概述
首先说下,本文只是从流程上以及整体的各个组件之间的关系进行分析Spring事务的实现原理,这部分的代码涉及到的内容非常庞大,代码量也很多,涉及到的细节也非常多。这部分代码可以作为Spring扩展模块的范例,其中涉及到的设计模式以及思想也非常值得学习。前面的相关内容引用了许多网上关于Spring事务的资料。
spring事务特性
Spring事务控制
JavaEE 体系进行分层开发,事务处理位于业务层,Spring提供了分层设计业务层的事务处理解决方案。
Spring 框架为我们提供了一组事务控制的接口,这组接口在spring-tx-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar中。
Spring 的事务控制都是基于AOP的,它既可以使用配置的方式实现,也可以使用编程的方式实现.推荐使用配置方式实现。
数据库事务的基础知识
(1)、事务的四大特性:ACID
- 原子性(Atomicity): 事务包含的所有操作要么全部成功,要么全部失败回滚;成功必须要完全应用到数据库,失败则不能对数据库产生影响.
- 一致性(Consistency):事务执行前和执行后必须处于一致性状态.例如:转账事务执行前后,两账户余额的总和不变.
- 隔离性(Isolation): 多个并发的事务之间要相互隔离.
- 持久性(Durability): 事务一旦提交,对数据库的改变是永久性的.
(2)、事务的隔离级别:
-
ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED: 读未提交.事务中的修改,即使没有提交,其他事务也可以看得到.会导致脏读,不可重复读,幻读。
-
ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED: 读已提交(Oracle数据库默认隔离级别).一个事务不会读到其它并行事务已修改但未提交的数据.避免了脏读,但会导致不可重复读,幻读。
-
ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ: 可重复读(Mysql数据库默认的隔离级别).一个事务不会读到其它并行事务已修改且已提交的数据,(只有当该事务提交之后才会看到其他事务提交的修改).避免了脏读,不可重复读,但会导致幻读。
-
ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE: 串行化.事务串行执行,一个时刻只能有一个事务被执行.避免了脏读,不可重复读,幻读。
事务的安全隐患有如下三种,他们可以通过设置合理的隔离级别来避免: -
脏读: 一个事务读到另外一个事务还未提交(可能被回滚)的脏数据.
-
不可重复读: 一个事务执行期间另一事务提交修改,导致第一个事务前后两次查询结果不一致.
-
幻读: 一个事务执行期间另一事务提交添加数据,导致第一个事务前后两次查询结果到的数据条数不同.
| 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED | ✕ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ |
| ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ |
Spring中事务控制的API
PlatformTransactionManager接口是Spring提供的事务管理器,它提供了操作事务的方法如下:
TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition): 获得事务状态信息
void commit(TransactionStatus status): 提交事务
void rollback(TransactionStatus status): 回滚事务
在实际开发中我们使用其实现类:
org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager使用SpringJDBC或iBatis进行持久化数据时使用
org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager使用Hibernate版本进行持久化数据时使用
TransactionDefinition: 事务定义信息对象,提供查询事务定义的方法如下:
String getName(): 获取事务对象名称
int getIsolationLevel(): 获取事务隔离级别,设置两个事务之间的数据可见性
事务的隔离级别由弱到强,依次有如下五种:(可以参考文章事务的四种隔离级别,数据库事务4种隔离级别及7种传播行为)
- ISOLATION_DEFAULT: Spring事务管理的的默认级别,使用数据库默认的事务隔离级别.
- ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED: 读未提交.
- ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED: 读已提交.
- ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ: 可重复读.
- ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE: 串行化.
getPropagationBehavior(): 获取事务传播行为,设置新事务是否事务以及是否使用当前事务.
我们通常使用的是前两种: REQUIRED和SUPPORTS.事务传播行为如下:
- REQUIRED: Spring默认事务传播行为. 若当前没有事务,就新建一个事务;若当前已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中.增删改查操作均可用
- SUPPORTS: 若当前没有事务,就不使用事务;若当前已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中.查询操作可用
- MANDATORY: 使用当前的事务,若当前没有事务,就抛出异常
- REQUERS_NEW: 新建事务,若当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起
- NOT_SUPPORTED: 以非事务方式执行操作,若当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起
- NEVER:以非事务方式运行,若当前存在事务,抛出异常
- NESTED:若当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行;若当前没有事务,则执行REQUIRED类似的操作
int getTimeout(): 获取事务超时时间. Spring默认设置事务的超时时间为-1,表示永不超时.
