(1)整体流程说明
后续补充:之前的记录仅仅是分析了代码的运行流程,并没有做到有一个宏观的框架去描述整体的设置属性的结构,所以其实还是没有说清楚整个的一个工作过程:希望借此来对这部分代码分层学习下,代码很复杂。
首先来由一个特殊场景来说明下属性设置的工作过程并由此展开:
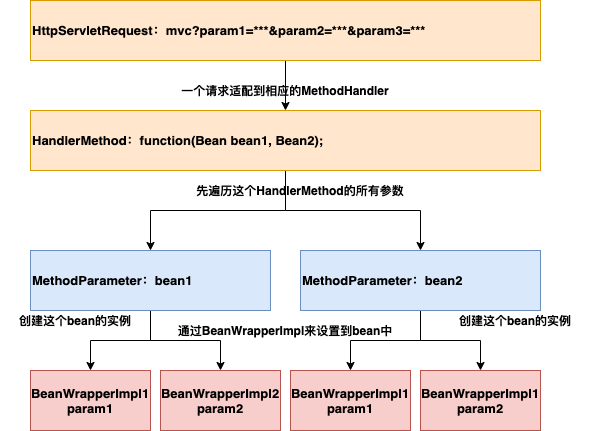
整体执行的结构图如下:
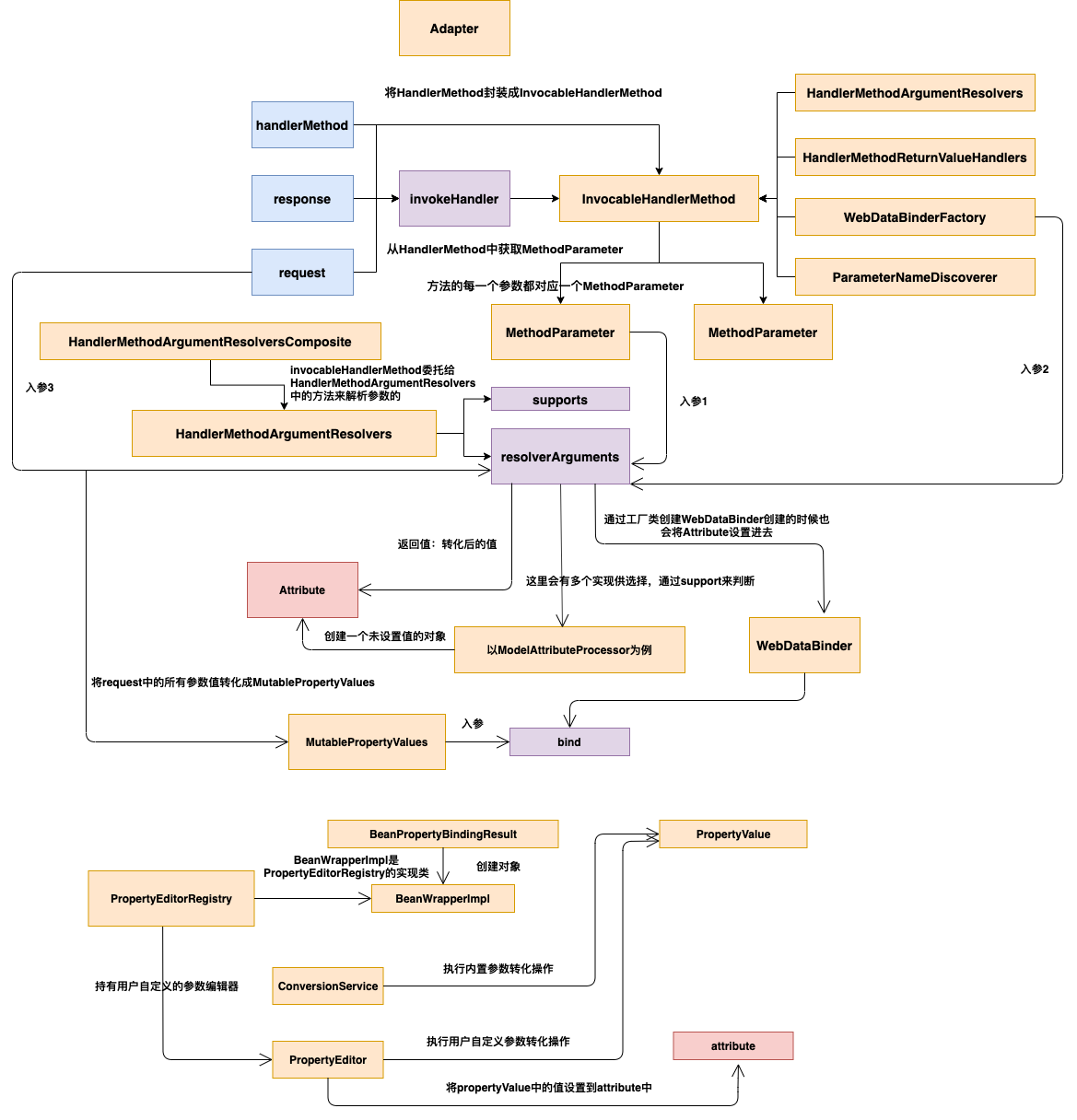
整体的框架是如此,只不过其他不同的场景会根据不同的HandlerMethodArgumentResolver来进行单独解析和绑定值的操作。
(2)、WebDataBinder组件
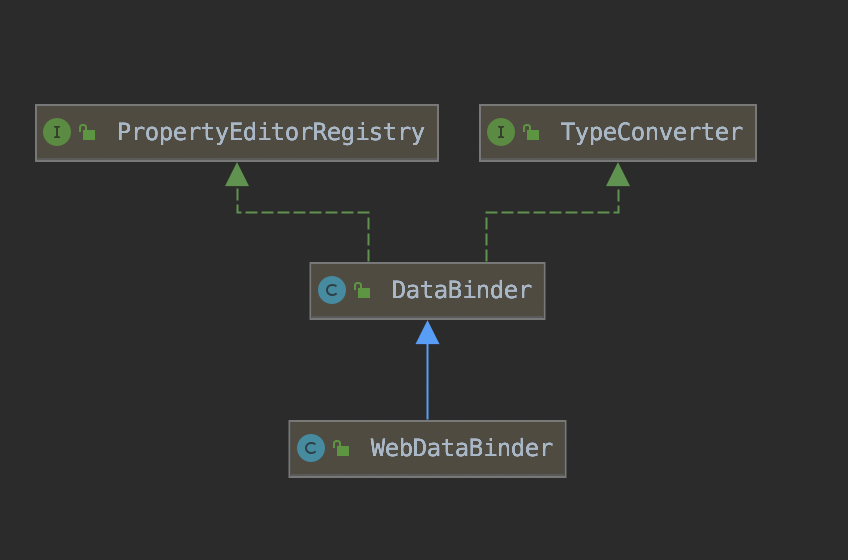
DataBinder的作用是:将一个数据转化成为一个指定的类型。
-93d70bbdfdf843a1a750a298461e9eef.png)
DataBinder有两部分核心操作:
第一:初始化自身操作。
第二:执行转换赋值操作。
1、初始化操作
首先初始化操作的入口是在ModelAttributeMethodProcessor类的resolveArgument方法中。
该类的结构如下:
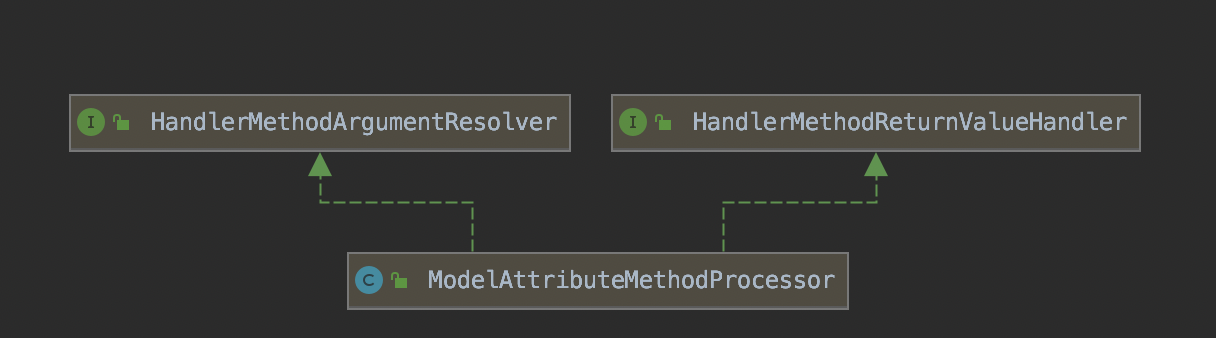
实现了HandlerMethodArgumentResolver接口,并实现了resolveArgument方法。
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
Assert.state(mavContainer != null, "ModelAttributeMethodProcessor requires ModelAndViewContainer");
Assert.state(binderFactory != null, "ModelAttributeMethodProcessor requires WebDataBinderFactory");
String name = ModelFactory.getNameForParameter(parameter);
ModelAttribute ann = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class);
if (ann != null) {
mavContainer.setBinding(name, ann.binding());
}
Object attribute = null;
BindingResult bindingResult = null;
if (mavContainer.containsAttribute(name)) {
attribute = mavContainer.getModel().get(name);
}
else {
// Create attribute instance
try {
attribute = createAttribute(name, parameter, binderFactory, webRequest);
}
catch (BindException ex) {
if (isBindExceptionRequired(parameter)) {
// No BindingResult parameter -> fail with BindException
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, expose null/empty value and associated BindingResult
if (parameter.getParameterType() == Optional.class) {
attribute = Optional.empty();
}
bindingResult = ex.getBindingResult();
}
}
