补充内容
ImportAware应用
该接口同样也是需要配合@Import注解进行使用,其主要作用就是配合@Enable××通过开关的形式开启某个功能时进行各项属性值的初始化工作。
其中比较典型的应用场景就是@EnableRedissonHttpSession
查看@EnableRedissonHttpSession源码:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Import({RedissonHttpSessionConfiguration.class})
@Configuration
public @interface EnableRedissonHttpSession {
int maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds() default 1800;
String keyPrefix() default "";
}
只要我们开启了RedissonHttpSession功能,spring就会自动导入RedissonHttpSessionConfiguration.class;该注解中提供了两个参数:
maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds:会话超时时间
keyPrefix:key的前缀
其最终就是在RedissonHttpSessionConfiguration中处理,并应用在配置类中:
@Configuration
public class RedissonHttpSessionConfiguration extends SpringHttpSessionConfiguration implements ImportAware {
private Integer maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds;
private String keyPrefix;
...
public void setImportMetadata(AnnotationMetadata importMetadata) {
Map<String, Object> map = importMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableRedissonHttpSession.class.getName());
AnnotationAttributes attrs = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(map);
this.keyPrefix = attrs.getString("keyPrefix");
this.maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds = (Integer)attrs.getNumber("maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds");
}
}
比如需要开发自己的插件,整合到spring时就可以基于这种模式,如下简单模拟下:
自定一个插件配置类:
@Component
public class MyDb implements ImportAware {
private int maxConnections;
@Override
public void setImportMetadata(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
Map<String, Object> attributesMap = annotationMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableMyDb.class.getName());
AnnotationAttributes attrs = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(attributesMap);
this.maxConnections = attrs.getNumber("maxConnections");
System.out.println(this.maxConnections);
}
public void store(){
System.out.println(this.maxConnections);
}
自定义注解实现开关功能:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Import(MyDb.class)
public @interface EnableMyDb {
int maxConnections() default 1000;
}
配置类开启自己定义的插件功能:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.tian")
//初始化插件值
@EnableMyDb(maxConnections = 2000)
public class AppConfig {
}
测试发现只要开启了EnableMyDb,就可以自动完成初始化功能。
定义配置类
@Configuration
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class SchedulingConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TaskManagementConfigUtils.SCHEDULED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor scheduledAnnotationProcessor() {
return new ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor();
}
}
ConcurrentTaskScheduler装饰模式
TaskScheduler接口结构如下:
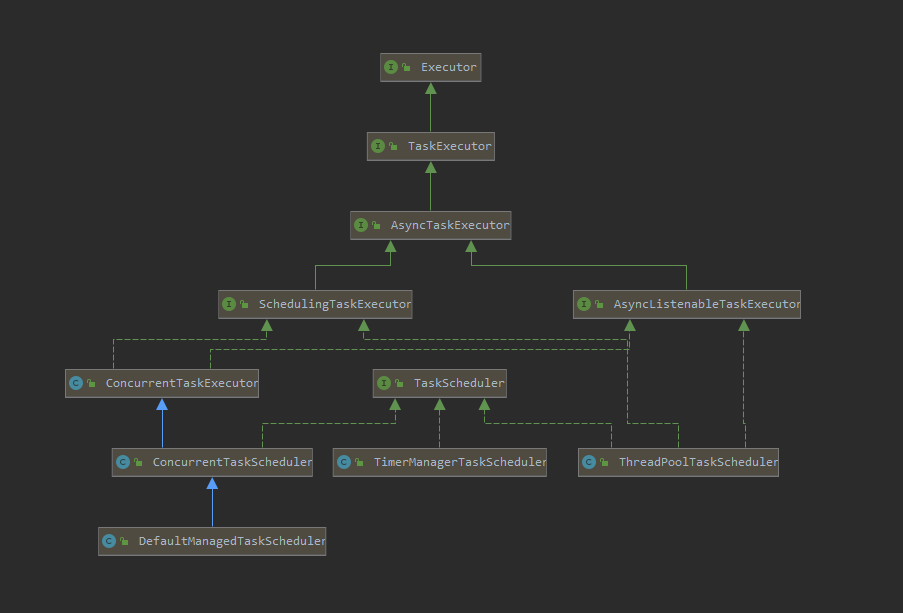
其中TaskScheduler接口的定义如下:
public interface TaskScheduler {
/**
* Schedule the given {@link Runnable}, invoking it whenever the trigger
* indicates a next execution time.