boolean isReadOnly(): 获取事务是否只读. Spring默认设置为false,建议查询操作中设置为true
TransactionStatus: 事务状态信息对象,提供操作事务状态的方法如下:
void flush(): 刷新事务
boolean hasSavepoint(): 查询是否存在存储点
boolean isCompleted(): 查询事务是否完成
boolean isNewTransaction(): 查询是否是新事务
boolean isRollbackOnly(): 查询事务是否回滚
void setRollbackOnly(): 设置事务回滚
事务管理方式
spring支持编程式事务管理和声明式事务管理两种方式。
编程式事务管理使用TransactionTemplate或者直接使用底层的PlatformTransactionManager。对于编程式事务管理,spring推荐使用TransactionTemplate。
声明式事务管理建立在AOP之上的。其本质是对方法前后进行拦截,然后在目标方法开始之前创建或者加入一个事务,在执行完目标方法之后根据执行情况提交或者回滚事务。声明式事务最大的优点就是不需要通过编程的方式管理事务,这样就不需要在业务逻辑代码中掺杂事务管理的代码,只需在配置文件中做相关的事务规则声明(或通过基于@Transactional注解的方式),便可以将事务规则应用到业务逻辑中。
显然声明式事务管理要优于编程式事务管理,这正是spring倡导的非侵入式的开发方式。声明式事务管理使业务代码不受污染,一个普通的POJO对象,只要加上注解就可以获得完全的事务支持。和编程式事务相比,声明式事务唯一不足地方是,后者的最细粒度只能作用到方法级别,无法做到像编程式事务那样可以作用到代码块级别。但是即便有这样的需求,也存在很多变通的方法,比如,可以将需要进行事务管理的代码块独立为方法等等。
声明式事务管理也有两种常用的方式,一种是基于tx和aop名字空间的xml配置文件,另一种就是基于@Transactional注解。显然基于注解的方式更简单易用,更清爽。
自动提交(AutoCommit)与连接关闭时的是否自动提交
自动提交
默认情况下,数据库处于自动提交模式。每一条语句处于一个单独的事务中,在这条语句执行完毕时,如果执行成功则隐式的提交事务,如果
执行失败则隐式的回滚事务。
有些数据连接池提供了关闭事务自动提交的设置,最好在设置连接池时就将其关闭。但C3P0没有提供这一特性,只能依靠spring来设置。
因为JDBC规范规定,当连接对象建立时应该处于自动提交模式,这是跨DBMS的缺省值,如果需要,必须显式的关闭自动提交。C3P0遵守这一规范,让客户代码来显式的设置需要的提交模式。
连接关闭时的是否自动提交
当一个连接关闭时,如果有未提交的事务应该如何处理?JDBC规范没有提及,C3P0默认的策略是回滚任何未提交的事务。这是一个正确的策略,但JDBC驱动提供商之间对此问题并没有达成一致。
C3P0的autoCommitOnClose属性默认是false,没有十分必要不要动它。或者可以显式的设置此属性为false,这样会更明确。
TransactionDefinition接口定义以下特性:
事务隔离级别
隔离级别是指若干个并发的事务之间的隔离程度。TransactionDefinition 接口中定义了五个表示隔离级别的常量:
- TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT:这是默认值,表示使用底层数据库的默认隔离级别。对大部分数据库而言,通常这值就是TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED。
- TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED:该隔离级别表示一个事务可以读取另一个事务修改但还没有提交的数据。该级别不能防止脏读,不可重复读和幻读,因此很少使用该隔离级别。比如PostgreSQL实际上并没有此级别。
- TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED:该隔离级别表示一个事务只能读取另一个事务已经提交的数据。该级别可以防止脏读,这也是大多数情况下的推荐值。
- TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ:该隔离级别表示一个事务在整个过程中可以多次重复执行某个查询,并且每次返回的记录都相同。该级别可以防止脏读和不可重复读。
- TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE:所有的事务依次逐个执行,这样事务之间就完全不可能产生干扰,也就是说,该级别可以防止脏读、不可重复读以及幻读。但是这将严重影响程序的性能。通常情况下也不会用到该级别。
事务传播行为
所谓事务的传播行为是指,如果在开始当前事务之前,一个事务上下文已经存在,此时有若干选项可以指定一个事务性方法的执行行为。在TransactionDefinition定义中包括了如下几个表示传播行为的常量:
- TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED:如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则创建一个新的事务。这是默认值。
- TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW:创建一个新的事务,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起。
- TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则以非事务的方式继续运行。
- TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起。
- TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
- TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY:如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则抛出异常。
- TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则创建一个事务作为当前事务的嵌套事务来运行;如果当前没有事务,则该取值等价于TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED。
