DispatcherServlet的工作原理
DispatcherServlet的工作原理分为两部分:
(1)、DispatcherServlet的初始化。
(2)、DispatcherServlet处理请求。
PS:第一部分在之前的SpringMVC初始化过程中已经介绍了,并且在SpringMVC相关组件中详细说明了。此处不再详细介绍。本文主要介绍DispatcherServlet处理请求。
1、DispatcherServlet处理请求原理
DispatcherServlet的类结构图如下:
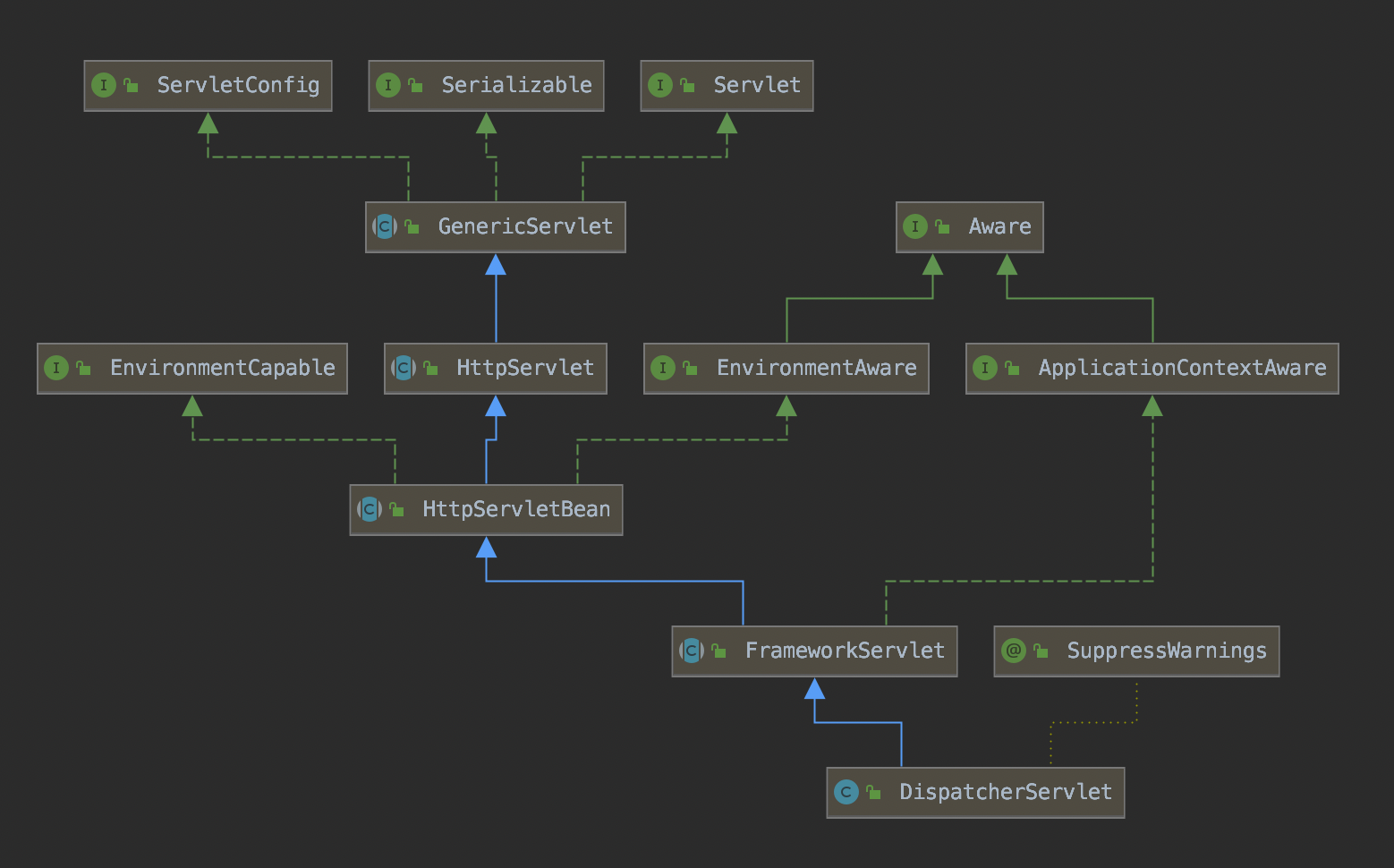
收到一个用户请求的起始位置是在HttpServlet的service方法中。
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
try {
request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
throw new ServletException(lStrings.getString("http.non_http"));
}
service(request, response);
}
最后会调用DispatcherServlet的doDispatch方法
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
(1)、处理多块请求
首先会判断这个请求是否是多块请求(比如上传文件),如果是,那么会将request封装成MultipartHttpServletRequest,如果不是则继续向下处理。(具体多块请求原理在组件介绍的时候已经讲过)
(2)、获取处理器
接下来会尝试获取HandlerExecutionChain。在讲述DispatcherServlet组件的时候对于流程已经大概说明了,这里详细再介绍下里面的原理及细节。
还是以RequestMappingHandlerMapping为例。RequestMappingHandlerMapping的结构图如下:
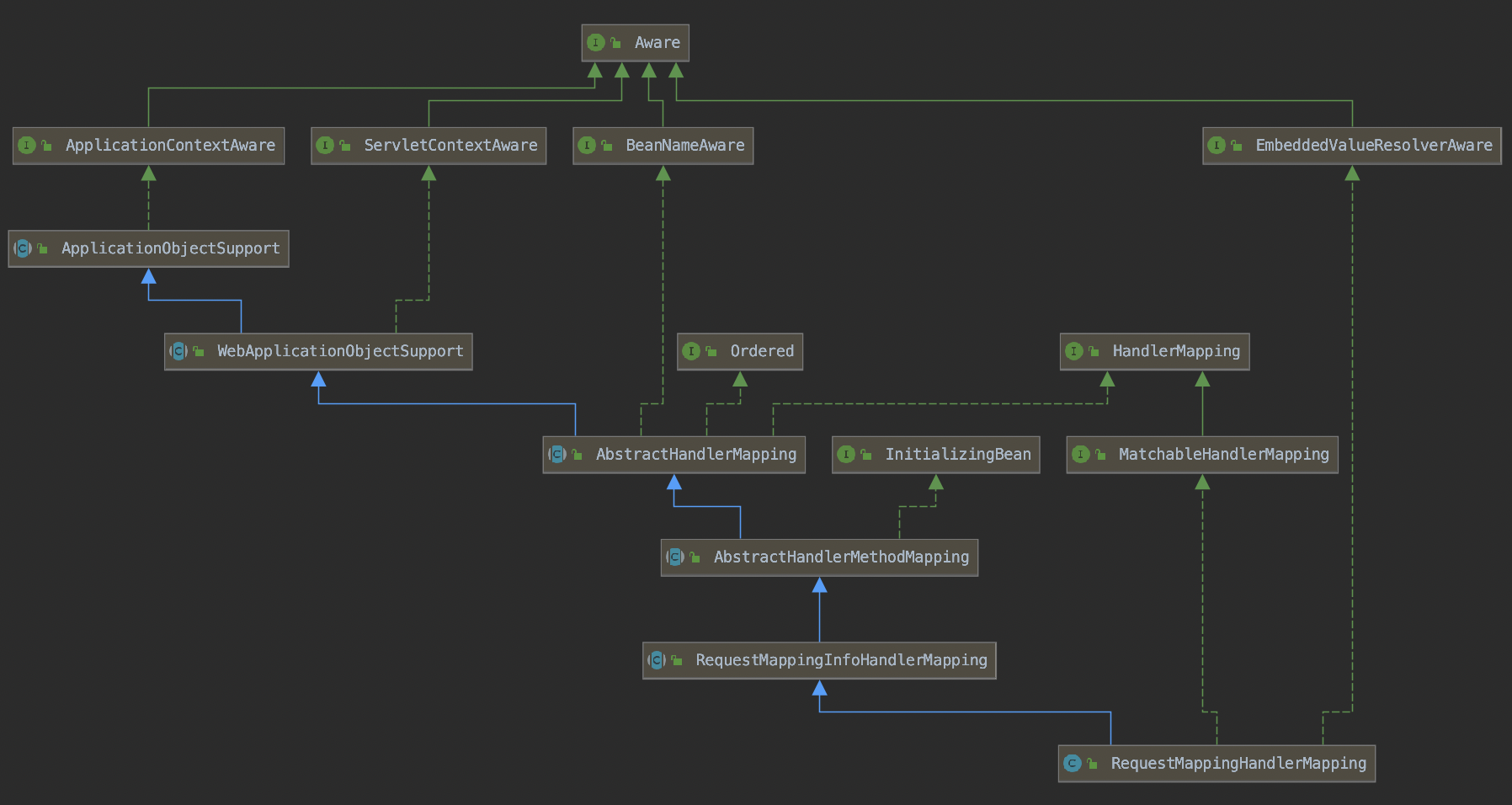
HandlerMapping的运行原理分为两部分:
第一部分是初始化操作,在初始化阶段HandlerMapping会加载所有被@Controller和@RequestMapping注解标记的类和方法供执行阶段使用。
第二部分是获取Handler的操作,在运行阶段DispatcherServlet会通过HandlerMapping获取HandlerExecutionChain。
初始化操作流程分析:
首先RequestMappingHandlerMapping由于该类实现了InitializingBean,那么在容器中创建这个类的实例的时候会调用afterPropertiesSet()执行初始化操作。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping中的afterPropertiesSet方法如下:
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(this.useSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(this.useTrailingSlashMatch);
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
具体的实现操作则是在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的initHandlerMethods方法中。
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
