1、概述
在数据持久层中,数据源是一个非常重要的组件,其性能直接关系到整个数据持久层的性能。在实践中比较常见的第三方数据源组件有Apache Common DBCP、C3P0、Proxool等,Mybatis不仅可以集成第三方数据源组件,还提供了自己的数据源实现。
2、DataSource
常见的数据源组件都实现了javax.sql.DataSource接口,Mybatis自身实现的数据源实现也不例外。Mybatis提供了两个javax.sql.DataSource接口实现,分别是PooledDataSource和UnpooledDataSource。Mybatis使用不同的DataSourceFactory接口实现创建不同类型的DataSource。
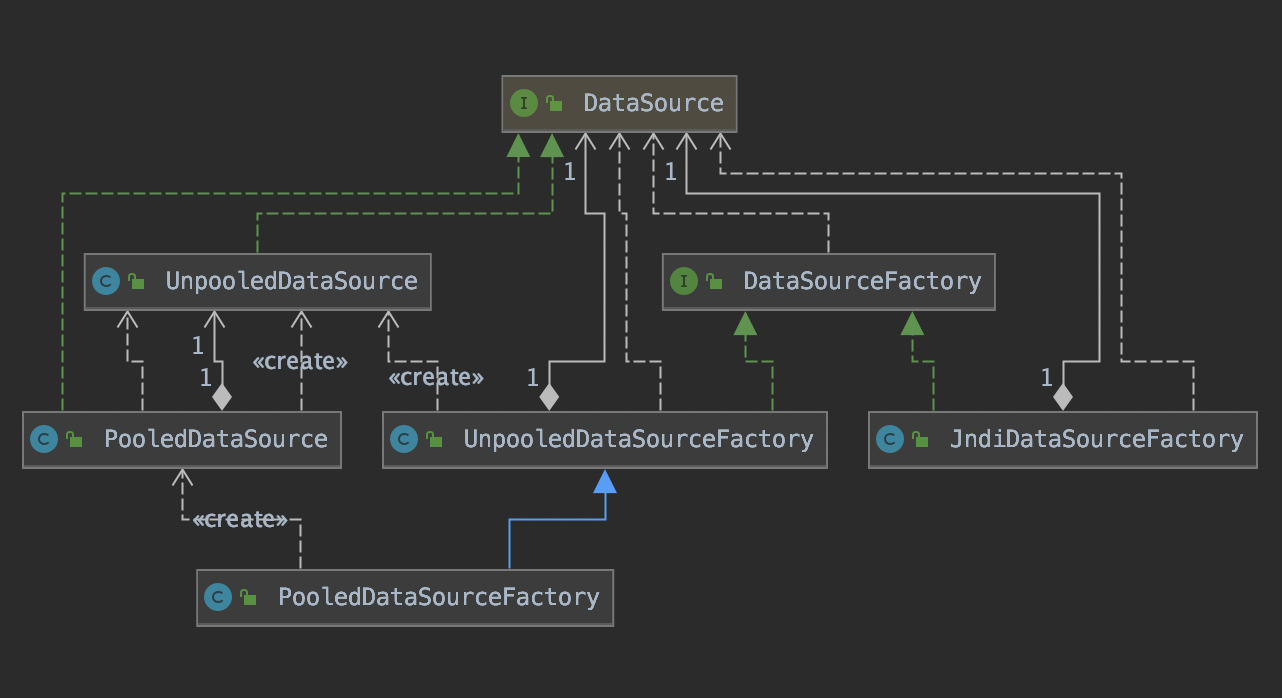
在解析配置文件时会创建DataSource。
创建DataSource的代码如下:
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (environment == null) {
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
// 解析environment节点的id属性
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
// 解析事务工厂类
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
// 解析DataSourceFactory
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
// 获取数据源
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
数据库连接池在初始化时,一般会创建一定数量的数据库连接并添加到连接池中备用。当程序需要使用数据库连接时,从池中请求连接。当程序不再使用该连接时,会将其返回到池中缓存,等待下次使用,而不是直接关闭。当然,数据库连接池会控制连接总数的上限以及空闲连接数上限,如果连接池创建的总连接数已达到上限,且都已被占用,则后续请求连接的线程会进入阻塞队列等待,知道有线程释放出可用的连接。如果连接池中空闲连接数较多,达到其上限,则后续返回的空闲连接不会放入池中,而是直接关闭,这样可以减少系统维护多余数据库连接的开销。
如果将总连接数的上限设置的过大,可能因连接数过多导致数据库僵死,系统整体性能下降,如果总连接数上限过小,则无法完全发挥数据库的性能,浪费数据库资源,如果将空闲连接的上限设置的过大,则会浪费系统资源来维护这些空闲连接;如果空闲连接上限过小,当出现瞬间的峰值请求时,系统的快速响应能力就比较弱,所以在设置数据库连接池的这两个值时,需要进行性能测试。
PooledDataSource实现了简单的数据库连接的功能,PooledDataSource创建数据库连接的功能是依赖其中封装的UnpooledDataSource对象实现的。
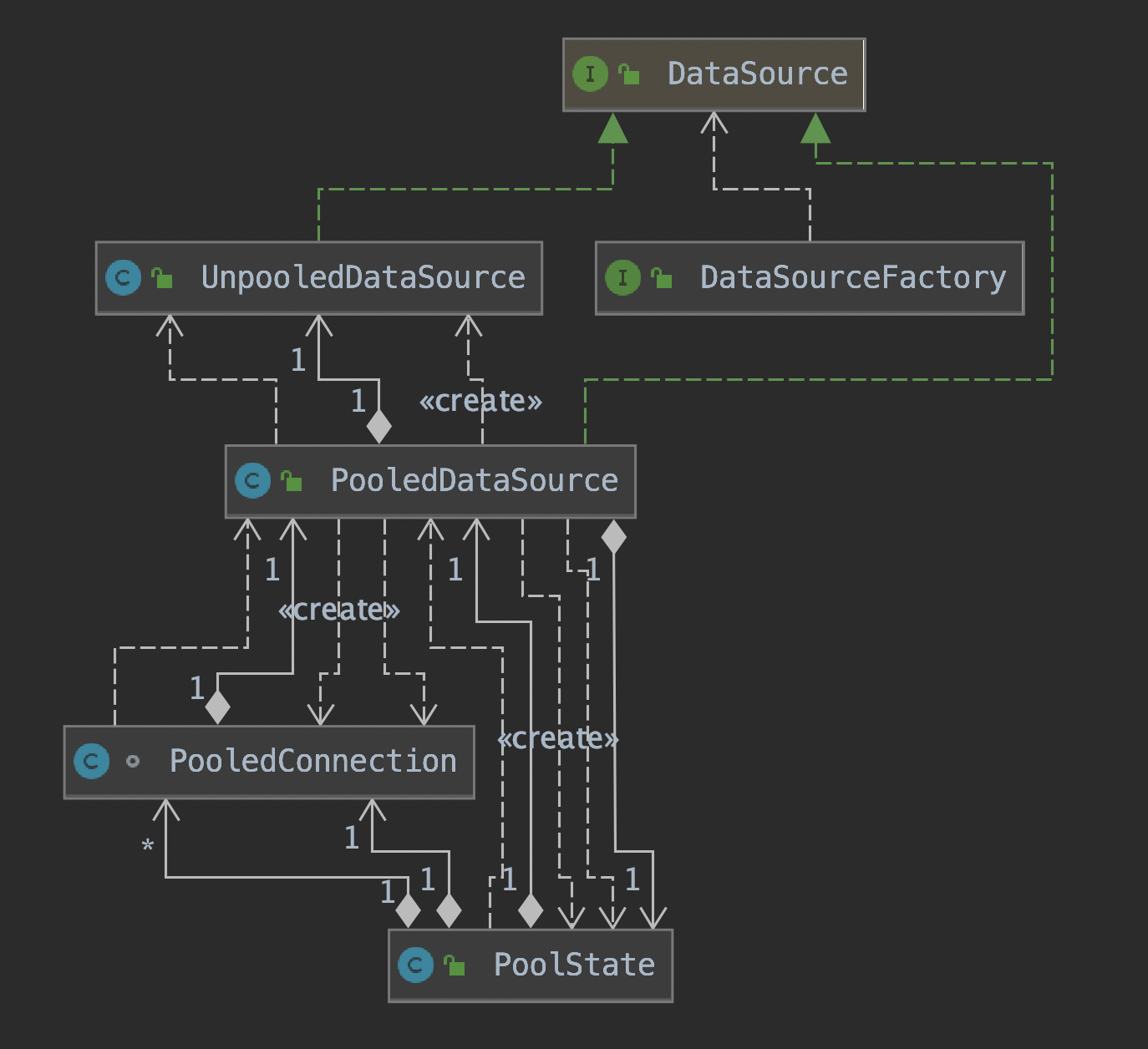
PooledDataSource并不会直接管理java.sql.Connection对象,而是管理PooledConnection对象。在PooledConnection中封装了真正的数据库连接对象以及其代理对象,这里的代理是通过JDK动态代理产生的。PooledConnection继承了InvocationHandler接口。
PooledConnection类的核心字段如下:
private final int hashCode;
// 记录当前PooledConnection对象所在的PooledDataSource对象。
// 该PooledConnection是从该PooledDataSource中获取的;
// 当调用close()方法时会将该PooledConnection方法该PooledDataSource中
private final PooledDataSource dataSource;
// 真正的数据库连接
private final Connection realConnection;