事务超时
所谓事务超时,就是指一个事务所允许执行的最长时间,如果超过该时间限制但事务还没有完成,则自动回滚事务。在 TransactionDefinition 中以 int 的值来表示超时时间,其单位是秒。
默认设置为底层事务系统的超时值,如果底层数据库事务系统没有设置超时值,那么就是none,没有超时限制。
事务只读属性
只读事务用于客户代码只读但不修改数据的情形,只读事务用于特定情景下的优化,比如使用Hibernate的时候。
默认为读写事务。
spring事务回滚规则
指示spring事务管理器回滚一个事务的推荐方法是在当前事务的上下文内抛出异常。spring事务管理器会捕捉任何未处理的异常,然后依据规则决定是否回滚抛出异常的事务。
默认配置下,spring只有在抛出的异常为运行时unchecked异常时才回滚该事务,也就是抛出的异常为RuntimeException的子类(Errors也会导致事务回滚),而抛出checked异常则不会导致事务回滚。
可以明确的配置在抛出那些异常时回滚事务,包括checked异常。也可以明确定义那些异常抛出时不回滚事务。
还可以编程性的通过setRollbackOnly()方法来指示一个事务必须回滚,在调用完setRollbackOnly()后你所能执行的唯一操作就是回滚。
@Transactional属性
| 属性 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| value | String | 可选的限定描述符,指定使用的事务管理器 |
| propagation | enum: Propagation | 可选的事务传播行为设置 |
| isolation | enum: Isolation | 可选的事务隔离级别设置 |
| readOnly | boolean | 读写或只读事务,默认读写 |
| timeout | int (in seconds granularity) | 事务超时时间设置 |
| rollbackFor | Class对象数组,必须继承自Throwable | 导致事务回滚的异常类数组 |
| rollbackForClassName | 类名数组,必须继承自Throwable | 导致事务回滚的异常类名字数组 |
| noRollbackFor | Class对象数组,必须继承自Throwable | 不会导致事务回滚的异常类数组 |
| noRollbackForClassName | 类名数组,必须继承自Throwable | 不会导致事务回滚的异常类名字数组 |
用法
-
- 在需要事务管理的地方加@Transactional 注解。@Transactional 注解可以被应用于接口定义和接口方法、类定义和类的 public 方法上。
-
- @Transactional 注解只能应用到 public 可见度的方法上。 如果你在 protected、private 或者 package-visible 的方法上使用 @Transactional 注解,它也不会报错, 但是这个被注解的方法将不会展示已配置的事务设置。
-
- 注意仅仅 @Transactional 注解的出现不足于开启事务行为,它仅仅 是一种元数据。必须在配置文件中使用配置元素,才真正开启了事务行为。
-
- 通过aop:config元素的 "proxy-target-class" 属性值来控制是基于接口的还是基于类的代理被创建。如果aop:config的 "proxy-target-class" 属值被设置为 "true",那么基于类的代理将起作用(这时需要CGLIB库cglib.jar在CLASSPATH中)。如果 "proxy-target-class" 属值被设置为 "false" 或者这个属性被省略,那么标准的JDK基于接口的代理将起作用。
<!-- 标准的JDK基于接口的代理将起作用-->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="false"/>
<!-- 基于类的代理将起作用 ,同时 cglib.jar必须在CLASSPATH中 -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true"/>
非JTA事务(即非分布式事务), 事务配置的时候 ,需要指定dataSource属性(非分布式事务,事务是在数据库创建的链接上开启。)
JTA事务(非分布式事务), 事务配置的时候 ,不能指定dataSource属性(分布式事务,是有全局事务来管理数据库链接的。
注解@Transactional cglib与java动态代理最大区别是代理目标对象不用实现接口,那么注解要是写到接口方法上,要是使用cglib代理,这是注解事物就失效了,为了保持兼容注解最好都写到实现类方法上。
-
- Spring团队建议在具体的类(或类的方法)上使用 @Transactional 注解,而不要使用在类所要实现的任何接口上。在接口上使用 @Transactional 注解,只能当你设置了基于接口的代理时它才生效。因为注解是不能继承的,这就意味着如果正在使用基于类的代理时,那么事务的设置将不能被基于类的代理所识别,而且对象也将不会被事务代理所包装。
-
- @Transactional 的事务开启 ,或者是基于接口的 或者是基于类的代理被创建。所以在同一个类中一个方法调用另一个方法有事务的方法,事务是不会起作用的。
@Transactional注解的解析及工作原理
@Transactional注解的解析
Spring中@Transactional注解对应的类是TransactionDefinition该类的子类如下:
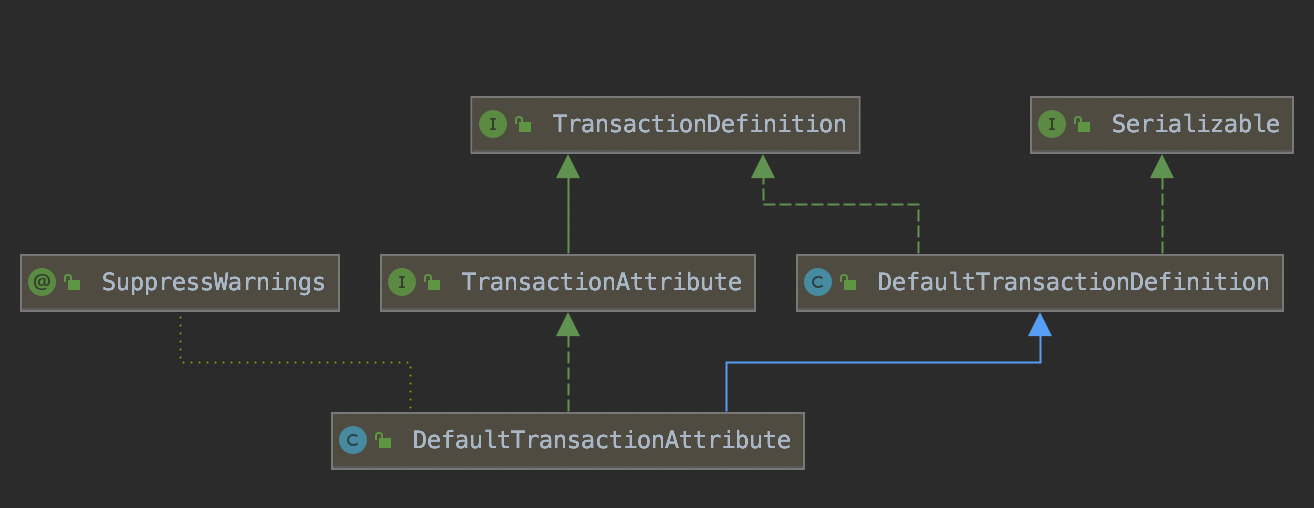
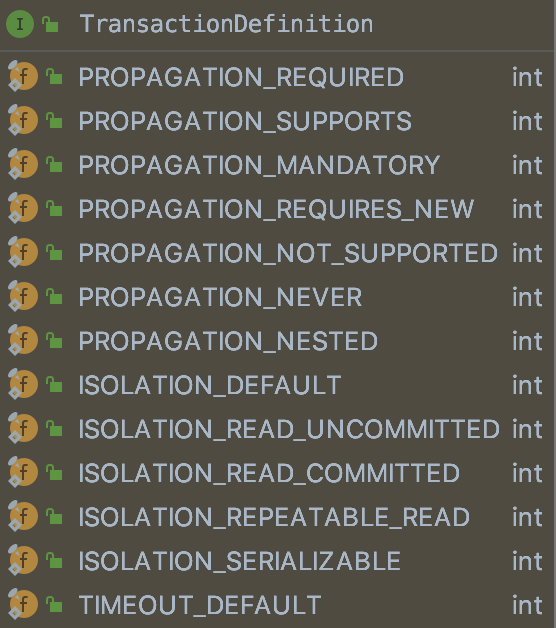
在TransactionDefinition类中定义了事务传播及隔离的级别:
@Transactional解析调用链如下所示。
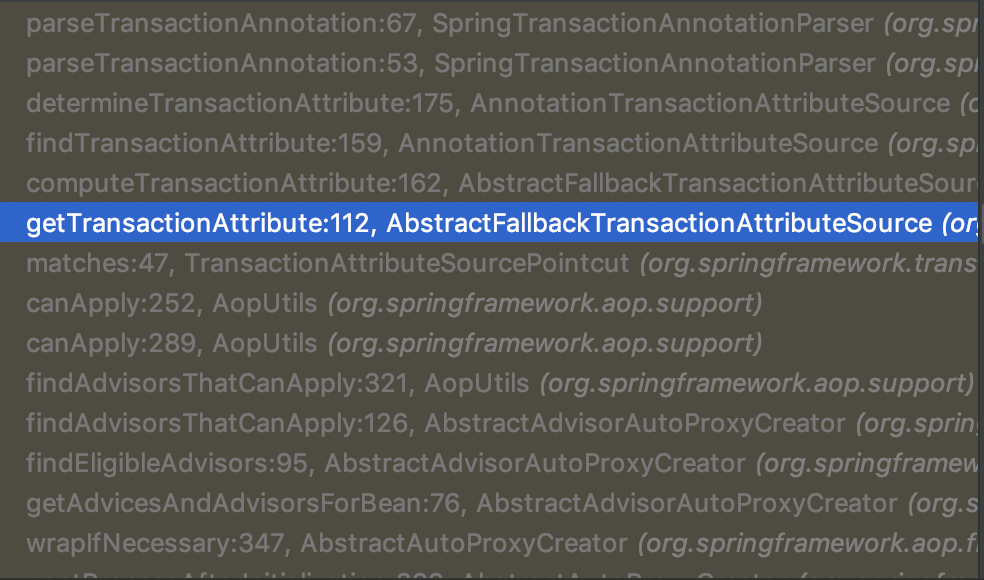
具体对于@Transactional注解的解析是在SpringTransactionAnnotationParser中进行的。
代码如下:
protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
// 获取传播信息
Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation");