方法中首先会获取容器中所有被注册的beanName,然后对所有的bean执行筛选操作。具体的方法是在processCandidateBean中执行的。PS:SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX官方注释中给出的解释是避免spring-aop硬依赖,目前还不理解为什么。
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
在processCandidateBean方法中,首先通过beanName来获取Class,接下来会判断这个Class是否是一个HandlerMapping。isHandler方法在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping是一个抽象方法,在具体的子类中会对其进行实现。在RequestMappingHandlerMapping的判断逻辑:
Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
会判断这个Class是否有Controller或者RequestMapping注解。
detectHandlerMethods是AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的一个模版方法,这个方法的核心内容是根据实现类的方法来获取指定条件的Method数组,然后将这些Method包装成HandlerMethod注册到MappingRegistry中。
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
首先如果此时的handler还是String的话还会从容器中获取Class,然后通过工具类MethodIntrospector的selectMethods方法根据指定的条件筛选出Method和元数据信息,具体的信息可以通过泛型指定。
public static <T> Map<Method, T> selectMethods(Class<?> targetType, final MetadataLookup<T> metadataLookup) {
final Map<Method, T> methodMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
Set<Class<?>> handlerTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
Class<?> specificHandlerType = null;
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetType)) {
specificHandlerType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetType);
handlerTypes.add(specificHandlerType);
}
handlerTypes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetType));
for (Class<?> currentHandlerType : handlerTypes) {
final Class<?> targetClass = (specificHandlerType != null ? specificHandlerType : currentHandlerType);
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, method -> {
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);