if (bindingResult == null) {
// Bean property binding and validation;
// skipped in case of binding failure on construction.
// 在这里创建WebDataBinder供后续使用。这里会调用Controller中或@ControllerAdvice中被@InitBinder标记的方法。
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, attribute, name);
if (binder.getTarget() != null) {
if (!mavContainer.isBindingDisabled(name)) {
bindRequestParameters(binder, webRequest);
}
validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter);
if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) {
throw new BindException(binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
// Value type adaptation, also covering java.util.Optional
if (!parameter.getParameterType().isInstance(attribute)) {
attribute = binder.convertIfNecessary(binder.getTarget(), parameter.getParameterType(), parameter);
}
bindingResult = binder.getBindingResult();
}
// Add resolved attribute and BindingResult at the end of the model
Map<String, Object> bindingResultModel = bindingResult.getModel();
mavContainer.removeAttributes(bindingResultModel);
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(bindingResultModel);
return attribute;
}
创建WebDataBinder实例的方式是通过WebDataFactory.createBinder来创建的。而这里的WebDatafactory下面的方法来设置到HandlerMethod属性中的。
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {
String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);
return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";
});
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
创建WebDataBinder对象的方法如下:
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public final WebDataBinder createBinder(
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable Object target, String objectName) throws Exception {
WebDataBinder dataBinder = createBinderInstance(target, objectName, webRequest);
