入口代码如下:
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
(1)、执行初始化时设置的listeners。这里面首先使用的是org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener这个listener来触发其他的listener的执行。
listener的执行过程如下:
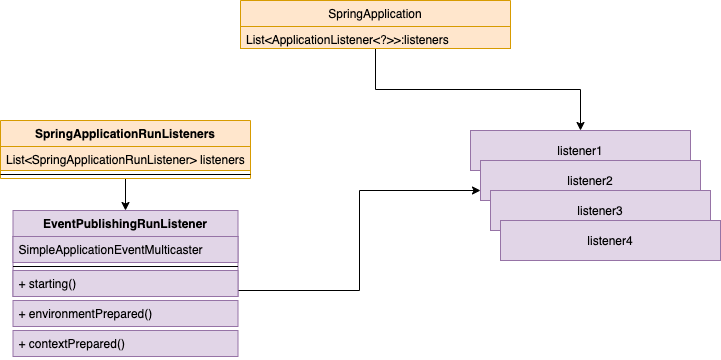
在SpringApplication的run方法中,获取SpringApplicationRunListener,这里面的实现类是EventPublishingRunListener,这个类负责持有所有的listener对象。SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,这个类负责根据Event类型来筛选出合适的listener。SpringApplicationRunListeners,这个类负责执行所有SpringApplicationRunListener。
(2)、创建ApplicationContext。
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
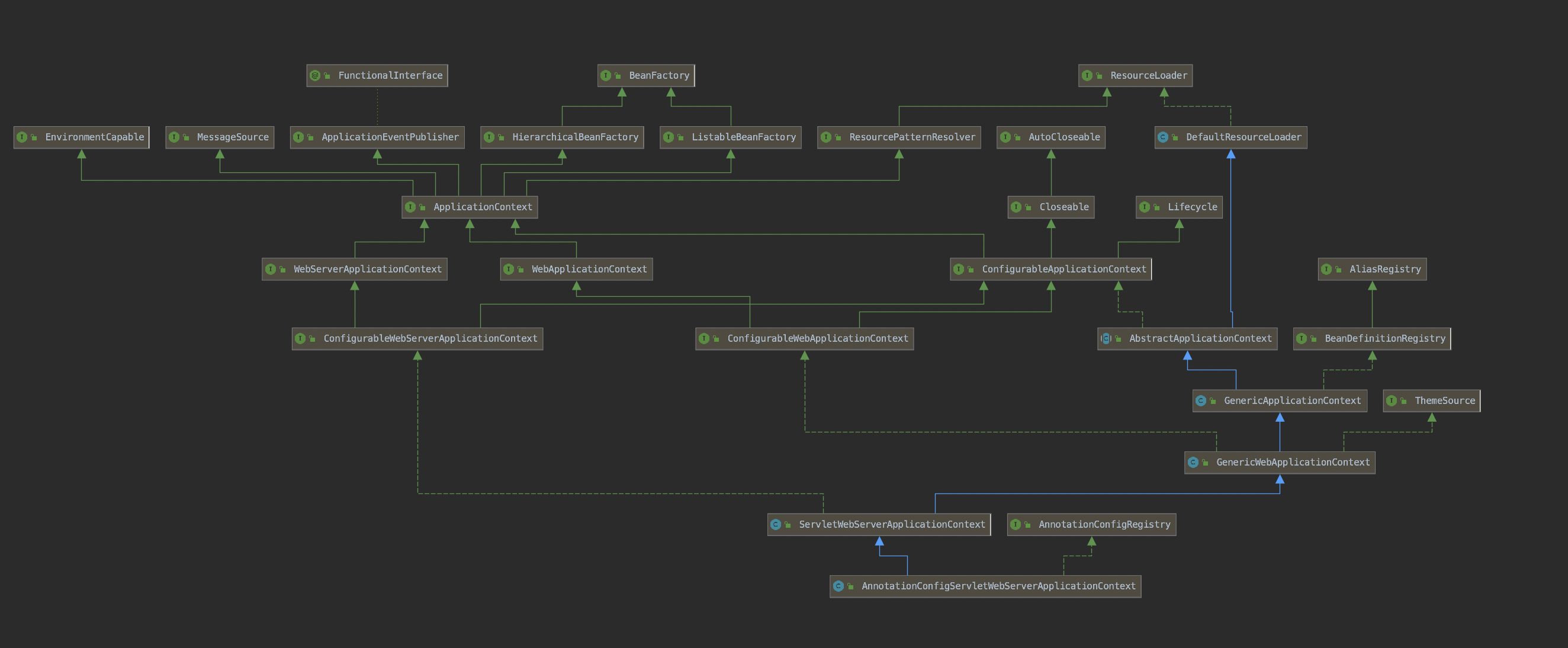
如果是Web环境那么此时会创建
public static final String DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot."