// 设置传播信息
rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value());
// 获取隔离信息
Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation");
// 设置隔离信息
rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value());
// 设置事务超时时间
rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue());
// 设置只读性
rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly"));
rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value"));
// 设置回滚滚则
List<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollbackRules = new ArrayList<>();
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
rbta.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return rbta;
}
这部分信息解析完成之后会存放在AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource中
private final Map<Object, TransactionAttribute> attributeCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(1024);
具体的代码如下:
@Override
@Nullable
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return null;
}
// 首先创建一个MethodClassKey,这个对象封装了method和class
// First, see if we have a cached value.
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass);
// 尝试从缓存中获取
TransactionAttribute cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached != null) {
// Value will either be canonical value indicating there is no transaction attribute,
// or an actual transaction attribute.
// 如果不为空,则需要判断是否是NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE
if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) {
return null;
}
else {
return cached;
}
}
else {
// 获取事务注解的信息
// We need to work it out.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// Put it in the cache.
if (txAttr == null) {
// 如果不存在@Transactional注解信息,则放入NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
// 获取方法名
String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass);
if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) {
((DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr).setDescriptor(methodIdentification);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Adding transactional method '" + methodIdentification + "' with attribute: " + txAttr);
}
// 将@Transactional信息放入集合中
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr);
}
return txAttr;
}
}
执行调用接口方法时则会调用如下的调用链
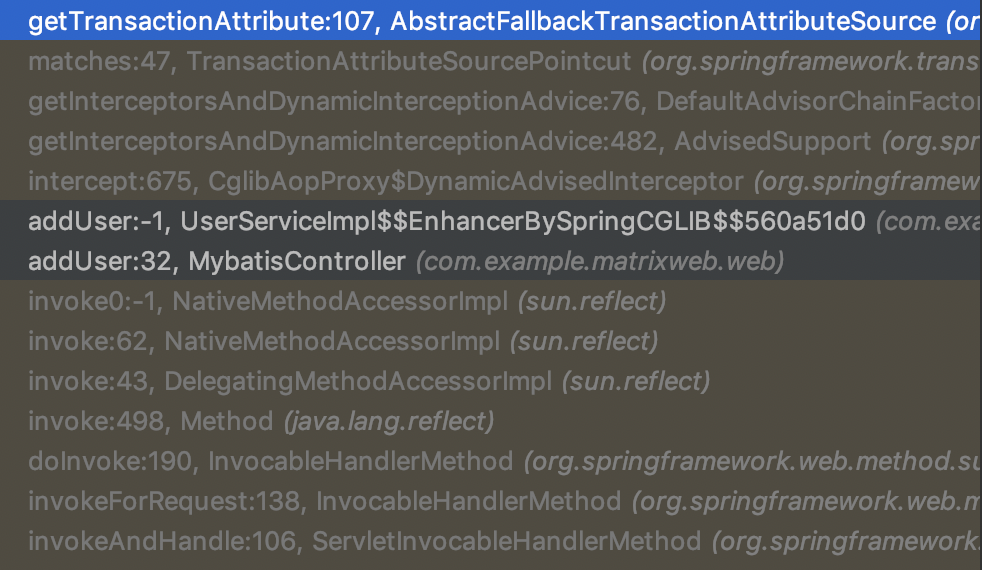
从缓存中获取方法注解信息。
@Transactional注解的工作
@Transactional注解的处理是在TransactionInterceptor中进行的。
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
// 获取实体类
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
// 调用invokeWithinTransaction方法
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}
invokeWithinTransaction()方法如下所示:
/**
* General delegate for around-advice-based subclasses, delegating to several other template
* methods on this class. Able to handle {@link CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager}
* as well as regular {@link PlatformTransactionManager} implementations.