if (this.initializer != null) {
this.initializer.initBinder(dataBinder, webRequest);
}
initBinder(dataBinder, webRequest);
return dataBinder;
}
具体的初始化操作是在InitBinderDataBinderFactory类中进行的。
@Override
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder dataBinder, NativeWebRequest request) throws Exception {
for (InvocableHandlerMethod binderMethod : this.binderMethods) {
if (isBinderMethodApplicable(binderMethod, dataBinder)) {
// 调用被@InitBinder注解标记的方法。
Object returnValue = binderMethod.invokeForRequest(request, null, dataBinder);
if (returnValue != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"@InitBinder methods must not return a value (should be void): " + binderMethod);
}
}
}
}
在@InitBinder标记的方法中,允许用户使用WebDataBinder的registerCustomEditor方法,向其中注册相应的字段的转换规则也就是PropertyEditorSupport。
DataBinder中的registerCustomEditor方法如下:
@Override
public void registerCustomEditor(@Nullable Class<?> requiredType, @Nullable String field, PropertyEditor propertyEditor) {
getPropertyEditorRegistry().registerCustomEditor(requiredType, field, propertyEditor);
}
protected PropertyEditorRegistry getPropertyEditorRegistry() {
if (getTarget() != null) {
return getInternalBindingResult().getPropertyAccessor();
}
else {
return getSimpleTypeConverter();
}
}
protected AbstractPropertyBindingResult getInternalBindingResult() {
if (this.bindingResult == null) {
initBeanPropertyAccess();
}
return this.bindingResult;
}
public void initBeanPropertyAccess() {
Assert.state(this.bindingResult == null,
"DataBinder is already initialized - call initBeanPropertyAccess before other configuration methods");
// 这里会初始化AbstractPropertyBindingResult。实际上这里创建的是BeanPropertyBindingResult
this.bindingResult = createBeanPropertyBindingResult();