* <p>Execution will end once the scheduler shuts down or the returned
* {@link ScheduledFuture} gets cancelled.
* @param task the Runnable to execute whenever the trigger fires
* @param trigger an implementation of the {@link Trigger} interface,
* e.g. a {@link org.springframework.scheduling.support.CronTrigger} object
* wrapping a cron expression
* @return a {@link ScheduledFuture} representing pending completion of the task,
* or {@code null} if the given Trigger object never fires (i.e. returns
* {@code null} from {@link Trigger#nextExecutionTime})
* @throws org.springframework.core.task.TaskRejectedException if the given task was not accepted
* for internal reasons (e.g. a pool overload handling policy or a pool shutdown in progress)
* @see org.springframework.scheduling.support.CronTrigger
*/
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable task, Trigger trigger);
/**
* Schedule the given {@link Runnable}, invoking it at the specified execution time.
* <p>Execution will end once the scheduler shuts down or the returned
* {@link ScheduledFuture} gets cancelled.
* @param task the Runnable to execute whenever the trigger fires
* @param startTime the desired execution time for the task
* (if this is in the past, the task will be executed immediately, i.e. as soon as possible)
* @return a {@link ScheduledFuture} representing pending completion of the task
* @throws org.springframework.core.task.TaskRejectedException if the given task was not accepted
* for internal reasons (e.g. a pool overload handling policy or a pool shutdown in progress)
*/
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable task, Date startTime);
/**
* Schedule the given {@link Runnable}, invoking it at the specified execution time
* and subsequently with the given period.
* <p>Execution will end once the scheduler shuts down or the returned
* {@link ScheduledFuture} gets cancelled.
* @param task the Runnable to execute whenever the trigger fires
* @param startTime the desired first execution time for the task
* (if this is in the past, the task will be executed immediately, i.e. as soon as possible)
* @param period the interval between successive executions of the task (in milliseconds)
* @return a {@link ScheduledFuture} representing pending completion of the task
* @throws org.springframework.core.task.TaskRejectedException if the given task was not accepted
* for internal reasons (e.g. a pool overload handling policy or a pool shutdown in progress)
*/
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable task, Date startTime, long period);
/**
* Schedule the given {@link Runnable}, starting as soon as possible and
* invoking it with the given period.
* <p>Execution will end once the scheduler shuts down or the returned
* {@link ScheduledFuture} gets cancelled.
* @param task the Runnable to execute whenever the trigger fires
* @param period the interval between successive executions of the task (in milliseconds)
* @return a {@link ScheduledFuture} representing pending completion of the task
* @throws org.springframework.core.task.TaskRejectedException if the given task was not accepted
* for internal reasons (e.g. a pool overload handling policy or a pool shutdown in progress)
*/
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable task, long period);
/**
* Schedule the given {@link Runnable}, invoking it at the specified execution time
* and subsequently with the given delay between the completion of one execution
* and the start of the next.
* <p>Execution will end once the scheduler shuts down or the returned
* {@link ScheduledFuture} gets cancelled.
* @param task the Runnable to execute whenever the trigger fires
* @param startTime the desired first execution time for the task
* (if this is in the past, the task will be executed immediately, i.e. as soon as possible)
* @param delay the delay between the completion of one execution and the start
* of the next (in milliseconds)
* @return a {@link ScheduledFuture} representing pending completion of the task
* @throws org.springframework.core.task.TaskRejectedException if the given task was not accepted
* for internal reasons (e.g. a pool overload handling policy or a pool shutdown in progress)
*/
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable task, Date startTime, long delay);
/**
* Schedule the given {@link Runnable}, starting as soon as possible and
* invoking it with the given delay between the completion of one execution
* and the start of the next.
* <p>Execution will end once the scheduler shuts down or the returned
* {@link ScheduledFuture} gets cancelled.