+ "web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext";
该类的关系如下:
(3)、接下来会为执行创建Environment并填充数据操作。
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
这里比较重要的就是listeners.environmentPrepared(environment),application.properties文件的读取操作就是在这里执行的。详细看下:
具体的读取操作是在ConfigFileApplicationListener类里面来完成的。
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
一路执行到这里,就是读取配置文件的入口了,这里将读取操作委托给一个叫Loader的内部类。
具体配置文件路径的加载顺序如下:
private static final String DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS = "classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/";
具体执行load操作的代码如下:
void load() {
FilteredPropertySource.apply(this.environment, DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, LOAD_FILTERED_PROPERTY,
(defaultProperties) -> {
this.profiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.activatedProfiles = false;
this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>();
initializeProfiles();
while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
Profile profile = this.profiles.poll();
if (isDefaultProfile(profile)) {
addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName());
}
load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter,
addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false));
this.processedProfiles.add(profile);
}
load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true));
addLoadedPropertySources();
applyActiveProfiles(defaultProperties);
});
}
private void load(PropertySourceLoader loader, String location, Profile profile, DocumentFilter filter,
DocumentConsumer consumer) {
try {
Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(location);
if (resource == null || !resource.exists()) {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
StringBuilder description = getDescription("Skipped missing config ", location, resource,
profile);
this.logger.trace(description);
}
return;
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(StringUtils.getFilenameExtension(resource.getFilename()))) {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
StringBuilder description = getDescription("Skipped empty config extension ", location,
resource, profile);
this.logger.trace(description);
}
return;
}
String name = "applicationConfig: [" + location + "]";
List<Document> documents = loadDocuments(loader, name, resource);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(documents)) {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
StringBuilder description = getDescription("Skipped unloaded config ", location, resource,
profile);
this.logger.trace(description);
}
return;
}
List<Document> loaded = new ArrayList<>();
for (Document document : documents) {
if (filter.match(document)) {