}
至此WebDataBinder初始化完成。PS:请记住BeanPropertyBindingResult后面会用。
2、执行转换赋值操作。
转换操作是通过WebDataBinder的bind方法来完成的。
bind方法是通过如下方法来调用的。
最开始是在resolveArgument中执行的,一路调用过来执行到bindRequestParameters方法。
@Override
protected void bindRequestParameters(WebDataBinder binder, NativeWebRequest request) {
ServletRequest servletRequest = request.getNativeRequest(ServletRequest.class);
Assert.state(servletRequest != null, "No ServletRequest");
ServletRequestDataBinder servletBinder = (ServletRequestDataBinder) binder;
// 开始执行WebDataBinder的bind方法。
servletBinder.bind(servletRequest);
}
至此开始由HandlerMethodArgumentResolver转到WebDataBinder中进行参数的转换操作。PS 这里最好把HandlerMethodArgumentResolver和WebDataBinder分开对待,因为WebDataBinder并不是专门给HandlerMethodArgumentResolver使用的。
// WebDataBinder的doBinder
@Override
protected void doBind(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
checkFieldDefaults(mpvs);
checkFieldMarkers(mpvs);
super.doBind(mpvs);
}
// DataBinder中的doBinder
protected void doBind(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
checkAllowedFields(mpvs);
checkRequiredFields(mpvs);
// 执行真正的赋值操作。
applyPropertyValues(mpvs);
}
请注意这里所说的赋值操作实际上是赋值给DataBinder中的target。也就是
@Nullable
private final Object target;
applyPropertyValues方法如下:
protected void applyPropertyValues(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
try {
// Bind request parameters onto target object.
getPropertyAccessor().setPropertyValues(mpvs, isIgnoreUnknownFields(), isIgnoreInvalidFields());
}
catch (PropertyBatchUpdateException ex) {
// Use bind error processor to create FieldErrors.
for (PropertyAccessException pae : ex.getPropertyAccessExceptions()) {
getBindingErrorProcessor().processPropertyAccessException(pae, getInternalBindingResult());
}
}
}
/**