if (result != null) {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {
methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);
}
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
}
return methodMap;
}
在selectMethods方法中核心处理逻辑是使用ReflectionUtils这个工具类的doWithMethods方法。
从网上查了些资料,这里详细讲下doWithMethods方法。
void doWithLocalMethods(Class<?> clazz, MethodCallback mc)
针对指定类型上的所有方法,依次调用MethodCallback回调;
首先来看看MethodCallback接口声明:
/**
* Action to take on each method.
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MethodCallback {
/**
* Perform an operation using the given method.
* @param method the method to operate on
*/
void doWith(Method method) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException;
}
其实就是一个正常的回调接口;来看看doWithLocalMethods实现:
public static void doWithLocalMethods(Class<?> clazz, MethodCallback mc) {
Method[] methods = getDeclaredMethods(clazz, false);
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
mc.doWith(method);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Not allowed to access method '" + method.getName() + "': " + ex);
}
}
}
其实实现很简单,就是得到类上的所有方法,然后执行回调接口;这个方法在Spring针对bean的方法上的标签处理时大量使用,比如@Init,@Resource,@Autowire等标签的预处理;
该方法有一个增强版:
void doWithMethods(Class<?> clazz, MethodCallback mc, MethodFilter mf)
该版本提供了一个方法匹配(过滤器)MethodFilter;
/**
* Callback optionally used to filter methods to be operated on by a method callback.
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MethodFilter {
/**
* Determine whether the given method matches.
* @param method the method to check
*/
boolean matches(Method method);
}
该接口就声明了一个匹配方法,用于匹配规则;
public static void doWithMethods(Class<?> clazz, MethodCallback mc, @Nullable MethodFilter mf) {
// Keep backing up the inheritance hierarchy.