addActiveProfiles(document.getActiveProfiles());
addIncludedProfiles(document.getIncludeProfiles());
loaded.add(document);
}
}
Collections.reverse(loaded);
if (!loaded.isEmpty()) {
loaded.forEach((document) -> consumer.accept(profile, document));
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
StringBuilder description = getDescription("Loaded config file ", location, resource, profile);
this.logger.debug(description);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to load property source from location '" + location + "'", ex);
}
}
private DocumentConsumer addToLoaded(BiConsumer<MutablePropertySources, PropertySource<?>> addMethod,
boolean checkForExisting) {
return (profile, document) -> {
if (checkForExisting) {
for (MutablePropertySources merged : this.loaded.values()) {
if (merged.contains(document.getPropertySource().getName())) {
return;
}
}
}
MutablePropertySources merged = this.loaded.computeIfAbsent(profile,
(k) -> new MutablePropertySources());
addMethod.accept(merged, document.getPropertySource());
};
}
这里通过循环获取Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(location)判断能否获取到配置文件。如果获取到就加载进ConfigurableEnvironment中。
(4)、接下来为创建好的context上下文配置数据。其中就有把刚刚解析到的environment参数配置到context中,这样就把配置文件中的数据也设置到context中。具体代码如下:
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
(5)、接下来会执行刷新上下文操作,该操作会执行Spring容器的全部实例加载。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
具体的onRefresh操作是在ServletWebServerApplicationContext中执行的:
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
这里会创建Web容器的实例。
private volatile WebServer webServer;
注意这里仅仅是创建容器的实例,还未发生启动操作。DispatcherServlet实例也不是在此处设置的。这里只是把设置DispatcherServlet的逻辑配置进去了,还不会执行。
设置DispatcherServlet到ServletContext中的代码如下:
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
prepareWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
registerApplicationScope(servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(getBeanFactory(), servletContext);
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
@Override
public final void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
String description = getDescription();
if (!isEnabled()) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (disabled)");
return;
}
register(description, servletContext);
}
@Override
protected final void register(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
D registration = addRegistration(description, servletContext);
if (registration == null) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (possibly already registered?)");
return;
}
configure(registration);
}
@Override
protected ServletRegistration.Dynamic addRegistration(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
String name = getServletName();