* Return the underlying PropertyAccessor of this binder's BindingResult.
*/
protected ConfigurablePropertyAccessor getPropertyAccessor() {
return getInternalBindingResult().getPropertyAccessor();
}
这里面是调用上面初始化WebDataBinder时设置的BeanPropertyBindingResult,创建BeanWrapperImpl。
@Override
public final ConfigurablePropertyAccessor getPropertyAccessor() {
if (this.beanWrapper == null) {
this.beanWrapper = createBeanWrapper();
this.beanWrapper.setExtractOldValueForEditor(true);
this.beanWrapper.setAutoGrowNestedPaths(this.autoGrowNestedPaths);
this.beanWrapper.setAutoGrowCollectionLimit(this.autoGrowCollectionLimit);
}
return this.beanWrapper;
}
这里会用到BeanWrapperImpl
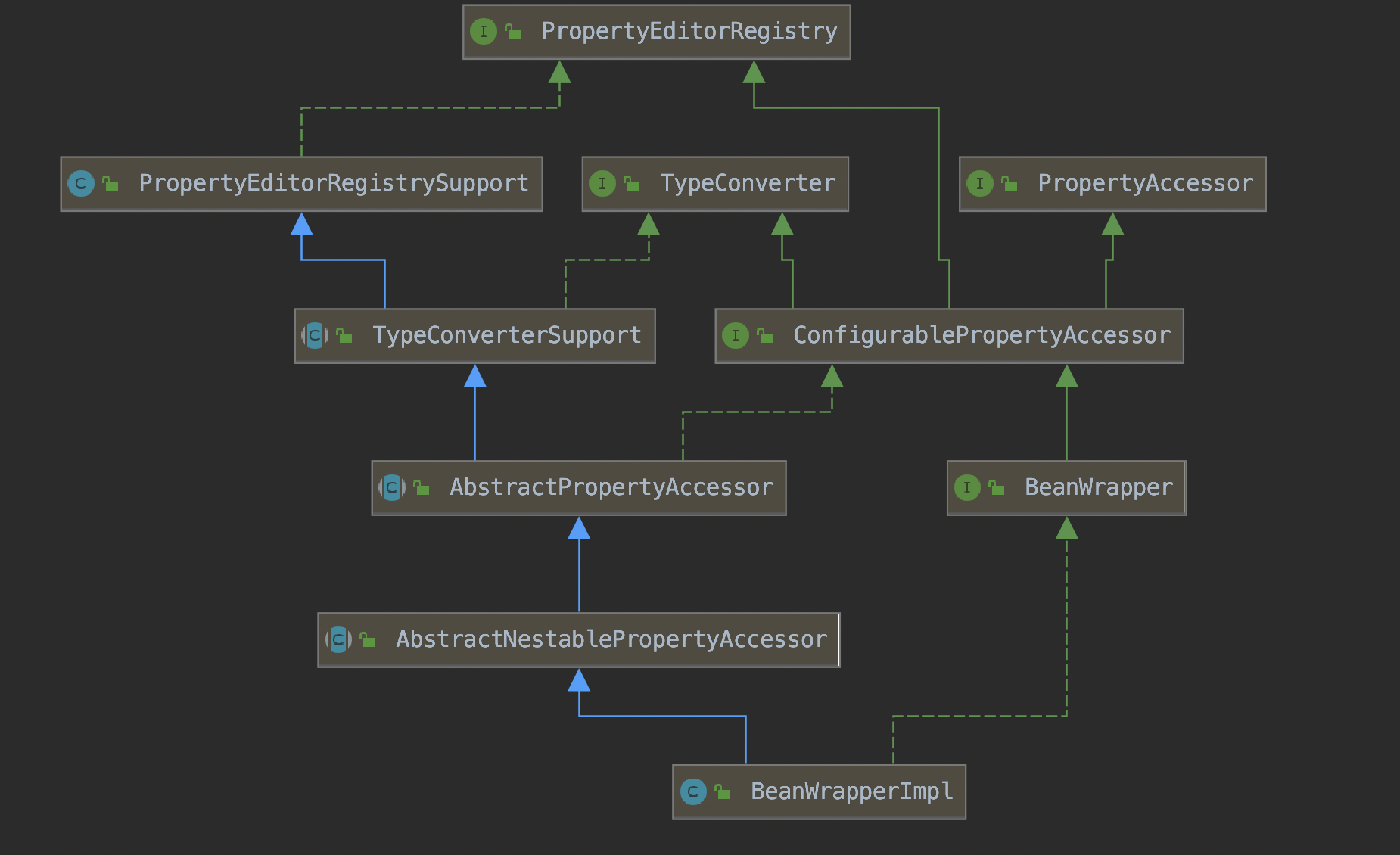
创建好BeanWrapperImpl之后,会继续调用BeanWrapperImpl的setPropertyValues方法。这里会调用BeanWrapperImpl的父类的setPropertyValues方法。
@Override
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, boolean ignoreUnknown, boolean ignoreInvalid)
throws BeansException {
List<PropertyAccessException> propertyAccessExceptions = null;
List<PropertyValue> propertyValues = (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues ?
((MutablePropertyValues) pvs).getPropertyValueList() : Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues()));
for (PropertyValue pv : propertyValues) {
try {
// This method may throw any BeansException, which won't be caught
// here, if there is a critical failure such as no matching field.
// We can attempt to deal only with less serious exceptions.
setPropertyValue(pv);
}
catch (NotWritablePropertyException ex) {
if (!ignoreUnknown) {
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, just ignore it and continue...
}
catch (NullValueInNestedPathException ex) {
if (!ignoreInvalid) {
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, just ignore it and continue...