* @param method the Method being invoked
* @param targetClass the target class that we're invoking the method on
* @param invocation the callback to use for proceeding with the target invocation
* @return the return value of the method, if any
* @throws Throwable propagated from the target invocation
*/
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
// 获取TransactionAttributeSource对象,TransactionAttributeSource对象的作用是存储方法名和对象的@Transactional注解信息。
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 获取TransactionAttribute,上面已经分析过
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
// 获取TransactionManager,默认会使用DataSourceTransactionManager
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager) {
ReactiveTransactionSupport txSupport = this.transactionSupportCache.computeIfAbsent(method, key -> {
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass()) && KotlinDelegate.isSuspend(method)) {
throw new TransactionUsageException(
"Unsupported annotated transaction on suspending function detected: " + method +
". Use TransactionalOperator.transactional extensions instead.");
}
ReactiveAdapter adapter = this.reactiveAdapterRegistry.getAdapter(method.getReturnType());
if (adapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply reactive transaction to non-reactive return type: " +
method.getReturnType());
}
return new ReactiveTransactionSupport(adapter);
});
return txSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(
method, targetClass, invocation, txAttr, (ReactiveTransactionManager) tm);
}
// 转化成PlatformTransactionManager对象
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 创建Transactional及Manager相关信息,数据库的Connection就是在这里获取的
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
// 执行方法调用
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// 处理抛出异常的情况
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
// 处理正常返回的情况
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) ptm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
Object retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
if (vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
return retVal;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
}
}
createTransactionIfNecessary()方法如下:
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
// 通过TransactionManager的getTransaction获取事务,该事务的对象为TransactionStatus,
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
getTransaction()方法实现如下:
@Override
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
TransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());
// 具体获取事务是由子类实现
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 下面对@Transaction的事务传播机制进行了实现。
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
if (def.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", def.getTimeout());
}
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + def.getName() + "]: " + def);
}
try {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
def, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
doBegin(transaction, def);
prepareSynchronization(status, def);
return status;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
}
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
if (def.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + def);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
doGetTransaction()方法如下:
@Override
protected Object doGetTransaction() {
// 封装真正的数据库事务对象,对象持有数据库连接Connection
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject();
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed());
// 从ThreadLocal中获取当前线程的的Connection。
ConnectionHolder conHolder =
(ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false);
return txObject;
}
异常回滚实现
异常回滚实现是在completeTransactionAfterThrowing()方法中完成的。
/**
* Handle a throwable, completing the transaction.
* We may commit or roll back, depending on the configuration.
* @param txInfo information about the current transaction
* @param ex throwable encountered
*/
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
// 首先判断TransactionStatus是否为空,如果为空则不会进行回滚操作
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
// 从transactionAttribute的回滚规则中判断是否需要回滚,
// 默认情况下会通过DefaultTransactionAttribute的rollbackOn进行判断,也就是所有RuntimeException的类型或者Error类型
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
// 执行回滚操作
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
else {
// 否则提交本次操作后抛出异常
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
接下来看下txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn()也就是判断是否需要回滚的逻辑。
这里面使用的是解析@Transactional注解时使用的RuleBasedTransactionAttribute。
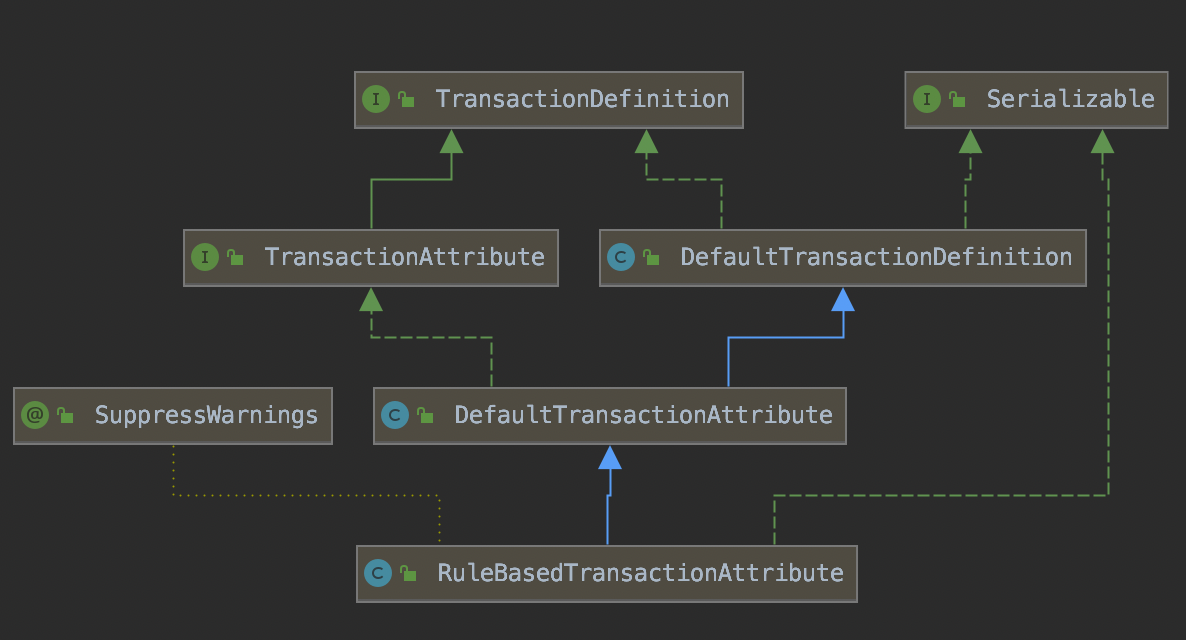
代码如下:
@Override
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Applying rules to determine whether transaction should rollback on " + ex);
}
RollbackRuleAttribute winner = null;
int deepest = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 循环判断回滚规则
if (this.rollbackRules != null) {
for (RollbackRuleAttribute rule : this.rollbackRules) {
int depth = rule.getDepth(ex);
if (depth >= 0 && depth < deepest) {
deepest = depth;
winner = rule;
}
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Winning rollback rule is: " + winner);
}
// User superclass behavior (rollback on unchecked) if no rule matches.