// 数据库连接的代理对象
private final Connection proxyConnection;
// 从连接池中取出该连接的时间戳
private long checkoutTimestamp;
// 该连接创建的时间戳
private long createdTimestamp;
// 最后一次使用该连接的时间戳
private long lastUsedTimestamp;
private int connectionTypeCode;
private boolean valid;
invoke()方法如下:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
if (CLOSE.hashCode() == methodName.hashCode() && CLOSE.equals(methodName)) {
// 如果是close方法,则将连接放回到连接池中
dataSource.pushConnection(this);
return null;
} else {
try {
if (!Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// issue #579 toString() should never fail
// throw an SQLException instead of a Runtime
// 检查连接的可用性
checkConnection();
}
// 调用Connection的对应的方法
return method.invoke(realConnection, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}
PoolState是用于管理PooledConnection对象状态的组件,它通过两个ArrayList
PooledDataSource中管理的真正的数据库连接对象是由PooledDataSource中封装的UnpooledDataSource对象创建的,并由PoolState管理所有的连接的状态。PooledDataSource中核心字段的含义和功能如下:
// 通过state管理连接池对象
private final PoolState state = new PoolState(this);
// 持有UnpooledDataSource对象,真正创建Connection对象
private final UnpooledDataSource dataSource;
// OPTIONAL CONFIGURATION FIELDS
// 最大活跃连接数
protected int poolMaximumActiveConnections = 10;
// 最大空闲连接数
protected int poolMaximumIdleConnections = 5;
// 最大checkout时长
protected int poolMaximumCheckoutTime = 20000;
// 在无法获取连接时,线程需要等待的时间
protected int poolTimeToWait = 20000;
protected int poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance = 3;
// 在检测一个数据库连接是否可用时,会给数据库发送一个测试SQL语句
protected String poolPingQuery = "NO PING QUERY SET";
// 是否允许发送测试SQL语句
protected boolean poolPingEnabled;
protected int poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor;
private int expectedConnectionTypeCode;
PooledDataSource实现了DataSource,getConnection()方法如下:
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 获取动态代理对象,这里加入动态代理实际上是为了实现close时,自动放回连接到连接池中。
return popConnection(dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()).getProxyConnection();
}
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
boolean countedWait = false;
PooledConnection conn = null;
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
int localBadConnectionCount = 0;
while (conn == null) {
synchronized (state) {
// 如果活跃连接不为空,则从活跃连接数组中获取连接
if (!state.idleConnections.isEmpty()) {
// Pool has available connection
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checked out connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " from pool.");
}
} else {
// 如果池中还没有活跃连接,则使用UnpooledDataSource来创建
// Pool does not have available connection
if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) {
// Can create new connection
conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Created connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// Cannot create new connection
PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0);
long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime();
if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) {
// Can claim overdue connection
state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += longestCheckoutTime;
state.activeConnections.remove(oldestActiveConnection);
if (!oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
try {
oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
/*
Just log a message for debug and continue to execute the following
statement like nothing happend.
Wrap the bad connection with a new PooledConnection, this will help
to not intterupt current executing thread and give current thread a
chance to join the next competion for another valid/good database
connection. At the end of this loop, bad {@link @conn} will be set as null.
