概述
在分析Transaction原理的时候,涉及到了Spring aop的原理,这里另写一篇文章详细说明下。cglib的具体使用需要提前看下,否则具体的代理部分不容易懂。另外本文分析的是基于Springboot中涉及到aop的部分代码。第一次看这部分源码,有很多漏洞,也不是很详细,会持续补充。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
(1)、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator注册
首先AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是通过AopAutoConfiguration来注册进容器的。代码如下:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
// 即使不存在spring.aop也会注册AopAutoConfiguration
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "auto", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
public class AopAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(Advice.class)
static class AspectJAutoProxyingConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "false",
matchIfMissing = false)
static class JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
// 默认情况下会注册CglibAutoProxyConfiguration
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true",
matchIfMissing = true)
static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("org.aspectj.weaver.Advice")
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true",
matchIfMissing = true)
static class ClassProxyingConfiguration {
ClassProxyingConfiguration(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
}
}
}
在CglibAutoProxyConfiguration上标记了EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解。代码如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
// 通过AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar注册BeanDefinition
@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy {
/**
* Indicate whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created as opposed
* to standard Java interface-based proxies. The default is {@code false}.
*/
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
/**
* Indicate that the proxy should be exposed by the AOP framework as a {@code ThreadLocal}
* for retrieval via the {@link org.springframework.aop.framework.AopContext} class.
* Off by default, i.e. no guarantees that {@code AopContext} access will work.
* @since 4.3.1
*/
boolean exposeProxy() default false;
}
AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar代码如下:
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(
AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 注册AspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreator到容器中。
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class);
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy != null) {
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry);
}
}
}
(2)、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator回调流程
在Spring创建完对象的实例之后会回调BeanPostProcessor
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
// 获取容器中的BeanPostProcessor对象,循环调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
在getBeanPostProcessors()返回的BeanPostProcessor中存在AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator。
该类的结构如下:
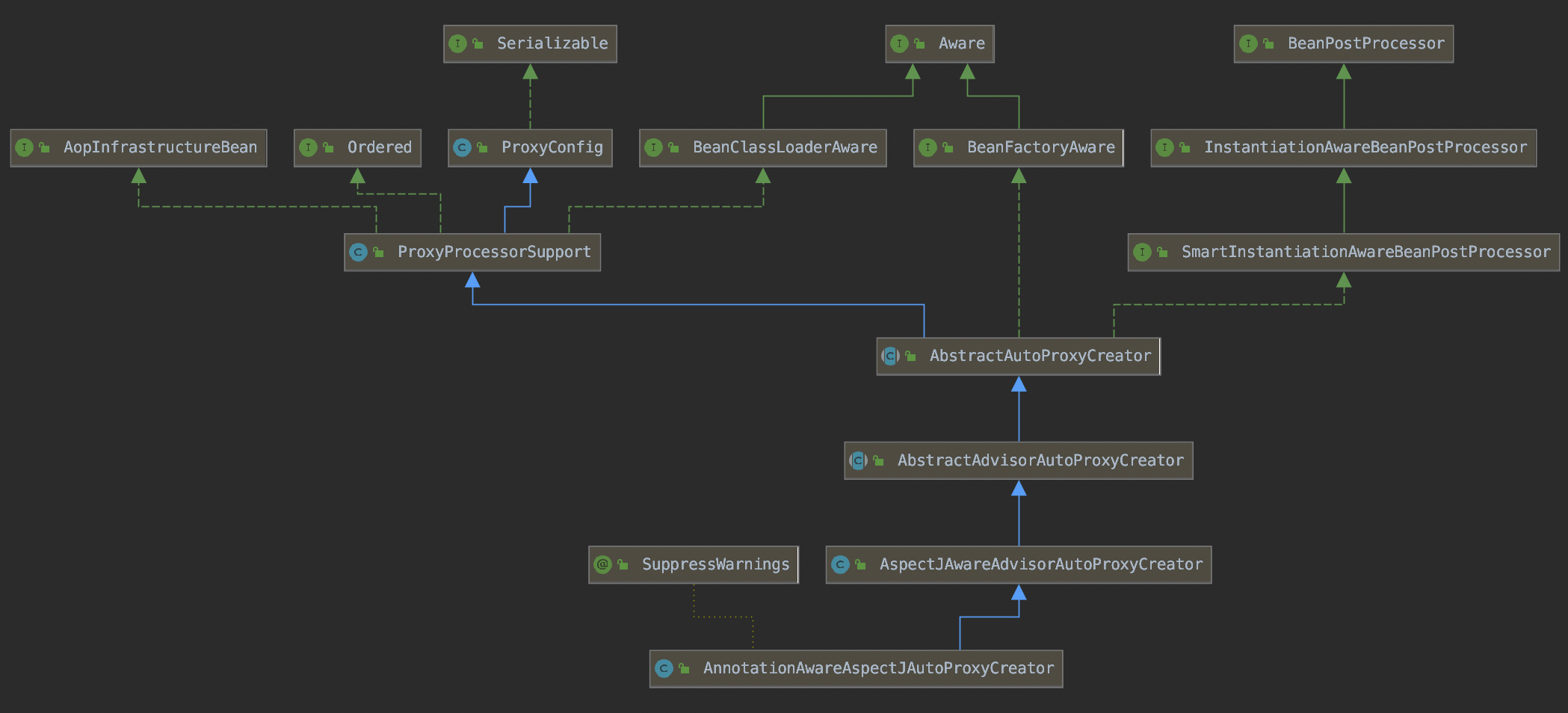
postProcessAfterInitialization()方法在AbstractAutoProxyCreator中进行了实现。
/**
* Create a proxy with the configured interceptors if the bean is
* identified as one to proxy by the subclass.