Method[] methods = getDeclaredMethods(clazz, false);
for (Method method : methods) {
if (mf != null && !mf.matches(method)) {
continue;
}
try {
mc.doWith(method);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Not allowed to access method '" + method.getName() + "': " + ex);
}
}
if (clazz.getSuperclass() != null && (mf != USER_DECLARED_METHODS || clazz.getSuperclass() != Object.class)) {
doWithMethods(clazz.getSuperclass(), mc, mf);
}
else if (clazz.isInterface()) {
for (Class<?> superIfc : clazz.getInterfaces()) {
doWithMethods(superIfc, mc, mf);
}
}
}
该方法实现就很明确了,首先得到类上所有方法,针对每一个方法,调用MethodFilter实现匹配检查,如果匹配上,调用MethodCallback回调方法。该方法会递归向上查询所有父类和实现的接口上的所有方法并处理;
所以在MethodIntrospector中的回调如下:
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, method -> {
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);
if (result != null) {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {
methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);
}
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
同样在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中注册的回调如下:
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
该方法中会通过模版模式来调用getMappingForMethod,getMappingForMethod方法每个具体的子类都会覆盖,在RequestMappingHandlerMapping中如下:
@Override
@Nullable
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
@Nullable
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}
最终封装成元数据RequestMappingInfo存入methods中。
接下来会将生成的methods的数据通过MappingRegistry注册到 Map<T, MappingRegistration
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
// Assert that the handler method is not a suspending one.
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass()) && KotlinDelegate.isSuspend(method)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unsupported suspending handler method detected: " + method);
}
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
至此,DispatcherServlet在初始化阶段执行的操作就介绍完成。
获取Handler操作流程分析:
入口如下:
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
这里获取HandlerExecutionChain还是以RequestMappingHandlerMapping为例。getHandler的主体方法还是在AbstractHandlerMapping中进行的。
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = (this.corsConfigurationSource != null ? this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request) : null);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
config = (config != null ? config.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
核心的获取getHandlerInternal的方法则是在AbstractHandlerMapping实现的,后来又调用了AbstractHandlerMapping的getHandlerInternal方法。
/**
* Look up a handler method for the given request.
*/
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 首先从request中获取patch
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
// 将patch属性设置到request的attribute中
request.setAttribute(LOOKUP_PATH, lookupPath);
// 加锁
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
// 获取HandlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
// 如果提供的beanName是String,那么会获取该对象。
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
//释放锁
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
通过lookupHandlerMethod获取HandlerMethod
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 匹配结果存放到这里
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
// 通过path直接获取匹配信息
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 将匹配到的结果封装成Match,Match定义了匹配信息和HandlerMethod
/**
* Match的结构如下:
* private final T mapping;
* private final HandlerMethod handlerMethod;
*/
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
// 如果没有任务匹配的,那么会将所有的Mapping信息放到Match信息。
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
// 这里的比较类是在RequestMappingInfo中的compareTo方法。
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
// 获取最佳的匹配结果
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
// 获取列表中第二个Match,如果两个比较之后相等,那么就抛出异常。
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod);
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
获取Mapping信息是从addMatchingMappings的getMatchingMapping方法获取的,这个方法在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中是抽象的,具体的实现是在子类RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping中。
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (T mapping : mappings) {
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
if (match != null) {
matches.add(new Match(match, this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().get(mapping)));
}
}
}
@Override
protected RequestMappingInfo getMatchingMapping(RequestMappingInfo info, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 使用RequestMappingInfo的getMatchingCondition方法来判断是否匹配。如果匹配成功就返回一个RequestMappingInfo,匹配失败就返回null。
return info.getMatchingCondition(request);
}
RequestMappingInfo中的getMatchingCondition方法如下:
@Override
@Nullable
public RequestMappingInfo getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
// 判断请求方法是否匹配,如果方法都不匹配则返回。
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (methods == null) {
return null;
}
// 请求参数匹配,params 元素可以进一步缩小请求映射的定位范围。使用 params 元素,可以让多个处理方法处理到同一个URL 的请求, 而这些请求的参数是不一样的。
ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (params == null) {
return null;