}
catch (PropertyAccessException ex) {
if (propertyAccessExceptions == null) {
propertyAccessExceptions = new ArrayList<>();
}
propertyAccessExceptions.add(ex);
}
}
// If we encountered individual exceptions, throw the composite exception.
if (propertyAccessExceptions != null) {
PropertyAccessException[] paeArray = propertyAccessExceptions.toArray(new PropertyAccessException[0]);
throw new PropertyBatchUpdateException(paeArray);
}
}
调用AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor中的processLocalProperty方法如下:
private void processLocalProperty(PropertyTokenHolder tokens, PropertyValue pv) {
PropertyHandler ph = getLocalPropertyHandler(tokens.actualName);
if (ph == null || !ph.isWritable()) {
if (pv.isOptional()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Ignoring optional value for property '" + tokens.actualName +
"' - property not found on bean class [" + getRootClass().getName() + "]");
}
return;
}
else {
throw createNotWritablePropertyException(tokens.canonicalName);
}
}
Object oldValue = null;
try {
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
Object valueToApply = originalValue;
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(pv.conversionNecessary)) {
if (pv.isConverted()) {
valueToApply = pv.getConvertedValue();
}
else {
if (isExtractOldValueForEditor() && ph.isReadable()) {
try {
oldValue = ph.getValue();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (ex instanceof PrivilegedActionException) {
ex = ((PrivilegedActionException) ex).getException();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not read previous value of property '" +
this.nestedPath + tokens.canonicalName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// 这里执行真正的赋值操作。
valueToApply = convertForProperty(
tokens.canonicalName, oldValue, originalValue, ph.toTypeDescriptor());
}
pv.getOriginalPropertyValue().conversionNecessary = (valueToApply != originalValue);
}
ph.setValue(valueToApply);
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
PropertyChangeEvent propertyChangeEvent = new PropertyChangeEvent(
getRootInstance(), this.nestedPath + tokens.canonicalName, oldValue, pv.getValue());
if (ex.getTargetException() instanceof ClassCastException) {
throw new TypeMismatchException(propertyChangeEvent, ph.getPropertyType(), ex.getTargetException());
}
else {
Throwable cause = ex.getTargetException();
if (cause instanceof UndeclaredThrowableException) {
// May happen e.g. with Groovy-generated methods
cause = cause.getCause();
}
throw new MethodInvocationException(propertyChangeEvent, cause);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
PropertyChangeEvent pce = new PropertyChangeEvent(
getRootInstance(), this.nestedPath + tokens.canonicalName, oldValue, pv.getValue());
throw new MethodInvocationException(pce, ex);
}
}
这里会调用BeanWrapperImpl的方法
private CachedIntrospectionResults getCachedIntrospectionResults() {
if (this.cachedIntrospectionResults == null) {
this.cachedIntrospectionResults = CachedIntrospectionResults.forClass(getWrappedClass());
}
return this.cachedIntrospectionResults;
}
这里目的是要获取PropertyHandler,这个类的作用是为了封装target类的bean的setter和getter方法,方便赋值的时候调用。
获取ProptertyHandler对象后会执行convertForProperty方法,进行转换数据。
@Nullable
protected Object convertForProperty(
String propertyName, @Nullable Object oldValue, @Nullable Object newValue, TypeDescriptor td)
throws TypeMismatchException {
return convertIfNecessary(propertyName, oldValue, newValue, td.getType(), td);
}
@Nullable
private Object convertIfNecessary(@Nullable String propertyName, @Nullable Object oldValue,
@Nullable Object newValue, @Nullable Class<?> requiredType, @Nullable TypeDescriptor td)
throws TypeMismatchException {
Assert.state(this.typeConverterDelegate != null, "No TypeConverterDelegate");
try {
return this.typeConverterDelegate.convertIfNecessary(propertyName, oldValue, newValue, requiredType, td);
}
catch (ConverterNotFoundException | IllegalStateException ex) {
PropertyChangeEvent pce =
new PropertyChangeEvent(getRootInstance(), this.nestedPath + propertyName, oldValue, newValue);
throw new ConversionNotSupportedException(pce, requiredType, ex);
}
catch (ConversionException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
PropertyChangeEvent pce =
new PropertyChangeEvent(getRootInstance(), this.nestedPath + propertyName, oldValue, newValue);
throw new TypeMismatchException(pce, requiredType, ex);
}
}
这里会调用TypeConverterDelegate的convertIfNecessary方法。而TypeConverterDelegate是在创建BeanWrapperImpl对象的时候会默认在构造函数中创建。
public void setWrappedInstance(Object object, @Nullable String nestedPath, @Nullable Object rootObject) {
this.wrappedObject = ObjectUtils.unwrapOptional(object);
Assert.notNull(this.wrappedObject, "Target object must not be null");
this.nestedPath = (nestedPath != null ? nestedPath : "");
this.rootObject = (!this.nestedPath.isEmpty() ? rootObject : this.wrappedObject);
this.nestedPropertyAccessors = null;
this.typeConverterDelegate = new TypeConverterDelegate(this, this.wrappedObject);
}
TypeConverterDelegate中的convertIfNecessary方法如下(非常长。):
@Nullable
public <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable String propertyName, @Nullable Object oldValue, @Nullable Object newValue,
@Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor) throws IllegalArgumentException {
// Custom editor for this type?