* @see #getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
wrapIfNecessary()方法如下:
/**
* Wrap the given bean if necessary, i.e. if it is eligible for being proxied.
* @param bean the raw bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param cacheKey the cache key for metadata access
* @return a proxy wrapping the bean, or the raw bean instance as-is
*/
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// 获取切面
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 创建代理对象
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
获取切面的代码如下所示:
// 整体代码的核心逻辑是从容器中获取Advisor对象。
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() {
// Determine list of advisor bean names, if not cached already.
String[] advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames;
if (advisorNames == null) {
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the auto-proxy creator apply to them!
advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);
this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames;
}
if (advisorNames.length == 0) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : advisorNames) {
if (isEligibleBean(name)) {
if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'");
}
}
else {
try {
advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
Throwable rootCause = ex.getMostSpecificCause();
if (rootCause instanceof BeanCurrentlyInCreationException) {
BeanCreationException bce = (BeanCreationException) rootCause;
String bceBeanName = bce.getBeanName();
if (bceBeanName != null && this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(bceBeanName)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Skipping advisor '" + name +
"' with dependency on currently created bean: " + ex.getMessage());
}
// Ignore: indicates a reference back to the bean we're trying to advise.
// We want to find advisors other than the currently created bean itself.
continue;
}
}
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
return advisors;
}
这里面能够使用的Advisor是BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor,该类在ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration中被定义。
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor(
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource,
TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor) {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor);
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
获取到切面之后需要创建代理对象。代码如下:
/**
* Create an AOP proxy for the given bean.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param specificInterceptors the set of interceptors that is
* specific to this bean (may be empty, but not null)
* @param targetSource the TargetSource for the proxy,
* already pre-configured to access the bean
* @return the AOP proxy for the bean
* @see #buildAdvisors
*/
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
// 构建Proxy工厂对象
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// 构建切面
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// 通过ProxyFactory创建代理对象。
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
具体获取切面的调用流程如下:
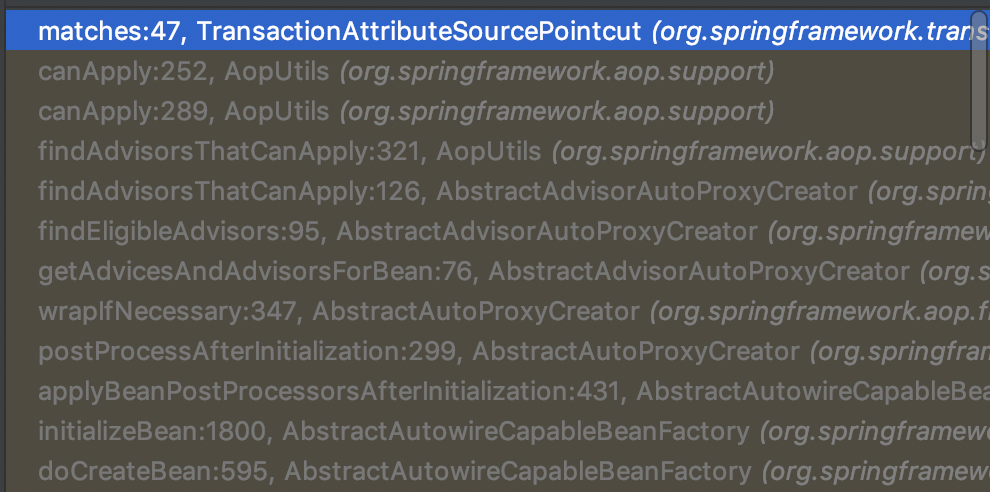
最后会调用AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource的getTransactionAttribute方法:
@Override
@Nullable
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return null;
}
// 首先从缓存中获取
// First, see if we have a cached value.
