使用的公共字段。
private final Executor executor;
private final Configuration configuration;
private final MappedStatement mappedStatement;
private final RowBounds rowBounds;
private final ParameterHandler parameterHandler;
private final ResultHandler<?> resultHandler; // 用户指定用于处理结果集的ResultHandler对象
private final BoundSql boundSql;
private final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry;
private final ObjectFactory objectFactory;
private final ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory;
handleResultSets()方法
通过select语句查询数据库得到的结果集由DefaultResultSetHandler.handleResultSets()方法进行处理,该方法不仅可以处理Statement、PreparedStatement产生的结果集,还可以处理CallableStatement调用存储过程产生的多结果集。
DefaultResultSetHandler.handlerResultSets()方法的具体如下:
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
// 该集合用于保存映射结果集得到的结果对象
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<Object>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
// 获取第一个ResultSet对象。
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
KeyGenerator
在默认情况下,insert语句并不会返回自动生成的主键,而是返回插入记录的条数。如果业务逻辑需要获取插入记录时产生的自增主键,则可以使用Mybatis提供的KeyGenerator接口。
不同的数据库产品对应的主键生成策略不一样。例如,Oracle、DB2等数据库产品是通过sequence实现自增的id,在执行insert语句之前必须明确指定主键的值,而MySQL、Postgresql等数据库在执行insert语句时,可以不指定主键,在插入过程中由数据库自动生成自增主键。KeyGenerator接口针对这些不同的数据产品提供了对应的处理方法,KeyGenerator接口的定义如下:
public interface KeyGenerator {
// 在执行insert之前执行,设置属性order="BEFORE"
void processBefore(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Statement stmt, Object parameter);
// 在执行insert之后执行,设置属性order="AFTER"
void processAfter(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Statement stmt, Object parameter);
}
Mybatis提供了三个KeyGenerator接口的实现
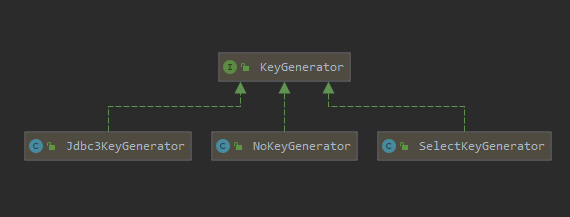
NoKeyGenerator虽然实现了KeyGenerator接口,但是其中的processBefore()方法和processAfter()方法都是空实现,所以不再单独介绍。
Jdbc3KeyGenerator
Jdbc3KeyGenerator用于返回数据库生成的自增id,它对应于mybatis-config.xml配置文件中的useGeneratedKeys全局配置,以及映射配置文件中SQL节点的useGeneratedKeys属性。Jdbc3KeyGenerator.processorBefore()方法是空实现,只实现了processorAfter()方法,该方法会调用Jdbc3KeyGenerator.processBatch()方法将SQL语句执行后生成的主键记录到用户传递的实参中。一般情况下,对于单行插入操作,传入的实参是一个JavaBean对象或是Map对象,则该对象对应一次插入操作的内容;对于多行插入,传入的实参可以是对象或Map对象的数组或集合,集合中每一个元素都对应一次插入操作。
Jdbc3KeyGenerator.processAfter()方法首先会调用Jdbc3KeyGenerator.getParameters()方法将用户传入的实参转换成Collection类型对象,代码如下:
private Collection<Object> getParameters(Object parameter) {
Collection<Object> parameters = null;
if (parameter instanceof Collection) { // 参数为Collection类型
parameters = (Collection) parameter;
} else if (parameter instanceof Map) {
Map parameterMap = (Map) parameter; // 参数为Map类型,则获取其中指定的key
if (parameterMap.containsKey("collection")) {
parameters = (Collection) parameterMap.get("collection");
} else if (parameterMap.containsKey("list")) {
parameters = (List) parameterMap.get("list");
} else if (parameterMap.containsKey("array")) {
parameters = Arrays.asList((Object[]) parameterMap.get("array"));
}
}
if (parameters == null) { // 参数为普通对象或不包含上述的Map集合,则创建ArrayList
parameters = new ArrayList<Object>();
parameters.add(parameter);
}
return parameters;
}
之后,processBatch()方法会遍历数据库生成的主键结果集,并设置到parameters集合对应元素的属性中。
@Override
public void processAfter(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Statement stmt, Object parameter) {
// 将用户传入的实参parameter对象或集合类型,然后传入processBatch()方法中处理
