1、概述
插件是一种常见的扩展方式,大多数开源框架也都支持用户通过添加自定义插件的方式来扩展或改变框架原有的功能,Mybatis中也提供了插件功能,虽然叫插件,但是实际上是通过拦截器(interceptor)实现的。在Mybatis的插件模块中涉及责任链模式和JDK动态代理。
2、Interceptor
Mybatis允许用户使用自定义拦截器对SQL语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截。默认情况下,Mybatis允许拦截器拦截Executor的方法、ParameterHandler方法、ResultSetHandler方法以及StatementHandler的方法。具体可拦截的方法如下:
(1)、Executor中的update()方法、query()方法、flushStatement()方法、commit()方法、rollback()方法、getTracsaction()方法、close()方法、isClosed()方法。
(2)、ParameterHandler中的getParameterObject()方法、setParameters()方法。
(3)、ResultSetHandler中的handleResultSets()方法、handleOutputParameters()方法。
(4)、StatementHandler中的prepare()方法、parameterize()方法、batch()方法、update()方法、query()方法。
Mybatis中使用拦截器都需要实现Interceptor接口。Interceptor接口是Mybatis插件模块的核心。其定义如下:
public interface Interceptor {
// 执行拦截逻辑的方法
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
// 决定是否触发intercept()方法
Object plugin(Object target);
// 根据配置初始化Interceptor对象
void setProperties(Properties properties);
}
用户自定义的拦截器除了继承Interceptor接口,还需要使用@Intercepts和@Signature两个注解进行标识。@Intercepts注解中指定了一个@Signature注解列表,每个@Signature注解中都标识了该插件需要拦截的方法信息,其中@Signature注解的type属性指定需要拦截的类型,method属性指定需要拦截的方法,args属性指定了被拦截方法的参数列表。通过这三个属性值,@Signature注解就可以表示一个方法签名,唯一确定一个方法。
举个例子:
// 拦截Executor类的query方法,并进行增强
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class,
Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
public class ExamplePlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("this is a plugin in mybatis");
Executor executor = (Executor)invocation.getTarget();
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
MappedStatement mappedStatement = (MappedStatement)args[0];
Object parameter = args[1];
int a= mappedStatement.getCache().getSize();
Cache cache = mappedStatement.getCache();
System.out.println("executor now cache is: " + a);
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
}
然后在configuration配置文件中配置插件:
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.matrix.plugin.ExamplePlugin"/>
</plugins>
3、plugin的实现原理
plugin是通过在Configuration的创建各个组件时实现的。代码如下:
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction) {
return newExecutor(transaction, defaultExecutorType);
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
每个组件在创建完成之前都统一调用了InterceptorChain的pluginAll方法通过动态代理实现对原对象的增强。
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<Interceptor>();
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
这里会统一调用从configuration中解析到的interceptor的plugin方法。
用户可以在实现Interceptor方法时,自定义一些逻辑。Mybatis提供了一个实现,就是通过Plugin类的wrap()方法来实现对目标类的动态代理。
这里介绍下Plugin类。
Plugin类实现了InvocationHandler接口。先来看看它的wrap方法:
// 该方法主要是生成一个目标类的动态代理对象
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 解析Interceptor实现类标注的注解。
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
// 获取目标类型,比如Executor、StatementHandler、ResultSetHandler、ParameterHandler
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
// 获取类型的接口,根据接口来实现动态代理
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
// 创建动态代理对象
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
signatureMap方法如下:
private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
// 获取用户实现的Interceptor类型的Intercepts注解。
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
// issue #251
// 如果没有Intercepts注解则抛出PluginException异常
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
// 获取Intercepts注解中的Signature注解
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, Set<Method>>();
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(sig.type());
if (methods == null) {
methods = new HashSet<Method>();
signatureMap.put(sig.type(), methods);
}
try {
// 获取Signature注解中指定的方法
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args());
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
return signatureMap;
}
接下来是创建plugin对象,plugin对象中持有刚刚解析注解的Map对象。
创建代理对象完成后,在执行target的对象的相关方法是会调用invoke()方法,代码如下:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 获取指定类型中指定拦截方法。
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
// 如果存在,则执行Interceptor接口的intercept()方法。
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
// 如果不是指定拦截的方法,则直接调用。
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
整体的结构图如下:
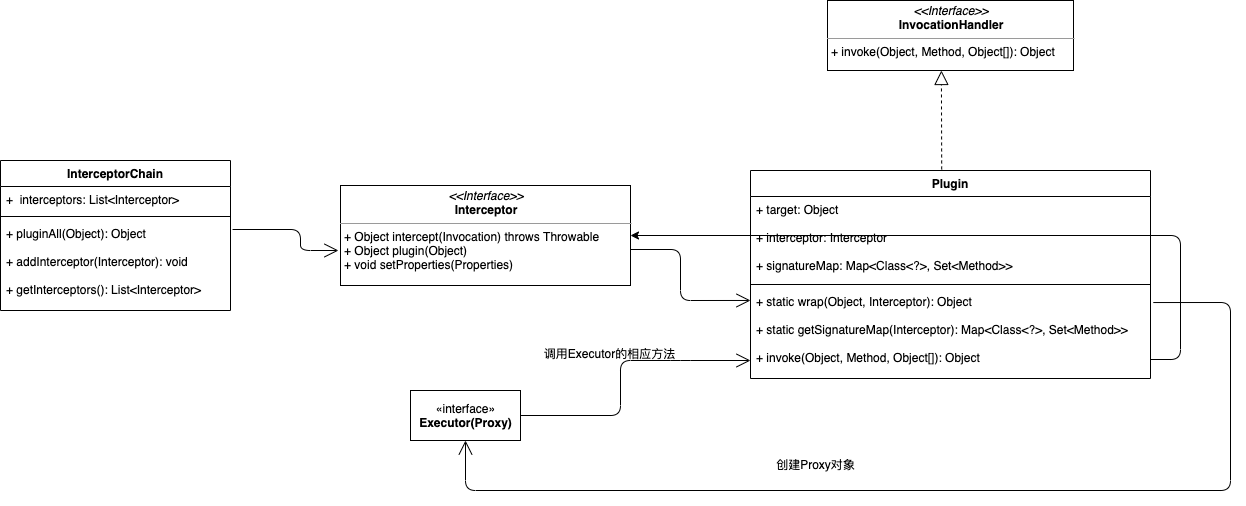
我们可以在执行invoke()方法时,获取method方法的参数对象,对相应对象进行操作,来实现相应的需求。