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass);
TransactionAttribute cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached != null) {
// Value will either be canonical value indicating there is no transaction attribute,
// or an actual transaction attribute.
if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) {
return null;
}
else {
return cached;
}
}
else {
// 如果没有获取到,则匹配下,如果成功则cache。
// We need to work it out.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// Put it in the cache.
if (txAttr == null) {
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass);
if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) {
((DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr).setDescriptor(methodIdentification);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Adding transactional method '" + methodIdentification + "' with attribute: " + txAttr);
}
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr);
}
return txAttr;
}
}
computeTransactionAttribute()方法代码如下:
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
// Don't allow no-public methods as required.
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
// The method may be on an interface, but we need attributes from the target class.
// If the target class is null, the method will be unchanged.
Method specificMethod = AopUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
// 首先从方法上获取@Transactional注解信息
// First try is the method in the target class.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// 如果没有获取到则从类上获取@Transactional注解信息
// Second try is the transaction attribute on the target class.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
if (specificMethod != method) {
// Fallback is to look at the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// Last fallback is the class of the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
}
return null;
}
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttribute determineTransactionAttribute(AnnotatedElement element) {
for (TransactionAnnotationParser parser : this.annotationParsers) {
// 获取@Transactional注解信息
TransactionAttribute attr = parser.parseTransactionAnnotation(element);
if (attr != null) {
return attr;
}
}
return null;
}
// SpringTransactionAnnotationParser
@Override
@Nullable
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement element) {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotationAttributes(
element, Transactional.class, false, false);
if (attributes != null) {
return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(Transactional ann) {
return parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationUtils.getAnnotationAttributes(ann, false, false));
}
protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation");
rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value());
Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation");
rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value());
rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue());
rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly"));
rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value"));
List<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollbackRules = new ArrayList<>();
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
rbta.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return rbta;
}
最后如果都不匹配则代表不需要Proxy:
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator:
@Override
@Nullable
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
// 如果没有匹配到则不需要代理
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