*/
log.debug("Bad connection. Could not roll back");
}
}
conn = new PooledConnection(oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection(), this);
conn.setCreatedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getCreatedTimestamp());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getLastUsedTimestamp());
oldestActiveConnection.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Claimed overdue connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// Must wait
try {
if (!countedWait) {
state.hadToWaitCount++;
countedWait = true;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Waiting as long as " + poolTimeToWait + " milliseconds for connection.");
}
long wt = System.currentTimeMillis();
state.wait(poolTimeToWait);
state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
if (conn != null) {
// ping to server and check the connection is valid or not
if (conn.isValid()) {
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password));
conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
state.activeConnections.add(conn);
state.requestCount++;
state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") was returned from the pool, getting another connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
localBadConnectionCount++;
conn = null;
if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
}
}
}
}
if (conn == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
return conn;
}
逻辑图如下:
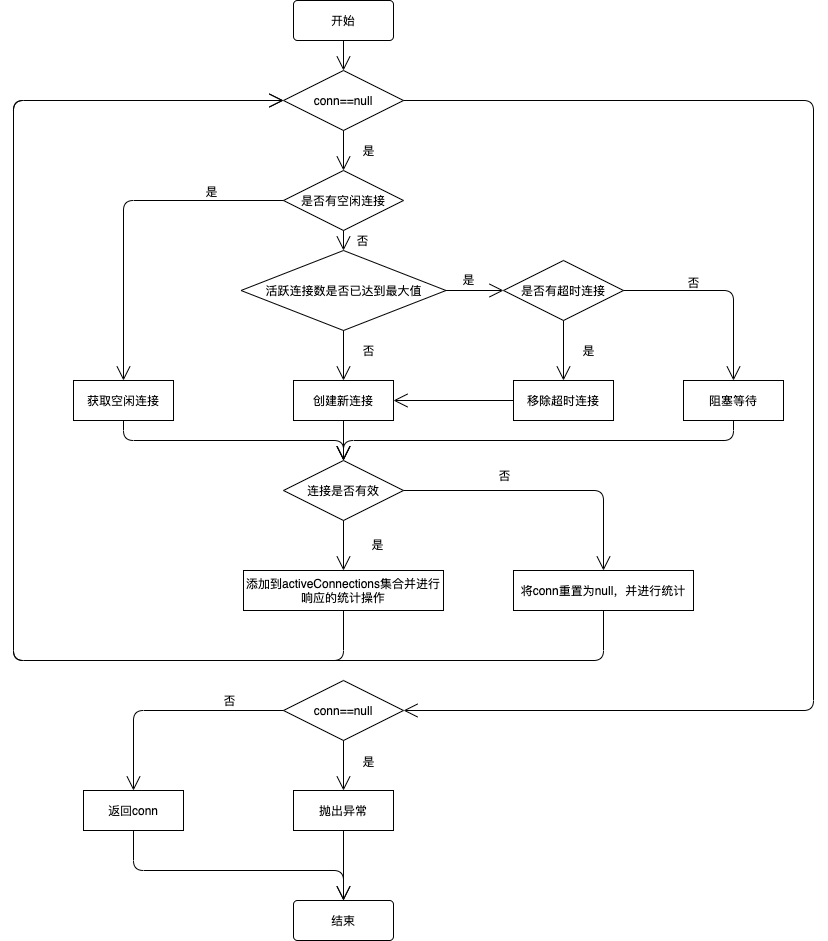
pushConnection()方法实现如下:
protected void pushConnection(PooledConnection conn) throws SQLException {
synchronized (state) {
// 从activeConnections中移除该PooledConnection对象
state.activeConnections.remove(conn);
if (conn.isValid()) { // 检测连接是否有效
// 检测活跃连接数是否已经达到上限,以及该PooledConnection是否为该连接池的连接。
if (state.idleConnections.size() < poolMaximumIdleConnections && conn.getConnectionTypeCode() == expectedConnectionTypeCode) {
// 累计checkout时长
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) { // 回滚未提交的事务
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 返还连接创建新的PooledConnection对象
PooledConnection newConn = new PooledConnection(conn.getRealConnection(), this);
// 添加到idleConnection集合中
state.idleConnections.add(newConn);
newConn.setCreatedTimestamp(conn.getCreatedTimestamp());
newConn.setLastUsedTimestamp(conn.getLastUsedTimestamp());
// 将原来的连接设置为无效
conn.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Returned connection " + newConn.getRealHashCode() + " to pool.");
}
// 唤醒阻塞等待线程
state.notifyAll();
} else { // 空闲连接数已达到上限或PooledConnection对象并不属于该连接池
// 累计checkout时长
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 关闭真正的数据库连接
conn.getRealConnection().close();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closed connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
//将PooledConnection对象设置为无效
conn.invalidate();
}
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") attempted to return to the pool, discarding connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
}
}
}