// 如果没有匹配成功,则使用DefaultTransactionAttribute的回滚规则。
if (winner == null) {
logger.trace("No relevant rollback rule found: applying default rules");
return super.rollbackOn(ex);
}
return !(winner instanceof NoRollbackRuleAttribute);
}
DefaultTransactionAttribute的rollbackOn方法如下:
@Override
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error);
}
上面的逻辑是确定什么时候触发回滚,下面来分析下回滚的实现。
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
这里获取的TransactionManager为默认的DataSourceTransactionManager。
在介绍DataSourceTransactionManager的rollback方法之前先来看下TransactionManager的类的结构。
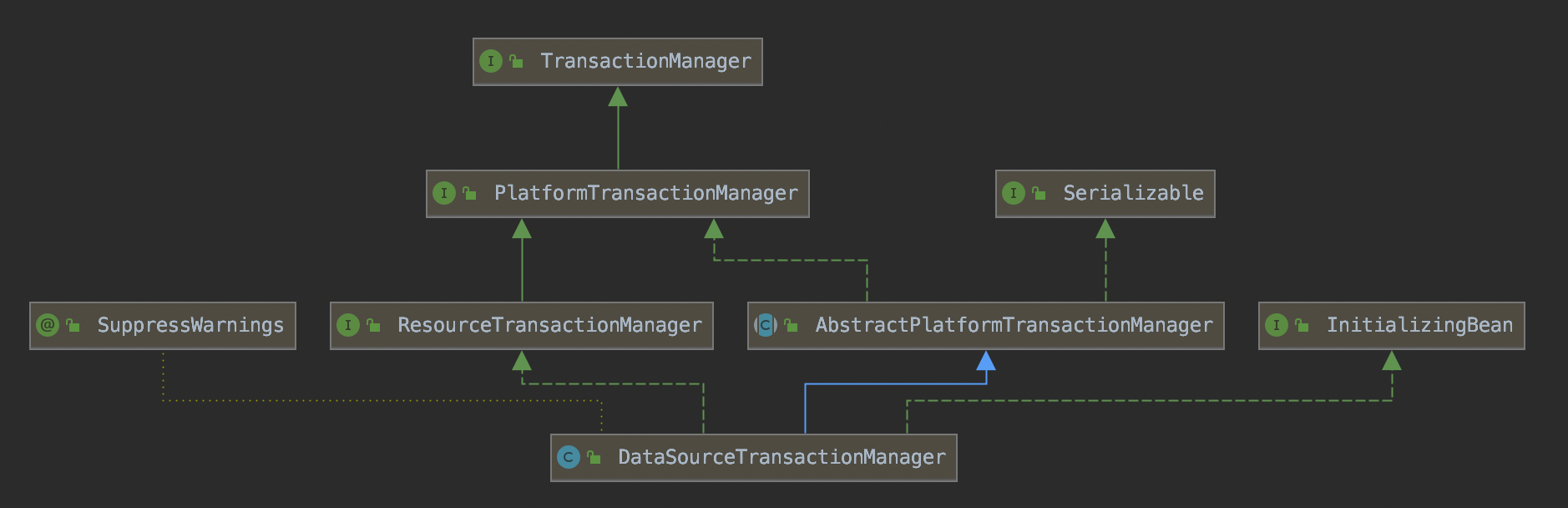
其中PlatformTransactionManager中的方法如下:
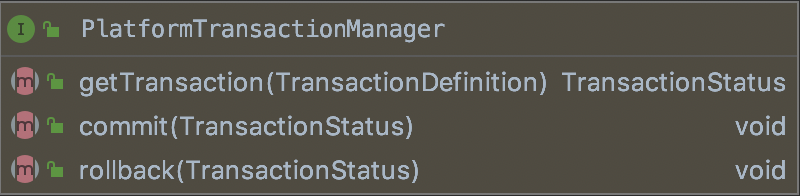
分别是获取事务对象,提交、回滚操作。
回滚操作这里使用了模版模式。
实现是在AbstractPlatformTransactionManager的rollback()方法中实现的。
@Override
public final void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
// 执行回滚操作
processRollback(defStatus, false);
}
processRollback()方法如下:
/**
* Process an actual rollback.
* The completed flag has already been checked.
* @param status object representing the transaction
* @throws TransactionException in case of rollback failure
*/
private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status, boolean unexpected) {
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = unexpected;
try {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back transaction to savepoint");
}
status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();
}
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback");
}
// 执行真正的回滚操作,该方法在具体子类中进行实现
doRollback(status);
}
else {
// Participating in larger transaction
if (status.hasTransaction()) {
if (status.isLocalRollbackOnly() || isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - marking existing transaction as rollback-only");
}
doSetRollbackOnly(status);
}
else {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - letting transaction originator decide on rollback");
}
}
}
else {
logger.debug("Should roll back transaction but cannot - no transaction available");
}
// Unexpected rollback only matters here if we're asked to fail early
if (!isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = false;
}
}
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
throw ex;
}
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
// Raise UnexpectedRollbackException if we had a global rollback-only marker
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
finally {
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
doRollback()在DataSourceTransactionManager的实现如下:
@Override
protected void doRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
// 获取Connection对象
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]");
}
try {
// 执行回滚操作
con.rollback();
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not roll back JDBC transaction", ex);
}
}
提交实现
提交是在commitTransactionAfterReturning中完成的。
/**
* Execute after successful completion of call, but not after an exception was handled.
* Do nothing if we didn't create a transaction.
* @param txInfo information about the current transaction
*/
protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
}
txInfo.getTransactionManager()与上述异常回滚逻辑一致,commit方法如下:
/**
* This implementation of commit handles participating in existing
* transactions and programmatic rollback requests.
* Delegates to {@code isRollbackOnly}, {@code doCommit}
* and {@code rollback}.
* @see org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus#isRollbackOnly()
* @see #doCommit
* @see #rollback
*/
@Override
public final void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
// 如果事务状态已经是完成,则抛出异常
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
// 事务状态为只需要本地回滚
if (defStatus.isLocalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Transactional code has requested rollback");
}
processRollback(defStatus, false);
return;
}
if (!shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() && defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Global transaction is marked as rollback-only but transactional code requested commit");
}
processRollback(defStatus, true);
return;
}
processCommit(defStatus);
}
processCommit()方法如下:
/**
* Process an actual commit.
* Rollback-only flags have already been checked and applied.
* @param status object representing the transaction
* @throws TransactionException in case of commit failure
*/
private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
try {
boolean beforeCompletionInvoked = false;
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = false;
prepareForCommit(status);
triggerBeforeCommit(status);
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
beforeCompletionInvoked = true;
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Releasing transaction savepoint");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
status.releaseHeldSavepoint();
}
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction commit");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
// 执行提交
doCommit(status);
}
else if (isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
}
// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException if we have a global rollback-only
// marker but still didn't get a corresponding exception from commit.