PropertyEditor editor = this.propertyEditorRegistry.findCustomEditor(requiredType, propertyName);
ConversionFailedException conversionAttemptEx = null;
// No custom editor but custom ConversionService specified?
ConversionService conversionService = this.propertyEditorRegistry.getConversionService();
if (editor == null && conversionService != null && newValue != null && typeDescriptor != null) {
TypeDescriptor sourceTypeDesc = TypeDescriptor.forObject(newValue);
if (conversionService.canConvert(sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor)) {
try {
return (T) conversionService.convert(newValue, sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor);
}
catch (ConversionFailedException ex) {
// fallback to default conversion logic below
conversionAttemptEx = ex;
}
}
}
Object convertedValue = newValue;
// Value not of required type?
if (editor != null || (requiredType != null && !ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(requiredType, convertedValue))) {
if (typeDescriptor != null && requiredType != null && Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(requiredType) &&
convertedValue instanceof String) {
TypeDescriptor elementTypeDesc = typeDescriptor.getElementTypeDescriptor();
if (elementTypeDesc != null) {
Class<?> elementType = elementTypeDesc.getType();
if (Class.class == elementType || Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(elementType)) {
convertedValue = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) convertedValue);
}
}
}
if (editor == null) {
editor = findDefaultEditor(requiredType);
}
convertedValue = doConvertValue(oldValue, convertedValue, requiredType, editor);
}
boolean standardConversion = false;
if (requiredType != null) {
// Try to apply some standard type conversion rules if appropriate.
if (convertedValue != null) {
if (Object.class == requiredType) {
return (T) convertedValue;
}
else if (requiredType.isArray()) {
// Array required -> apply appropriate conversion of elements.
if (convertedValue instanceof String && Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(requiredType.getComponentType())) {
convertedValue = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) convertedValue);
}
return (T) convertToTypedArray(convertedValue, propertyName, requiredType.getComponentType());
}
else if (convertedValue instanceof Collection) {
// Convert elements to target type, if determined.
convertedValue = convertToTypedCollection(
(Collection<?>) convertedValue, propertyName, requiredType, typeDescriptor);
standardConversion = true;
}
else if (convertedValue instanceof Map) {
// Convert keys and values to respective target type, if determined.
convertedValue = convertToTypedMap(
(Map<?, ?>) convertedValue, propertyName, requiredType, typeDescriptor);
standardConversion = true;
}
if (convertedValue.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(convertedValue) == 1) {
convertedValue = Array.get(convertedValue, 0);
standardConversion = true;
}
if (String.class == requiredType && ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(convertedValue.getClass())) {
// We can stringify any primitive value...
return (T) convertedValue.toString();
}
else if (convertedValue instanceof String && !requiredType.isInstance(convertedValue)) {
if (conversionAttemptEx == null && !requiredType.isInterface() && !requiredType.isEnum()) {
try {
Constructor<T> strCtor = requiredType.getConstructor(String.class);
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(strCtor, convertedValue);
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
// proceed with field lookup
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No String constructor found on type [" + requiredType.getName() + "]", ex);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Construction via String failed for type [" + requiredType.getName() + "]", ex);
}
}
}
String trimmedValue = ((String) convertedValue).trim();
if (requiredType.isEnum() && trimmedValue.isEmpty()) {
// It's an empty enum identifier: reset the enum value to null.