* @param task the Runnable to execute whenever the trigger fires
* @param delay the interval between successive executions of the task (in milliseconds)
* @return a {@link ScheduledFuture} representing pending completion of the task
* @throws org.springframework.core.task.TaskRejectedException if the given task was not accepted
* for internal reasons (e.g. a pool overload handling policy or a pool shutdown in progress)
*/
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable task, long delay);
}
该接口定义了周期执行任务的方法。
ConcurrentTaskScheduler的字段如下:
// 周期执行器
private ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutor;
private boolean enterpriseConcurrentScheduler = false;
private ErrorHandler errorHandler;
// 装饰的方法如下
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable task, Trigger trigger) {
try {
if (this.enterpriseConcurrentScheduler) {
return new EnterpriseConcurrentTriggerScheduler().schedule(decorateTask(task, true), trigger);
}
else {
ErrorHandler errorHandler =
(this.errorHandler != null ? this.errorHandler : TaskUtils.getDefaultErrorHandler(true));
return new ReschedulingRunnable(task, trigger, this.scheduledExecutor, errorHandler).schedule();
}
}
catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {
throw new TaskRejectedException("Executor [" + this.scheduledExecutor + "] did not accept task: " + task, ex);
}
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable task, Date startTime) {
long initialDelay = startTime.getTime() - System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
return this.scheduledExecutor.schedule(decorateTask(task, false), initialDelay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {
throw new TaskRejectedException("Executor [" + this.scheduledExecutor + "] did not accept task: " + task, ex);
}
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable task, Date startTime, long period) {
long initialDelay = startTime.getTime() - System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
return this.scheduledExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(decorateTask(task, true), initialDelay, period, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {
throw new TaskRejectedException("Executor [" + this.scheduledExecutor + "] did not accept task: " + task, ex);
}
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable task, long period) {
try {
return this.scheduledExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(decorateTask(task, true), 0, period, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {
throw new TaskRejectedException("Executor [" + this.scheduledExecutor + "] did not accept task: " + task, ex);
}
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable task, Date startTime, long delay) {
long initialDelay = startTime.getTime() - System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
return this.scheduledExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(decorateTask(task, true), initialDelay, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {
throw new TaskRejectedException("Executor [" + this.scheduledExecutor + "] did not accept task: " + task, ex);
}
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable task, long delay) {
try {
return this.scheduledExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(decorateTask(task, true), 0, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {
throw new TaskRejectedException("Executor [" + this.scheduledExecutor + "] did not accept task: " + task, ex);
}
}
private Runnable decorateTask(Runnable task, boolean isRepeatingTask) {
Runnable result = TaskUtils.decorateTaskWithErrorHandler(task, this.errorHandler, isRepeatingTask);
if (this.enterpriseConcurrentScheduler) {
result = ManagedTaskBuilder.buildManagedTask(result, task.toString());
}
return result;
}
ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor原理
ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor主要是用来解析被@Scheduled注解标记的方法,注册到对应的List中,以及执行ConcurrentTaskScheduler
该类结构如下:
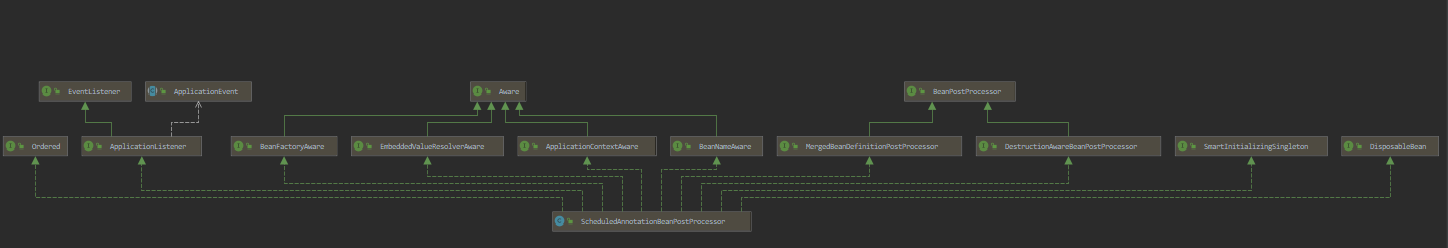
ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor实现了BeanPostProcessor,所以在实例化之后会调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法,在ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor中该方法的实现如下:
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof AopInfrastructureBean) {
// Ignore AOP infrastructure such as scoped proxies.