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction silently rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
catch (UnexpectedRollbackException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
throw ex;
}
catch (TransactionException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
if (isRollbackOnCommitFailure()) {
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
}
else {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
}
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
}
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
throw ex;
}
// Trigger afterCommit callbacks, with an exception thrown there
// propagated to callers but the transaction still considered as committed.
try {
triggerAfterCommit(status);
}
finally {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED);
}
}
finally {
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
doCommit()方法由子类实现代码如下:
@Override
protected void doCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Committing JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]");
}
try {
con.commit();
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not commit JDBC transaction", ex);
}
}
方式上与rollback()方法一致。
下面逐项的分析Spring事务的各个组件。
TransactionManager事务管理器
Spring中提供了TransactionManager接口用于表示Spring的事务管理器。
TransactionManager事务管理器的类结构图如下:
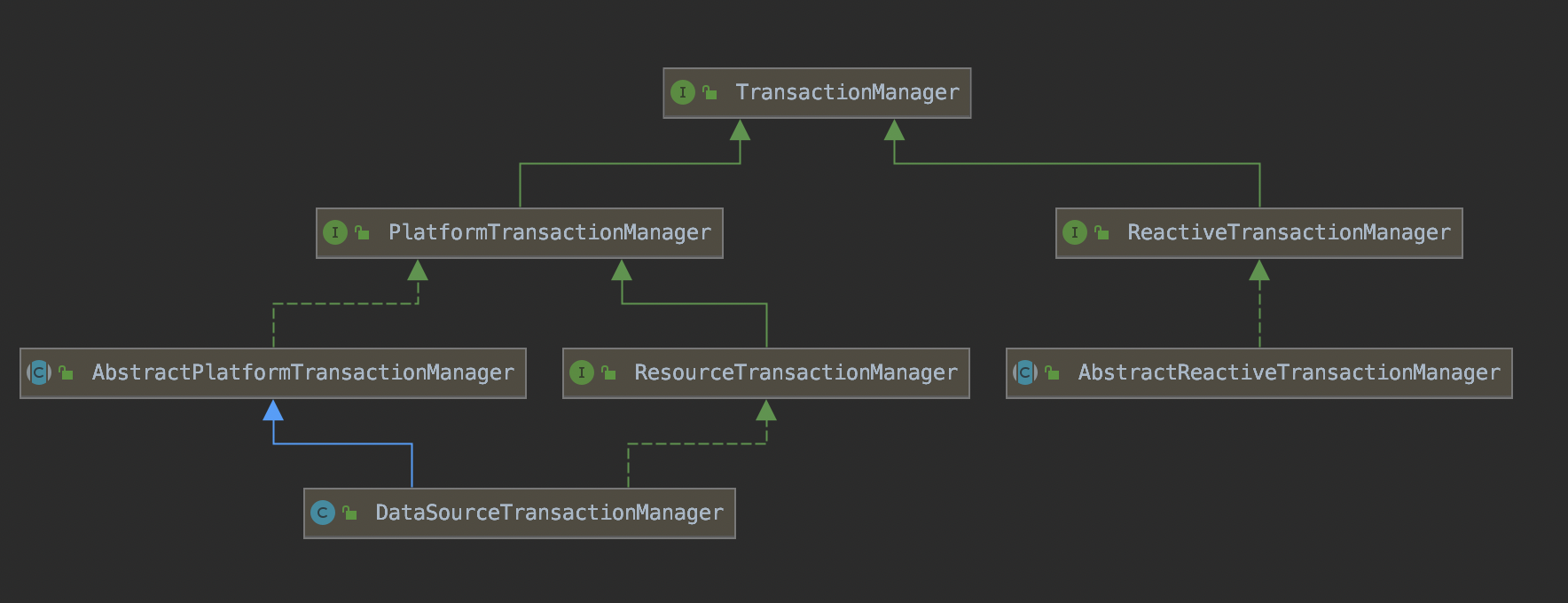
TransactionManager是一个标记接口,其主要有两个子接口用于使用。以下是摘自Spring源码中的注释。
- PlatformTransactionManager:这是Spring事务基础设施中的中心接口。应用程序可以直接使用它,但它主要不是指API:通常,应用程序将使用TransactionTemplate或通过AOP进行声明性事务划分。对于实现者,建议从提供的AbstractPlatformTransactionManager类派生,该类预先实现定义的传播行为并负责事务同步处理。子类必须为底层事务的特定状态实现模板方法,例如:begin、suspend、resume、commit。
PlatformTransactionManager中的方法详细介绍如下:
// 根据事务隔离级别返回一个当前已存在的事务或者创建一个新的事务。
// 请注意,隔离级别或超时等参数将仅应用于新事务,因此在活动事务时将被忽略。
// 此外,并非每个事务管理器都支持所有事务定义设置:当遇到不支持的设置时,正确的事务管理器实现应引发异常。
// 上述规则的一个例外是只读标志,如果不支持显式只读模式,则应忽略该标志。
// 实际上,只读标志只是潜在优化的提示。
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;
PlatformTransactionManager的默认实现的抽象类为AbstractPlatformTransactionManager。该类实现了关于Spring中的传播机制。
getTransaction()方法,如下所示
/**
* This implementation handles propagation behavior. Delegates to
* {@code doGetTransaction}, {@code isExistingTransaction}
* and {@code doBegin}.