}
// 通过header元素来根据请求中的消息头内容缩小请求映射的范围。
HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.(request);
if (headers == null) {
return null;
}
// produces 和 consumes 这两个元素来缩小请求映射类型的范围
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (consumes == null) {
return null;
}
ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (produces == null) {
return null;
}
// 对应RequestMapping中的path来缩小请求映射的范围
PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (patterns == null) {
return null;
}
RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (custom == null) {
return null;
}
return new RequestMappingInfo(this.name, patterns,
methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom.getCondition());
}
匹配好RequestMapping之后,会从已经注册的Map<T, HandlerMethod> mappingLookup中根据RequestMappingInfo取出HandlerMethod。并封装成Match后存储起来。这里对于各个Condition的getMatchingCondition缺少了详细的分析。需要补上。
接下来就是根据匹配到的结果进行排序。排序List
private class MatchComparator implements Comparator<Match> {
private final Comparator<T> comparator;
public MatchComparator(Comparator<T> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
@Override
public int compare(Match match1, Match match2) {
return this.comparator.compare(match1.mapping, match2.mapping);
}
}
内部实际上是依赖于构造器中传入的comparator来实现的。
排序的方法会调用
@Override
public int compareTo(RequestMappingInfo other, HttpServletRequest request) {
int result;
// Automatic vs explicit HTTP HEAD mapping
if (HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(request.getMethod())) {
result = this.methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
}
// 通过URL比较。
result = this.patternsCondition.compareTo(other.getPatternsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
// 通过param参数比较。
result = this.paramsCondition.compareTo(other.getParamsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
// 通过header比较。
result = this.headersCondition.compareTo(other.getHeadersCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
// 通过consumers和produces比较。
result = this.consumesCondition.compareTo(other.getConsumesCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.producesCondition.compareTo(other.getProducesCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
// Implicit (no method) vs explicit HTTP method mappings
// 通过method来比较。
result = this.methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.customConditionHolder.compareTo(other.customConditionHolder, request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
return 0;
}
分别再分析下每个Condition中的compareTo方法,它们是实现比较的核心逻辑。
(1)、PatternsRequestCondition:根据请求路径比较。这个属性也是最开始进行比较的
@Override
public int compareTo(PatternsRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 获取本次请求的path
String lookupPath = this.pathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, HandlerMapping.LOOKUP_PATH);
// 通过path获取Comparator,这里用的是PathMatcher的实现类AntPathMatcher里面的AntPatternComparator
Comparator<String> patternComparator = this.pathMatcher.getPatternComparator(lookupPath);
Iterator<String> iterator = this.patterns.iterator();
Iterator<String> iteratorOther = other.patterns.iterator();
// 通过AntPatternComparator进行比较。
while (iterator.hasNext() && iteratorOther.hasNext()) {
int result = patternComparator.compare(iterator.next(), iteratorOther.next());
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
}
if (iterator.hasNext()) {
return -1;
}
else if (iteratorOther.hasNext()) {
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
@Override
public int compare(String pattern1, String pattern2) {
PatternInfo info1 = new PatternInfo(pattern1);
PatternInfo info2 = new PatternInfo(pattern2);
if (info1.isLeastSpecific() && info2.isLeastSpecific()) {
return 0;
}
else if (info1.isLeastSpecific()) {
return 1;
}
else if (info2.isLeastSpecific()) {
return -1;
}
boolean pattern1EqualsPath = pattern1.equals(this.path);
boolean pattern2EqualsPath = pattern2.equals(this.path);
if (pattern1EqualsPath && pattern2EqualsPath) {
return 0;
}
else if (pattern1EqualsPath) {
return -1;
}
else if (pattern2EqualsPath) {
return 1;
}
if (info1.isPrefixPattern() && info2.isPrefixPattern()) {
return info2.getLength() - info1.getLength();
}
else if (info1.isPrefixPattern() && info2.getDoubleWildcards() == 0) {
return 1;
}
else if (info2.isPrefixPattern() && info1.getDoubleWildcards() == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (info1.getTotalCount() != info2.getTotalCount()) {
return info1.getTotalCount() - info2.getTotalCount();
}
if (info1.getLength() != info2.getLength()) {
return info2.getLength() - info1.getLength();
}
if (info1.getSingleWildcards() < info2.getSingleWildcards()) {
return -1;
}
else if (info2.getSingleWildcards() < info1.getSingleWildcards()) {
return 1;
}
if (info1.getUriVars() < info2.getUriVars()) {
return -1;
}
else if (info2.getUriVars() < info1.getUriVars()) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
这里附上关于AntPathMatcher这个类的注释:
/**
* {@link PathMatcher} implementation for Ant-style path patterns.
*
* <p>Part of this mapping code has been kindly borrowed from <a href="https://ant.apache.org">Apache Ant</a>.