至此已经分析了哪些类型需要被代理。这里由于代码量太多就没有详细分析类的分层等内容,这部分需要补充上。接下来分析具体的代理工作原理。
代理工作的原理要从createProxy开始:
AbstractAutoProxyCreator:
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// 构建切面
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// 创建代理
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
这里面创建代理是通过ProxyFactory工厂类来实现的。
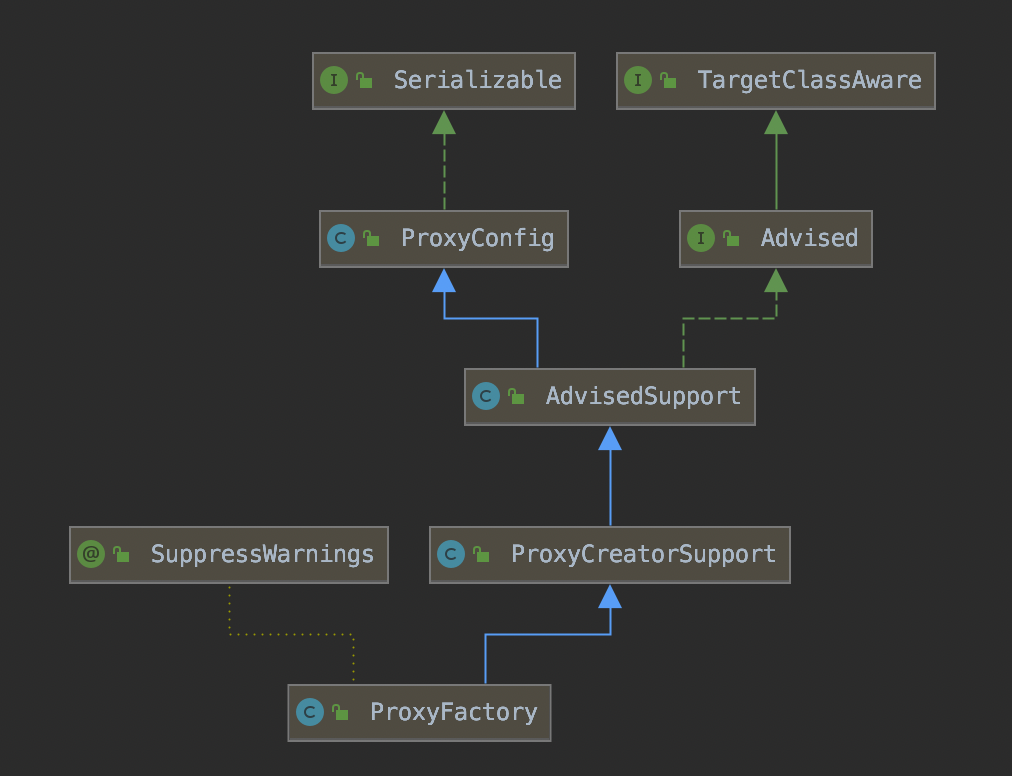
ProxyFactory的getProxy()方法如下所示:
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
// 使用CGLIB动态代理
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
该类的结构如下:
CglibAopProxy类的getProxy方法如下:
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
// 获取对应的回调
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
// 设置回调的拦截器与Callback配合使用
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// 创建代理对象
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}
关于Callback的使用这里举个例子:
在CGLib回调时可以设置对不同方法执行不同的回调逻辑,或者根本不执行回调。
在JDK动态代理中并没有类似的功能,对InvocationHandler接口方法的调用对代理类内的所以方法都有效。
生成代理类前,设置了CallbackFilter,上文中ConcreteClassCallbackFilter实现类的返回值对应Callback[]数组中的位置索引。此处包含了CGLib中的3种回调方式:
(1)MethodInterceptor:方法拦截器
(2)NoOp.INSTANCE:这个NoOp表示no operator,即什么操作也不做,代理类直接调用被代理的方法不进行拦截。
(3)FixedValue:表示锁定方法返回值,无论被代理类的方法返回什么值,回调方法都返回固定值。
public class Bootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(CallbackClass.class);
CallbackFilter callbackFilter = new CallbackFilterClass();
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(callbackFilter);
Callback interceptor=new SpecialMethodInterceptor();//(1)
Callback noOp= NoOp.INSTANCE;//(2)
Callback[] callbacks=new Callback[]{interceptor,noOp};
enhancer.setCallbacks(callbacks);
CallbackClass callbackClass = (CallbackClass) enhancer.create();
callbackClass.show0("gaoming");
callbackClass.show1(1);
}
private static class SpecialMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Before:"+method);
Object object=methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
System.out.println("After:"+method);
return object;
}
}
}
public class CallbackFilterClass implements CallbackFilter {
// 指定方法对应的增强器,其中return值为被代理类的各个方法在回调数组Callback[]中的位置索引
@Override
public int accept(Method method) {
String methodName = method.getName();
// 如果是show0则使用Callback数组中的第一个
if (methodName.equals("show0")) {
return 0;
// 如果是show0则使用Callback数组中的第二个
} else if (methodName.equals("show1")) {
return 1;
}
return 1;
}
}
// 被增强的类
public class CallbackClass {
public void show0(String string) {
System.out.println("show0" + ":" + string);
}
public void show1(int a) {
System.out.println("show1" + ":" + a);
}
}
所以先从上面获取Callback的数组开始:
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception {
// Parameters used for optimization choices...
boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();
boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();
boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();
// Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls).
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
// Choose a "straight to target" interceptor. (used for calls that are
// unadvised but can return this). May be required to expose the proxy.
Callback targetInterceptor;
if (exposeProxy) {
targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?
new StaticUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :
new DynamicUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));
}
else {
targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?
new StaticUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :
new DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));
}
// Choose a "direct to target" dispatcher (used for
// unadvised calls to static targets that cannot return this).