* @see #doGetTransaction
* @see #isExistingTransaction
* @see #doBegin
*/
@Override
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException {
// 这里判断一下TransactionDefinition是否为空,如果不为空,提供一个默认的TransactionDefinition实现。
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
TransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());
// 获取事务,该方法由子类实现。
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 判断该事务是否存在。
// 首先判断事务存在的依据就是connection是否存在及事务状态是否为活跃状态。
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
// 处理已存在事务的情况。
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
if (def.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", def.getTimeout());
}
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
// 如果当前没有事务则抛出异常
if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// 处理可以新建事务的情况
else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + def.getName() + "]: " + def);
}
try {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
// 创建一个事务
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
def, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
// 开启一个事务
doBegin(transaction, def);
// 准备事务同步回调
prepareSynchronization(status, def);
return status;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
}
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
// 其他撞他则直接将transaction赋值为null
if (def.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + def);
}
// 计算newSynchronization状态
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
// 初始化TransactionStatus状态
return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
doGetConnection()方法如下:
@Override
protected Object doGetTransaction() {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject();
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed());
ConnectionHolder conHolder =
(ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false);
return txObject;
}
isExistingTransaction()判断当前是否存在事务。
@Override
protected boolean isExistingTransaction(Object transaction) {
// 判断当前是否已经存在事务了。
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
return (txObject.hasConnectionHolder() && txObject.getConnectionHolder().isTransactionActive());
}
handleExistingTransaction()方法如下:
/**
* Create a TransactionStatus for an existing transaction.
*/
private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction(
TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, boolean debugEnabled)
throws TransactionException {
// 如果事务的传播级别为NEVER则直接抛出异常。
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'");
}
// 以非事务方式执行操作,若当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction");
}
Object suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(
definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
// 新建事务,若当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [" +
definition.getName() + "]");
}
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
try {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
doBegin(transaction, definition);
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error beginEx) {
resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginEx);
throw beginEx;
}
}
// 若当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行;若当前没有事务,则执行REQUIRED类似的操作
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) {
throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
"Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " +
"specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'");
}
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]");
}
if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) {
// Create savepoint within existing Spring-managed transaction,
// through the SavepointManager API implemented by TransactionStatus.
// Usually uses JDBC 3.0 savepoints. Never activates Spring synchronization.
DefaultTransactionStatus status =
prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
status.createAndHoldSavepoint();
return status;
}
else {
// Nested transaction through nested begin and commit/rollback calls.
// Usually only for JTA: Spring synchronization might get activated here
// in case of a pre-existing JTA transaction.
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
doBegin(transaction, definition);
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
}
// 处理SUPPORTS和REQUIRED
// Assumably PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS or PROPAGATION_REQUIRED.
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Participating in existing transaction");
}
if (isValidateExistingTransaction()) {
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) {
Integer currentIsolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
if (currentIsolationLevel == null || currentIsolationLevel != definition.getIsolationLevel()) {
Constants isoConstants = DefaultTransactionDefinition.constants;
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] specifies isolation level which is incompatible with existing transaction: " +
(currentIsolationLevel != null ?
isoConstants.toCode(currentIsolationLevel, DefaultTransactionDefinition.PREFIX_ISOLATION) :
"(unknown)"));
}
}
if (!definition.isReadOnly()) {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] is not marked as read-only but existing transaction is");
}
}
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
doBegin()方法的作用是开启一个事务:
@Override
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
Connection con = null;
try {
if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction");
}
txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
}
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
txObject.setReadOnly(definition.isReadOnly());
// Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers,
// so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly
// configured the connection pool to set it already).
if (con.getAutoCommit()) {
txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit");
}
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition);
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);
int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);
if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);
}
// Bind the connection holder to the thread.
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false);
}
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex);
}
}
commit()方法如下:
// 就给定事务的状态提交该事务。如果事务仅以编程方式标记为回滚,请执行回滚。
// 如果事务不是新事务,则省略提交以正确参与周围事务。如果上一个事务已被挂起以能够创建新事务,请在提交新事务后继续上一个事务。
// 请注意,当提交调用完成时,无论是正常还是引发异常,事务都必须完全完成并清理。在这种情况下,不应期望回滚调用。
// 如果此方法引发TransactionException以外的异常,则提交前的某个错误会导致提交尝试失败。例如,一个O/R映射工具可能在提交之前尝试刷新对数据库的更改,结果是DataAccessException导致事务失败。在这种情况下,原始异常将传播到此提交方法的调用方。
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
commit()方法的实现:
/**
* This implementation of commit handles participating in existing
* transactions and programmatic rollback requests.
* Delegates to {@code isRollbackOnly}, {@code doCommit}
* and {@code rollback}.
* @see org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus#isRollbackOnly()
* @see #doCommit
* @see #rollback
*/
@Override
public final void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
// 如果事务状态显示已经完成了,则抛出异常
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
if (defStatus.isLocalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Transactional code has requested rollback");
}
processRollback(defStatus, false);
return;
}
if (!shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() && defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Global transaction is marked as rollback-only but transactional code requested commit");
}
processRollback(defStatus, true);
return;
}
// 执行commit操作
processCommit(defStatus);
}
processCommit()方法如下:
/**
* Process an actual commit.
* Rollback-only flags have already been checked and applied.
* @param status object representing the transaction
* @throws TransactionException in case of commit failure
*/
private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
try {
boolean beforeCompletionInvoked = false;
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = false;
// 该方法是一个空实现
prepareForCommit(status);
// 触发TransactionSynchronization的beforeCommit方法
triggerBeforeCommit(status);
// 触发TransactionSynchronization的beforeCompletion方法
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
beforeCompletionInvoked = true;
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Releasing transaction savepoint");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
status.releaseHeldSavepoint();
}
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction commit");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
// 如果事务状态是一个新事务,则执行提交
doCommit(status);
}
else if (isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
}
// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException if we have a global rollback-only
// marker but still didn't get a corresponding exception from commit.
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction silently rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
catch (UnexpectedRollbackException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
// 触发TransactionSynchronization的afterCompletion方法
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
throw ex;
}
catch (TransactionException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
if (isRollbackOnCommitFailure()) {
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
}
else {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
}
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
}
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
throw ex;
}
// Trigger afterCommit callbacks, with an exception thrown there
// propagated to callers but the transaction still considered as committed.
try {
// 触发TransactionSynchronization的afterCommit方法
triggerAfterCommit(status);
}
finally {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED);
}
}
finally {
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
DefaultTransactionStatus的主要字段如下所示:
// 代表一个事务
@Nullable
private final Object transaction;
// 是否为新事务
private final boolean newTransaction;
// 是否为刚初始化的事务
private final boolean newSynchronization;