*
* <p>The mapping matches URLs using the following rules:<br>
* <ul>
* <li>{@code ?} matches one character</li>
* <li>{@code *} matches zero or more characters</li>
* <li>{@code **} matches zero or more <em>directories</em> in a path</li>
* <li>{@code {spring:[a-z]+}} matches the regexp {@code [a-z]+} as a path variable named "spring"</li>
* </ul>
*
* <h3>Examples</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@code com/t?st.jsp} — matches {@code com/test.jsp} but also
* {@code com/tast.jsp} or {@code com/txst.jsp}</li>
* <li>{@code com/*.jsp} — matches all {@code .jsp} files in the
* {@code com} directory</li>
* <li><code>com/**/test.jsp</code> — matches all {@code test.jsp}
* files underneath the {@code com} path</li>
* <li><code>org/springframework/**/*.jsp</code> — matches all
* {@code .jsp} files underneath the {@code org/springframework} path</li>
* <li><code>org/**/servlet/bla.jsp</code> — matches
* {@code org/springframework/servlet/bla.jsp} but also
* {@code org/springframework/testing/servlet/bla.jsp} and {@code org/servlet/bla.jsp}</li>
* <li>{@code com/{filename:\\w+}.jsp} will match {@code com/test.jsp} and assign the value {@code test}
* to the {@code filename} variable</li>
* </ul>
*
* <p><strong>Note:</strong> a pattern and a path must both be absolute or must
* both be relative in order for the two to match. Therefore it is recommended
* that users of this implementation to sanitize patterns in order to prefix
* them with "/" as it makes sense in the context in which they're used.
*
*/
(2)、ParamsRequestCondition:根据请求参数进行比较。
@Override
public int compareTo(ParamsRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 主要是根据请求参数的多少进行判断,多的在前。
int result = other.expressions.size() - this.expressions.size();
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
return (int) (getValueMatchCount(other.expressions) - getValueMatchCount(this.expressions));
}
(3)、HeadersRequestCondition:根据请求头进行比较。
@Override
public int compareTo(HeadersRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 根据请求头多少进行判断,多的在前。
int result = other.expressions.size() - this.expressions.size();
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
return (int) (getValueMatchCount(other.expressions) - getValueMatchCount(this.expressions));
}
(4)、ConsumesRequestCondition:根据消息内容进行比较。
@Override
public int compareTo(ConsumesRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 如果两个比较的消息内容都为空,那么就认为相等
if (this.expressions.isEmpty() && other.expressions.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
// 如果“其他”有更多特定的媒体类型表达式,则大于0
else if (this.expressions.isEmpty()) {
return 1;
}
// 如果“this”有更多特定的媒体类型表达式,则小于0
else if (other.expressions.isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
else {
return this.expressions.get(0).compareTo(other.expressions.get(0));
}
}
(5)、ProducesRequestCondition:根据接受类型进行比较。
@Override
public int compareTo(ProducesRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
// 首先获取本次请求的所有的可接受的类型
List<MediaType> acceptedMediaTypes = getAcceptedMediaTypes(request);
// 对这些类型进行迭代
for (MediaType acceptedMediaType : acceptedMediaTypes) {
// 获取this类型的type的索引
int thisIndex = this.indexOfEqualMediaType(acceptedMediaType);
// 获取other类型的type的索引
int otherIndex = other.indexOfEqualMediaType(acceptedMediaType);
比较两个类型的索引
int result = compareMatchingMediaTypes(this, thisIndex, other, otherIndex);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