return bean;
}
Class<?> targetClass = AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(bean);
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetClass)) {
Map<Method, Set<Scheduled>> annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetClass,
new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<Set<Scheduled>>() {
@Override
public Set<Scheduled> inspect(Method method) {
Set<Scheduled> scheduledMethods = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedRepeatableAnnotations(
method, Scheduled.class, Schedules.class);
return (!scheduledMethods.isEmpty() ? scheduledMethods : null);
}
});
if (annotatedMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetClass);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No @Scheduled annotations found on bean class: " + targetClass);
}
}
else {
// Non-empty set of methods
for (Map.Entry<Method, Set<Scheduled>> entry : annotatedMethods.entrySet()) {
Method method = entry.getKey();
for (Scheduled scheduled : entry.getValue()) {
processScheduled(scheduled, method, bean);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(annotatedMethods.size() + " @Scheduled methods processed on bean '" + beanName +
"': " + annotatedMethods);
}
}
}
return bean;
}
该方法中主要调用了processScheduled来解析含有@Scheduled注解的方法。
/**
* Process the given {@code @Scheduled} method declaration on the given bean.
* @param scheduled the @Scheduled annotation
* @param method the method that the annotation has been declared on
* @param bean the target bean instance
*/
protected void processScheduled(Scheduled scheduled, Method method, Object bean) {
try {
Assert.isTrue(method.getParameterTypes().length == 0,
"Only no-arg methods may be annotated with @Scheduled");
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, bean.getClass());
Runnable runnable = new ScheduledMethodRunnable(bean, invocableMethod);
boolean processedSchedule = false;
String errorMessage =
"Exactly one of the 'cron', 'fixedDelay(String)', or 'fixedRate(String)' attributes is required";
Set<ScheduledTask> tasks = new LinkedHashSet<ScheduledTask>(4);
// Determine initial delay
long initialDelay = scheduled.initialDelay();
String initialDelayString = scheduled.initialDelayString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(initialDelayString)) {
Assert.isTrue(initialDelay < 0, "Specify 'initialDelay' or 'initialDelayString', not both");
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
initialDelayString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(initialDelayString);
}
try {
initialDelay = Long.parseLong(initialDelayString);
}
catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid initialDelayString value \"" + initialDelayString + "\" - cannot parse into integer");
}
}
// Check cron expression
String cron = scheduled.cron();
if (StringUtils.hasText(cron)) {
Assert.isTrue(initialDelay == -1, "'initialDelay' not supported for cron triggers");
processedSchedule = true;
String zone = scheduled.zone();
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
cron = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(cron);
zone = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(zone);
}
TimeZone timeZone;
if (StringUtils.hasText(zone)) {
timeZone = StringUtils.parseTimeZoneString(zone);
}
else {
timeZone = TimeZone.getDefault();
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleCronTask(new CronTask(runnable, new CronTrigger(cron, timeZone))));
}
// At this point we don't need to differentiate between initial delay set or not anymore
if (initialDelay < 0) {
initialDelay = 0;
}
// Check fixed delay
long fixedDelay = scheduled.fixedDelay();
if (fixedDelay >= 0) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedDelayTask(new IntervalTask(runnable, fixedDelay, initialDelay)));
}
String fixedDelayString = scheduled.fixedDelayString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(fixedDelayString)) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
fixedDelayString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(fixedDelayString);
}
try {
fixedDelay = Long.parseLong(fixedDelayString);
}
catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid fixedDelayString value \"" + fixedDelayString + "\" - cannot parse into integer");
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedDelayTask(new IntervalTask(runnable, fixedDelay, initialDelay)));
}
// Check fixed rate
long fixedRate = scheduled.fixedRate();
if (fixedRate >= 0) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedRateTask(new IntervalTask(runnable, fixedRate, initialDelay)));
}
String fixedRateString = scheduled.fixedRateString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(fixedRateString)) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
fixedRateString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(fixedRateString);
}
try {
fixedRate = Long.parseLong(fixedRateString);
}
catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid fixedRateString value \"" + fixedRateString + "\" - cannot parse into integer");