return servletContext.addServlet(name, this.servlet);
}
@Override
protected void configure(ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration) {
super.configure(registration);
String[] urlMapping = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.urlMappings);
if (urlMapping.length == 0 && this.alwaysMapUrl) {
urlMapping = DEFAULT_MAPPINGS;
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urlMapping)) {
registration.addMapping(urlMapping);
}
registration.setLoadOnStartup(this.loadOnStartup);
if (this.multipartConfig != null) {
registration.setMultipartConfig(this.multipartConfig);
}
}
@Override
public Set<String> addMapping(String... urlPatterns) {
if (urlPatterns == null) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
Set<String> conflicts = new HashSet<>();
for (String urlPattern : urlPatterns) {
String wrapperName = context.findServletMapping(urlPattern);
if (wrapperName != null) {
Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) context.findChild(wrapperName);
if (wrapper.isOverridable()) {
// Some Wrappers (from global and host web.xml) may be
// overridden rather than generating a conflict
context.removeServletMapping(urlPattern);
} else {
conflicts.add(urlPattern);
}
}
}
if (!conflicts.isEmpty()) {
return conflicts;
}
for (String urlPattern : urlPatterns) {
context.addServletMappingDecoded(
UDecoder.URLDecode(urlPattern, StandardCharsets.UTF_8), wrapper.getName());
}
if (constraint != null) {
context.addServletSecurity(this, constraint);
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
这里可以看到,在这个类中ServletRegistrationBean分别将DispatcherServlet和URLMapping设置到ServletContext中。这部分触发逻辑是依赖Tomcat在启动的时候执行。
在执行完onRefresh之后,在finishRefresh()中执行web容器启动。
至此,Spring容器和web容器已经全部启动起来,至于Spring的context是如何跟Web容器关联起来,在SpringMVC的原理中讲述。
下面讲下,Web容器的配置是如何搭建起来的:
首先是ServletWebServer工厂的注册与初始化:
ServletWebServerFactory接口的实现类有三个可实例化的类。
TomcatServletWebServerFactory,
JettyServletWebServerFactory,
UndertowServletWebServerFactory。
默认的实现的是Tomcat。
创建及初始化ServerFactory的流程图如下:
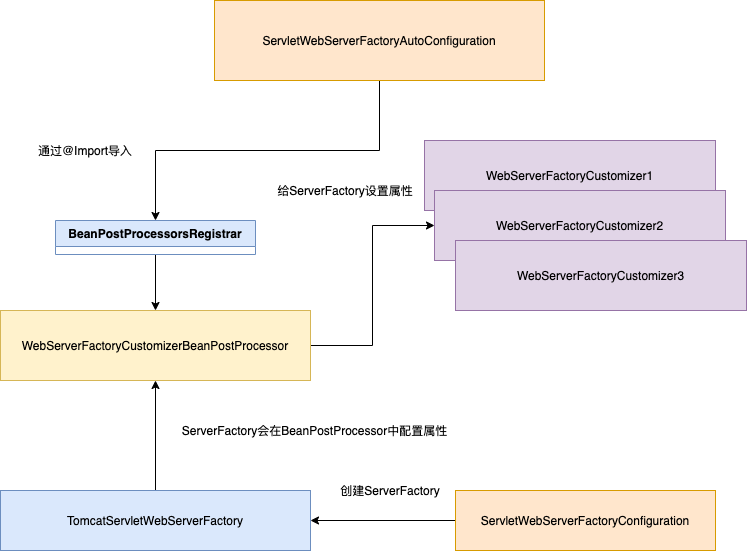
其中ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration这个类是创建WebServerFactoryCustomizer,这个类下面会介绍,并通过@Import导入BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar,这个类会在Spring容器初始化的时候获取并执行WebServerFactoryCustomizer的customize方法。
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration这个类是创建TomcatServletWebServerFactory。
WebServerFactoryCustomizer这个类是执行设置WebServerFactory的属性的方法。
类结构如下:
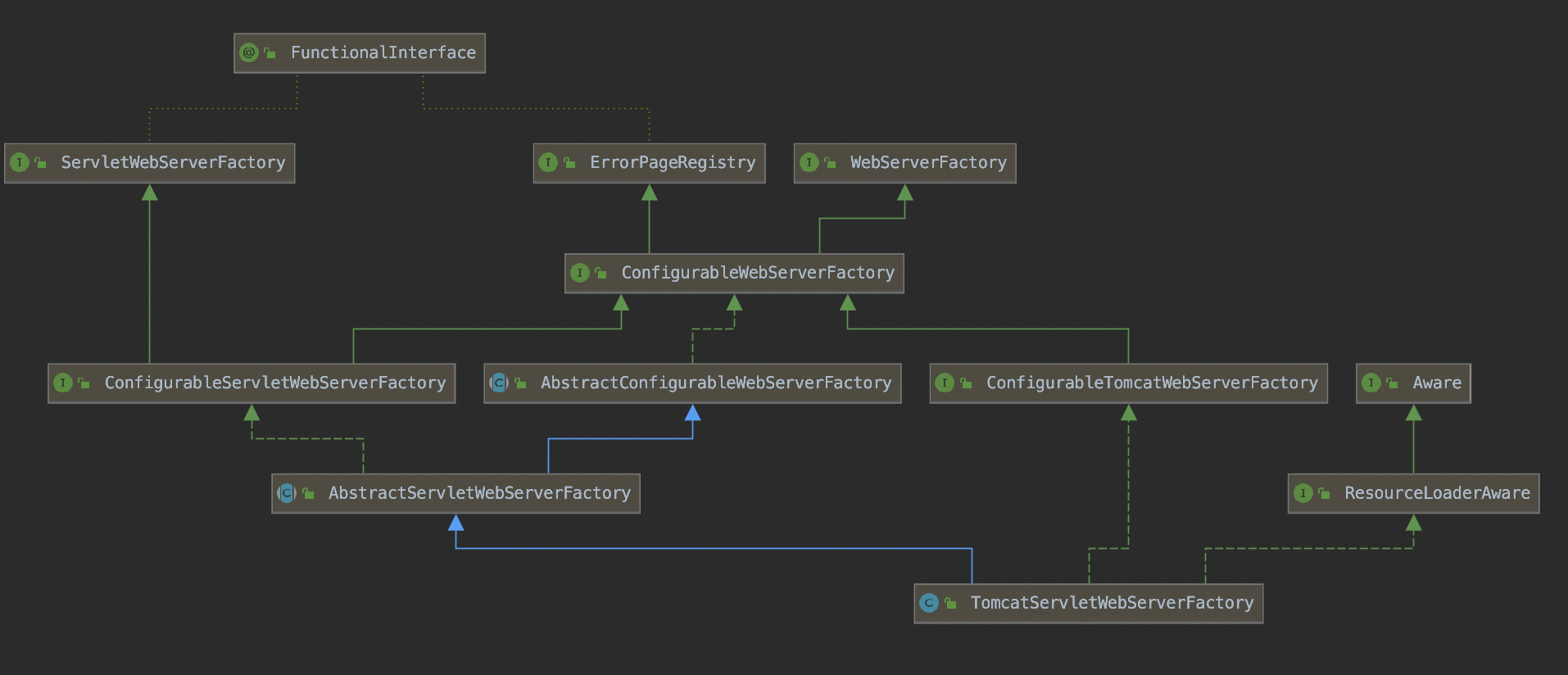
以上就是Tomcat服务被配置和创建的过程。
DispatcherServlet的创建与注册
首先DispatcherServlet是通过DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration类里面的DispatcherServletConfiguration的类创建DispatcherServlet实例,然后通过上面介绍启动容器的逻辑中将DispatcherServlet注册到容器中。