thisIndex = this.indexOfIncludedMediaType(acceptedMediaType);
otherIndex = other.indexOfIncludedMediaType(acceptedMediaType);
result = compareMatchingMediaTypes(this, thisIndex, other, otherIndex);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
}
return 0;
}
catch (HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException ex) {
// should never happen
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot compare without having any requested media types", ex);
}
}
(6)、RequestMethodsRequestCondition:根据请求方法进行比较。
@Override
public int compareTo(RequestMethodsRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
if (other.methods.size() != this.methods.size()) {
return other.methods.size() - this.methods.size();
}
else if (this.methods.size() == 1) {
if (this.methods.contains(RequestMethod.HEAD) && other.methods.contains(RequestMethod.GET)) {
return -1;
}
else if (this.methods.contains(RequestMethod.GET) && other.methods.contains(RequestMethod.HEAD)) {
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
这里同样也是根据方法的数目进行比较。
以上就是当存在多个匹配结果的时候进行排序的依据,排序完成之后会从取出第一个Match,获取其中的HandlerMethod,并封装成HandlerExecutionChain返回。
(3)、获取处理适配器
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
// 循环判断当前的适配器是否支持Handler,如果支持则返回该适配器
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
PS:handlerAdapters是在DispatcherServlet初始化的时候被注册进去的。
这里仍以RequestMappingHandlerAdapter为例。
该类的结构图如下:
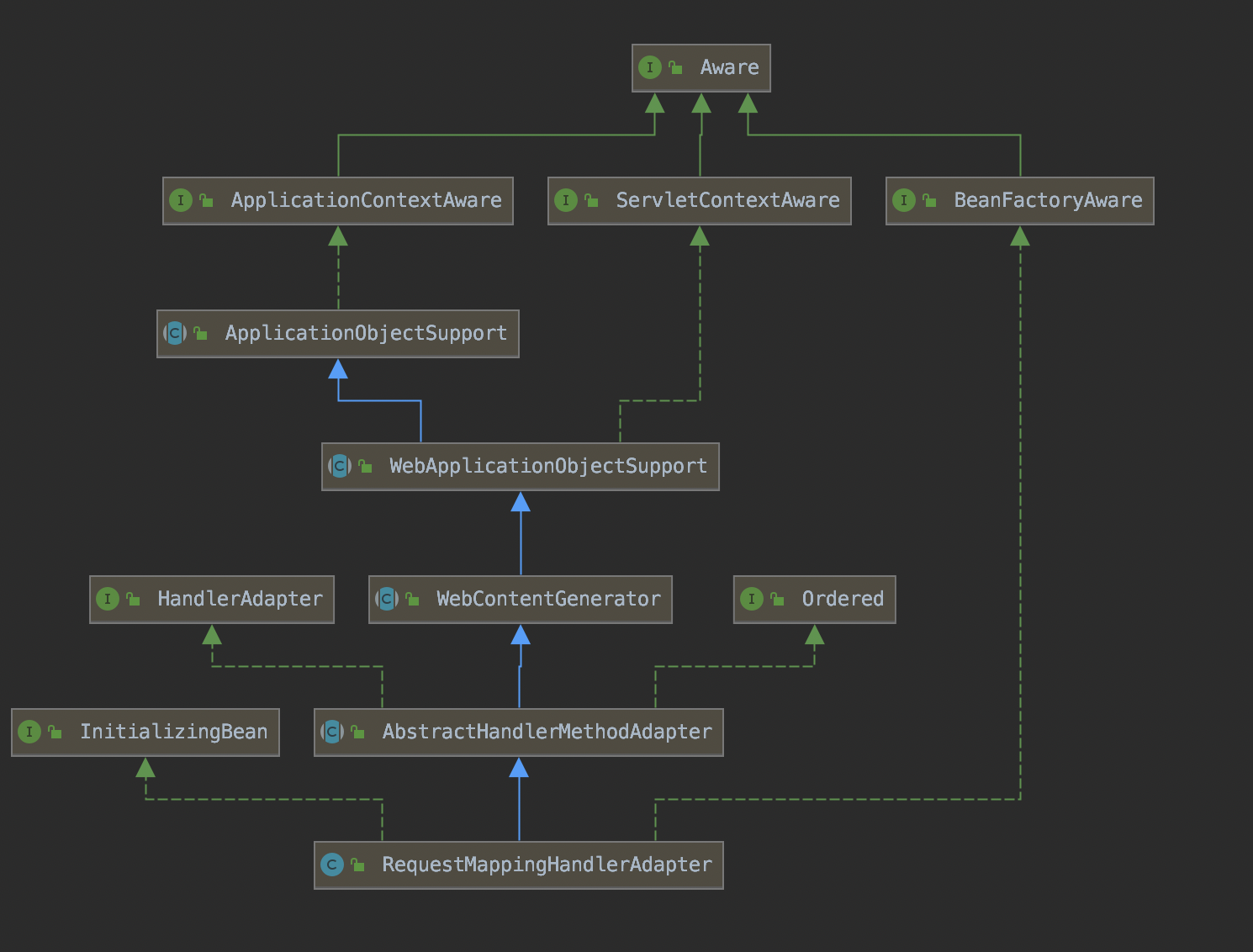
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter实现了HandlerAdapter,该接口的方法如下:
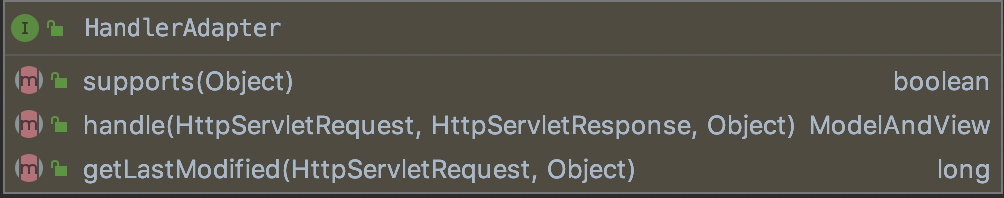
(1)、是否支持Handler。
(2)、执行Handler。
(3)、获取上次的修改的时间。
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter类同样也分为两部分:
第一部分初始化操作
第二部分执行handler操作
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的初始化操作
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter同时也实现了InitializingBean,那么它在被创建的时候也会调用afterPropertiesSet方法。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// Do this first, it may add ResponseBody advice beans
// 初始化被ControllerAdvice注解标记的类
initControllerAdviceCache();
// 初始化参数解析器
if (this.argumentResolvers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultArgumentResolvers();
this.argumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite().addResolvers(resolvers);
}
// 初始化参数绑定器
if (this.initBinderArgumentResolvers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultInitBinderArgumentResolvers();
this.initBinderArgumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite().addResolvers(resolvers);
}
// 初始化返回值处理器
if (this.returnValueHandlers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> handlers = getDefaultReturnValueHandlers();
this.returnValueHandlers = new HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite().addHandlers(handlers);
}
}
最开始的时候会初始化ControllerAdvice,这里从相关资料上查找并介绍下这个注解的作用:
(1)、数据绑定:通过注解@InitBinder可以为数据绑定器WebDataBinder添加新的类型转化器。在所有需进行类型转换的参数绑定过程中,都需要用到WebDataBinder的数据转换功能把请求数据转换为目标参数类型。
(2)、异常处理:当处理器方法中发生异常且未被处理器捕获时,会通过异常处理器对该异常进行处理。通过@ExceptionHandler可以为处理器方法声明异常处理方法。
(3)、模型属性:通过在非处理器方法上标记@ModelAttribute,可以为所有的处理器方法附加模型属性。在执行处理器方法前先执行@ModelAttribute标记的方法,并添加该方法的返回值到Model中。
(4)、请求体与响应体增强:在@RequestBody与@ResponseBody的处理中增强信息转换功能,可以在读取请求体前,读请求体后,写相应器前对数据做一些特殊处理。
private void initControllerAdviceCache() {
if (getApplicationContext() == null) {
return;
}