Callback targetDispatcher = (isStatic ?
new StaticDispatcher(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new SerializableNoOp());
Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] {
aopInterceptor, // for normal advice
targetInterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimized
new SerializableNoOp(), // no override for methods mapped to this
targetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher,
new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised),
new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)
};
Callback[] callbacks;
// If the target is a static one and the advice chain is frozen,
// then we can make some optimizations by sending the AOP calls
// direct to the target using the fixed chain for that method.
if (isStatic && isFrozen) {
Method[] methods = rootClass.getMethods();
Callback[] fixedCallbacks = new Callback[methods.length];
this.fixedInterceptorMap = new HashMap<>(methods.length);
// TODO: small memory optimization here (can skip creation for methods with no advice)
for (int x = 0; x < methods.length; x++) {
Method method = methods[x];
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, rootClass);
fixedCallbacks[x] = new FixedChainStaticTargetInterceptor(
chain, this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget(), this.advised.getTargetClass());
this.fixedInterceptorMap.put(method, x);
}
// Now copy both the callbacks from mainCallbacks
// and fixedCallbacks into the callbacks array.
callbacks = new Callback[mainCallbacks.length + fixedCallbacks.length];
System.arraycopy(mainCallbacks, 0, callbacks, 0, mainCallbacks.length);
System.arraycopy(fixedCallbacks, 0, callbacks, mainCallbacks.length, fixedCallbacks.length);
this.fixedInterceptorOffset = mainCallbacks.length;
}
else {
callbacks = mainCallbacks;
}
return callbacks;
}
而对于CallbackFilter的accept方法如下:
/**
* Implementation of CallbackFilter.accept() to return the index of the
* callback we need.
* <p>The callbacks for each proxy are built up of a set of fixed callbacks
* for general use and then a set of callbacks that are specific to a method
* for use on static targets with a fixed advice chain.
* <p>The callback used is determined thus:
* <dl>
* <dt>For exposed proxies</dt>
* <dd>Exposing the proxy requires code to execute before and after the
* method/chain invocation. This means we must use
* DynamicAdvisedInterceptor, since all other interceptors can avoid the
* need for a try/catch block</dd>
* <dt>For Object.finalize():</dt>
* <dd>No override for this method is used.</dd>
* <dt>For equals():</dt>
* <dd>The EqualsInterceptor is used to redirect equals() calls to a
* special handler to this proxy.</dd>
* <dt>For methods on the Advised class:</dt>
* <dd>the AdvisedDispatcher is used to dispatch the call directly to
* the target</dd>
* <dt>For advised methods:</dt>
* <dd>If the target is static and the advice chain is frozen then a
* FixedChainStaticTargetInterceptor specific to the method is used to
* invoke the advice chain. Otherwise a DynamicAdvisedInterceptor is
* used.</dd>
* <dt>For non-advised methods:</dt>
* <dd>Where it can be determined that the method will not return {@code this}
* or when {@code ProxyFactory.getExposeProxy()} returns {@code false},
* then a Dispatcher is used. For static targets, the StaticDispatcher is used;
* and for dynamic targets, a DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor is used.
* If it possible for the method to return {@code this} then a
* StaticUnadvisedInterceptor is used for static targets - the
* DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor already considers this.</dd>
* </dl>
*/
@Override
public int accept(Method method) {
if (AopUtils.isFinalizeMethod(method)) {
logger.trace("Found finalize() method - using NO_OVERRIDE");
return NO_OVERRIDE;
}
if (!this.advised.isOpaque() && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method is declared on Advised interface: " + method);
}
return DISPATCH_ADVISED;
}
// We must always proxy equals, to direct calls to this.
if (AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found 'equals' method: " + method);
}
return INVOKE_EQUALS;
}
// We must always calculate hashCode based on the proxy.
if (AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found 'hashCode' method: " + method);
}
return INVOKE_HASHCODE;
}
Class<?> targetClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
// Proxy is not yet available, but that shouldn't matter.
List<?> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
boolean haveAdvice = !chain.isEmpty();
boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();
boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();
boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();
if (haveAdvice || !isFrozen) {
// If exposing the proxy, then AOP_PROXY must be used.
if (exposeProxy) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Must expose proxy on advised method: " + method);
}
return AOP_PROXY;
}
Method key = method;
// Check to see if we have fixed interceptor to serve this method.
// Else use the AOP_PROXY.
if (isStatic && isFrozen && this.fixedInterceptorMap.containsKey(key)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method has advice and optimizations are enabled: " + method);
}
// We know that we are optimizing so we can use the FixedStaticChainInterceptors.
int index = this.fixedInterceptorMap.get(key);
return (index + this.fixedInterceptorOffset);
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Unable to apply any optimizations to advised method: " + method);
}
return AOP_PROXY;
}
}
else {
// See if the return type of the method is outside the class hierarchy of the target type.