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedRateTask(new IntervalTask(runnable, fixedRate, initialDelay)));
}
// Check whether we had any attribute set
Assert.isTrue(processedSchedule, errorMessage);
// Finally register the scheduled tasks
synchronized (this.scheduledTasks) {
Set<ScheduledTask> registeredTasks = this.scheduledTasks.get(bean);
if (registeredTasks == null) {
registeredTasks = new LinkedHashSet<ScheduledTask>(4);
this.scheduledTasks.put(bean, registeredTasks);
}
registeredTasks.addAll(tasks);
}
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Encountered invalid @Scheduled method '" + method.getName() + "': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
解析到的方法被注册到ScheduledTaskRegistrar中,该类主要用于存放被解析到的用于定时执行的方法。该类中的字段如下:
private TaskScheduler taskScheduler;
private ScheduledExecutorService localExecutor;
private List<TriggerTask> triggerTasks;
private List<CronTask> cronTasks;
private List<IntervalTask> fixedRateTasks;
private List<IntervalTask> fixedDelayTasks;
private final Map<Task, ScheduledTask> unresolvedTasks = new HashMap<Task, ScheduledTask>(16);
private final Set<ScheduledTask> scheduledTasks = new LinkedHashSet<ScheduledTask>(16);
解析完成之后会在实例创建完成之后开始定时任务的执行。
ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor实现了SmartInitializingSingleton,所以在实例创建完成后会调用ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的afterSingletonsInstantiated方法。
该方法的实现如下:
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
// Remove resolved singleton classes from cache
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.clear();
if (this.applicationContext == null) {
// Not running in an ApplicationContext -> register tasks early...
finishRegistration();
}
}
finishRegistration方法的实现如下:
private void finishRegistration() {
if (this.scheduler != null) {
this.registrar.setScheduler(this.scheduler);
}
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ListableBeanFactory) {
Map<String, SchedulingConfigurer> beans =
((ListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory).getBeansOfType(SchedulingConfigurer.class);
List<SchedulingConfigurer> configurers = new ArrayList<SchedulingConfigurer>(beans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(configurers);
for (SchedulingConfigurer configurer : configurers) {
configurer.configureTasks(this.registrar);
}
}
if (this.registrar.hasTasks() && this.registrar.getScheduler() == null) {
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "BeanFactory must be set to find scheduler by type");
try {
// Search for TaskScheduler bean...
this.registrar.setTaskScheduler(resolveSchedulerBean(TaskScheduler.class, false));
}
catch (NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException ex) {
logger.debug("Could not find unique TaskScheduler bean", ex);
try {
this.registrar.setTaskScheduler(resolveSchedulerBean(TaskScheduler.class, true));
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex2) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("More than one TaskScheduler bean exists within the context, and " +
"none is named 'taskScheduler'. Mark one of them as primary or name it 'taskScheduler' " +
"(possibly as an alias); or implement the SchedulingConfigurer interface and call " +
"ScheduledTaskRegistrar#setScheduler explicitly within the configureTasks() callback: " +
ex.getBeanNamesFound());
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
logger.debug("Could not find default TaskScheduler bean", ex);
// Search for ScheduledExecutorService bean next...
try {
this.registrar.setScheduler(resolveSchedulerBean(ScheduledExecutorService.class, false));
}
catch (NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException ex2) {
logger.debug("Could not find unique ScheduledExecutorService bean", ex2);
try {
this.registrar.setScheduler(resolveSchedulerBean(ScheduledExecutorService.class, true));
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex3) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("More than one ScheduledExecutorService bean exists within the context, and " +
"none is named 'taskScheduler'. Mark one of them as primary or name it 'taskScheduler' " +
"(possibly as an alias); or implement the SchedulingConfigurer interface and call " +
"ScheduledTaskRegistrar#setScheduler explicitly within the configureTasks() callback: " +
ex2.getBeanNamesFound());
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex2) {
logger.debug("Could not find default ScheduledExecutorService bean", ex2);
// Giving up -> falling back to default scheduler within the registrar...
logger.info("No TaskScheduler/ScheduledExecutorService bean found for scheduled processing");
}
}
}
// 调用注册器的方法执行启动操作
this.registrar.afterPropertiesSet();
}
afterPropertiesSet方法的实现如下:
/**
* Calls {@link #scheduleTasks()} at bean construction time.
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
scheduleTasks();
}
/**
* Schedule all registered tasks against the underlying {@linkplain
* #setTaskScheduler(TaskScheduler) task scheduler}.