processBatch(ms, stmt, getParameters(parameter));
}
public void processBatch(MappedStatement ms, Statement stmt, Collection<Object> parameters) {
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 获取数据库自动生成的主键,如果没有生成主键,则返回结果集为空
rs = stmt.getGeneratedKeys();
final Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// 获得keyProperties属性指定的属性名称,它表示主键对应的属性名称
final String[] keyProperties = ms.getKeyProperties();
// 获取ResultSet的元数据信息
final ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
TypeHandler<?>[] typeHandlers = null;
// 检测数据库生成的主键的列数与keyProperties属性指定的列数是否匹配
if (keyProperties != null && rsmd.getColumnCount() >= keyProperties.length) {
for (Object parameter : parameters) {
// there should be one row for each statement (also one for each parameter)
if (!rs.next()) {
break;
}
// 为用户传入的实参创建相应的MetaObject对象
final MetaObject metaParam = configuration.newMetaObject(parameter);
if (typeHandlers == null) {
typeHandlers = getTypeHandlers(typeHandlerRegistry, metaParam, keyProperties, rsmd);
}
将生成的主键设置到用户传入的参数对应位置
populateKeys(rs, metaParam, keyProperties, typeHandlers);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ExecutorException("Error getting generated key or setting result to parameter object. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// ignore
}
}
}
}
SelectKeyGenerator
对于不支持自动生成自增主键的数据库,例如Oracle数据库,用户可以利用Mybatis提供的SelectKeyGenerator来生成主键,SelectKeyGenerator也可以实现类似于Jdbc3KeyGenerator提供的、获取数据库自动生成的主键的功能。
SelectKeyGenerator主要用于生成主键,它会执行映射配置中定义的selectKey节点的SQL语句,该语句会获取insert语句所需要的主键。
SelectKeyGenerator中定义的字段的含义如下:
private final boolean executeBefore;
private final MappedStatement keyStatement;
private void processGeneratedKeys(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) {
try {
// 检测用户传入的实参
if (parameter != null && keyStatement != null && keyStatement.getKeyProperties() != null) {
// 获取selectKey节点的keyProperties配置的属性名称,它表示主键对应的属性
String[] keyProperties = keyStatement.getKeyProperties();
final Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
final MetaObject metaParam = configuration.newMetaObject(parameter);
if (keyProperties != null) {
// Do not close keyExecutor.
// The transaction will be closed by parent executor.
Executor keyExecutor = configuration.newExecutor(executor.getTransaction(), ExecutorType.SIMPLE);
List<Object> values = keyExecutor.query(keyStatement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
if (values.size() == 0) {
throw new ExecutorException("SelectKey returned no data.");
} else if (values.size() > 1) {
throw new ExecutorException("SelectKey returned more than one value.");
} else {
MetaObject metaResult = configuration.newMetaObject(values.get(0));
if (keyProperties.length == 1) {
if (metaResult.hasGetter(keyProperties[0])) {
setValue(metaParam, keyProperties[0], metaResult.getValue(keyProperties[0]));
} else {
// no getter for the property - maybe just a single value object
// so try that
setValue(metaParam, keyProperties[0], values.get(0));
}
} else {
handleMultipleProperties(keyProperties, metaParam, metaResult);
}
}
}
}
} catch (ExecutorException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ExecutorException("Error selecting key or setting result to parameter object. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}