List<ControllerAdviceBean> adviceBeans = ControllerAdviceBean.findAnnotatedBeans(getApplicationContext());
List<Object> requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans = new ArrayList<>();
for (ControllerAdviceBean adviceBean : adviceBeans) {
Class<?> beanType = adviceBean.getBeanType();
if (beanType == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unresolvable type for ControllerAdviceBean: " + adviceBean);
}
Set<Method> attrMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(beanType, MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS);
if (!attrMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.modelAttributeAdviceCache.put(adviceBean, attrMethods);
}
Set<Method> binderMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(beanType, INIT_BINDER_METHODS);
if (!binderMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.initBinderAdviceCache.put(adviceBean, binderMethods);
}
if (RequestBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanType) || ResponseBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanType)) {
requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans.add(adviceBean);
}
}
if (!requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.requestResponseBodyAdvice.addAll(0, requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
int modelSize = this.modelAttributeAdviceCache.size();
int binderSize = this.initBinderAdviceCache.size();
int reqCount = getBodyAdviceCount(RequestBodyAdvice.class);
int resCount = getBodyAdviceCount(ResponseBodyAdvice.class);
if (modelSize == 0 && binderSize == 0 && reqCount == 0 && resCount == 0) {
logger.debug("ControllerAdvice beans: none");
}
else {
logger.debug("ControllerAdvice beans: " + modelSize + " @ModelAttribute, " + binderSize +
" @InitBinder, " + reqCount + " RequestBodyAdvice, " + resCount + " ResponseBodyAdvice");
}
}
}
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter执行handler操作
执行handler操作是在AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter中进行的。
@Override
@Nullable
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
// 真正执行处理的方法,由子类覆盖。
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter中的handleInternal:
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
// 校验request,如果支持的方法列表中不存在就抛出异常。
checkRequest(request);
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No synchronization on session demanded at all...
// 调用HandlerMethod方法。
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
invokeHandlerMethod方法代码如下:
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
// 首先将请求封装成ServletWebRequest。
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
// 构建参数绑定器工厂,DataBinder的主要功能是将String类型的值转成相应的数据
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
// 构建ModelAttribute属性器工厂
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
// 根据HandlerMethod对象构建ServletInvocableHandlerMethod
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
// 设置各种解析器
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
// 异步请求处理
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {
String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);
return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";
});
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
// 执行调用HandlerMethod
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
// 将请求的结果封装成ModelAndView
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
通过上述流程完成了方法的调用,并将结果封装成ModelAndView。