*/
protected void scheduleTasks() {
if (this.taskScheduler == null) {
this.localExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
this.taskScheduler = new ConcurrentTaskScheduler(this.localExecutor);
}
if (this.triggerTasks != null) {
for (TriggerTask task : this.triggerTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleTriggerTask(task));
}
}
if (this.cronTasks != null) {
for (CronTask task : this.cronTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleCronTask(task));
}
}
if (this.fixedRateTasks != null) {
for (IntervalTask task : this.fixedRateTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleFixedRateTask(task));
}
}
if (this.fixedDelayTasks != null) {
for (IntervalTask task : this.fixedDelayTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleFixedDelayTask(task));
}
}
}
private void addScheduledTask(ScheduledTask task) {
if (task != null) {
this.scheduledTasks.add(task);
}
}
/**
* Schedule the specified trigger task, either right away if possible
* or on initialization of the scheduler.
* @return a handle to the scheduled task, allowing to cancel it
* @since 4.3
*/
public ScheduledTask scheduleTriggerTask(TriggerTask task) {
ScheduledTask scheduledTask = this.unresolvedTasks.remove(task);
boolean newTask = false;
if (scheduledTask == null) {
scheduledTask = new ScheduledTask();
newTask = true;
}
if (this.taskScheduler != null) {
scheduledTask.future = this.taskScheduler.schedule(task.getRunnable(), task.getTrigger());
}
else {
addTriggerTask(task);
this.unresolvedTasks.put(task, scheduledTask);
}
return (newTask ? scheduledTask : null);
}
/**
* Schedule the specified cron task, either right away if possible
* or on initialization of the scheduler.
* @return a handle to the scheduled task, allowing to cancel it
* (or {@code null} if processing a previously registered task)
* @since 4.3
*/
public ScheduledTask scheduleCronTask(CronTask task) {
ScheduledTask scheduledTask = this.unresolvedTasks.remove(task);
boolean newTask = false;
if (scheduledTask == null) {
scheduledTask = new ScheduledTask();
newTask = true;
}
if (this.taskScheduler != null) {
scheduledTask.future = this.taskScheduler.schedule(task.getRunnable(), task.getTrigger());
}
else {
addCronTask(task);
this.unresolvedTasks.put(task, scheduledTask);
}
return (newTask ? scheduledTask : null);
}
/**
* Schedule the specified fixed-rate task, either right away if possible
* or on initialization of the scheduler.
* @return a handle to the scheduled task, allowing to cancel it
* (or {@code null} if processing a previously registered task)
* @since 4.3
*/
public ScheduledTask scheduleFixedRateTask(IntervalTask task) {
ScheduledTask scheduledTask = this.unresolvedTasks.remove(task);
boolean newTask = false;
if (scheduledTask == null) {
scheduledTask = new ScheduledTask();
newTask = true;
}
if (this.taskScheduler != null) {
if (task.getInitialDelay() > 0) {
Date startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + task.getInitialDelay());
scheduledTask.future =
this.taskScheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(task.getRunnable(), startTime, task.getInterval());
}
else {
scheduledTask.future =
this.taskScheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(task.getRunnable(), task.getInterval());
}
}
else {
addFixedRateTask(task);
this.unresolvedTasks.put(task, scheduledTask);
}
return (newTask ? scheduledTask : null);
}
/**
* Schedule the specified fixed-delay task, either right away if possible
* or on initialization of the scheduler.
* @return a handle to the scheduled task, allowing to cancel it
* (or {@code null} if processing a previously registered task)
* @since 4.3
*/
public ScheduledTask scheduleFixedDelayTask(IntervalTask task) {
ScheduledTask scheduledTask = this.unresolvedTasks.remove(task);
boolean newTask = false;
if (scheduledTask == null) {
scheduledTask = new ScheduledTask();
newTask = true;
}
if (this.taskScheduler != null) {
if (task.getInitialDelay() > 0) {
Date startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + task.getInitialDelay());
scheduledTask.future =
this.taskScheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(task.getRunnable(), startTime, task.getInterval());
}
else {
scheduledTask.future =
this.taskScheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(task.getRunnable(), task.getInterval());
}
}
else {
addFixedDelayTask(task);
this.unresolvedTasks.put(task, scheduledTask);
}
return (newTask ? scheduledTask : null);
}
具体的执行方式如上所示。