// If so we know it never needs to have return type massage and can use a dispatcher.
// If the proxy is being exposed, then must use the interceptor the correct one is already
// configured. If the target is not static, then we cannot use a dispatcher because the
// target needs to be explicitly released after the invocation.
if (exposeProxy || !isStatic) {
return INVOKE_TARGET;
}
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (targetClass != null && returnType.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method return type is assignable from target type and " +
"may therefore return 'this' - using INVOKE_TARGET: " + method);
}
return INVOKE_TARGET;
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method return type ensures 'this' cannot be returned - " +
"using DISPATCH_TARGET: " + method);
}
return DISPATCH_TARGET;
}
}
}
根据callback数组的索引,普通的方法使用的是DynamicAdvisedInterceptor,intercept方法如下所示:
@Override
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// 获取拦截器链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
// 如果为空则不进行处理直接调用。
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// 使用CglibMethodInvocation调用proceed方法
// We need to create a method invocation...
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
ReflectiveMethodInvocation:
proceed()方法如下:
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
try {
// 调用父类的proceed方法
return super.proceed();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (ReflectionUtils.declaresException(getMethod(), ex.getClass())) {
throw ex;
}
else {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(ex);
}
}
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
TransactionInterceptor:
invoke():
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}
/**
* General delegate for around-advice-based subclasses, delegating to several other template
* methods on this class. Able to handle {@link CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager}
* as well as regular {@link PlatformTransactionManager} implementations.
* @param method the Method being invoked
* @param targetClass the target class that we're invoking the method on
* @param invocation the callback to use for proceeding with the target invocation
* @return the return value of the method, if any
* @throws Throwable propagated from the target invocation
*/
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager) {
ReactiveTransactionSupport txSupport = this.transactionSupportCache.computeIfAbsent(method, key -> {
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass()) && KotlinDelegate.isSuspend(method)) {
throw new TransactionUsageException(
"Unsupported annotated transaction on suspending function detected: " + method +
". Use TransactionalOperator.transactional extensions instead.");
}
ReactiveAdapter adapter = this.reactiveAdapterRegistry.getAdapter(method.getReturnType());
if (adapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply reactive transaction to non-reactive return type: " +
method.getReturnType());
}
return new ReactiveTransactionSupport(adapter);
});
return txSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(
method, targetClass, invocation, txAttr, (ReactiveTransactionManager) tm);
}
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) ptm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
Object retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
if (vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
return retVal;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
}
}
如果在方法执行过程中出现异常则会执行如下的调用链:
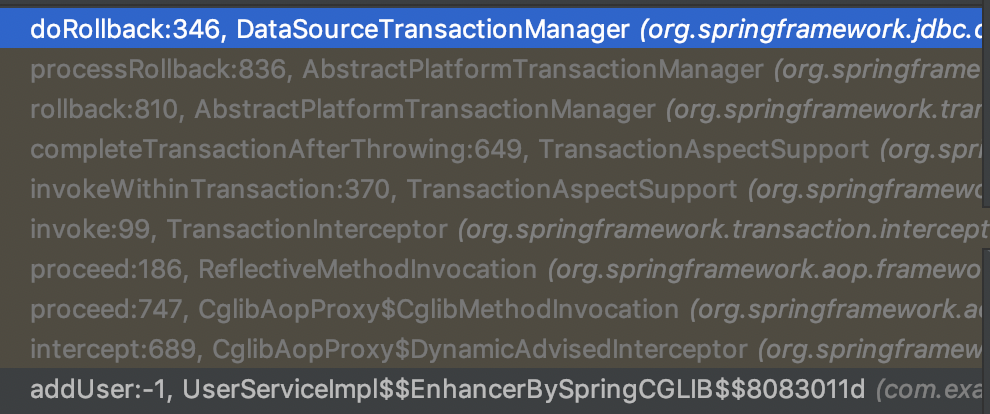
DataSourceTransactionManager的doRollback方法如下所示:
@Override
protected void doRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]");
}
try {
// 执行回滚
con.rollback();
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not roll back JDBC transaction", ex);
}
}
如果正常执行完成则会执行如下的方法:
commitTransactionAfterReturning()
/**
* Execute after successful completion of call, but not after an exception was handled.
* Do nothing if we didn't create a transaction.
* @param txInfo information about the current transaction
*/
protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
}
全部的流程至此结束。细节需要补充。很多流程及类之间的关系并没有分析。