return null;
}
convertedValue = attemptToConvertStringToEnum(requiredType, trimmedValue, convertedValue);
standardConversion = true;
}
else if (convertedValue instanceof Number && Number.class.isAssignableFrom(requiredType)) {
convertedValue = NumberUtils.convertNumberToTargetClass(
(Number) convertedValue, (Class<Number>) requiredType);
standardConversion = true;
}
}
else {
// convertedValue == null
if (requiredType == Optional.class) {
convertedValue = Optional.empty();
}
}
if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(requiredType, convertedValue)) {
if (conversionAttemptEx != null) {
// Original exception from former ConversionService call above...
throw conversionAttemptEx;
}
else if (conversionService != null && typeDescriptor != null) {
// ConversionService not tried before, probably custom editor found
// but editor couldn't produce the required type...
TypeDescriptor sourceTypeDesc = TypeDescriptor.forObject(newValue);
if (conversionService.canConvert(sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor)) {
return (T) conversionService.convert(newValue, sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor);
}
}
// Definitely doesn't match: throw IllegalArgumentException/IllegalStateException
StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder();
msg.append("Cannot convert value of type '").append(ClassUtils.getDescriptiveType(newValue));
msg.append("' to required type '").append(ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType)).append("'");
if (propertyName != null) {
msg.append(" for property '").append(propertyName).append("'");
}
if (editor != null) {
msg.append(": PropertyEditor [").append(editor.getClass().getName()).append(
"] returned inappropriate value of type '").append(
ClassUtils.getDescriptiveType(convertedValue)).append("'");
throw new IllegalArgumentException(msg.toString());
}
else {
msg.append(": no matching editors or conversion strategy found");
throw new IllegalStateException(msg.toString());
}
}
}
if (conversionAttemptEx != null) {
if (editor == null && !standardConversion && requiredType != null && Object.class != requiredType) {
throw conversionAttemptEx;
}
logger.debug("Original ConversionService attempt failed - ignored since " +
"PropertyEditor based conversion eventually succeeded", conversionAttemptEx);
}
return (T) convertedValue;
}
上面的方法调用doConvertValue来进行value的转换。
@Nullable
private Object doConvertValue(@Nullable Object oldValue, @Nullable Object newValue,
@Nullable Class<?> requiredType, @Nullable PropertyEditor editor) {
Object convertedValue = newValue;
if (editor != null && !(convertedValue instanceof String)) {
// Not a String -> use PropertyEditor's setValue.
// With standard PropertyEditors, this will return the very same object;
// we just want to allow special PropertyEditors to override setValue
// for type conversion from non-String values to the required type.
try {
editor.setValue(convertedValue);
Object newConvertedValue = editor.getValue();
if (newConvertedValue != convertedValue) {
convertedValue = newConvertedValue;
// Reset PropertyEditor: It already did a proper conversion.
// Don't use it again for a setAsText call.
editor = null;
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("PropertyEditor [" + editor.getClass().getName() + "] does not support setValue call", ex);
}
// Swallow and proceed.
}
}
Object returnValue = convertedValue;
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isArray() && convertedValue instanceof String[]) {
// Convert String array to a comma-separated String.
// Only applies if no PropertyEditor converted the String array before.
// The CSV String will be passed into a PropertyEditor's setAsText method, if any.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Converting String array to comma-delimited String [" + convertedValue + "]");
}
convertedValue = StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString((String[]) convertedValue);
}
if (convertedValue instanceof String) {
if (editor != null) {
// Use PropertyEditor's setAsText in case of a String value.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Converting String to [" + requiredType + "] using property editor [" + editor + "]");
}
String newTextValue = (String) convertedValue;
return doConvertTextValue(oldValue, newTextValue, editor);
}
else if (String.class == requiredType) {
returnValue = convertedValue;
}
}
return returnValue;
}
private Object doConvertTextValue(@Nullable Object oldValue, String newTextValue, PropertyEditor editor) {
try {
editor.setValue(oldValue);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("PropertyEditor [" + editor.getClass().getName() + "] does not support setValue call", ex);
}
// Swallow and proceed.
}
// 最终在这里执行了用户自定义的PropertyEditorSupport。设置值
editor.setAsText(newTextValue);
// 这里获取target的值,是一个object对象。
return editor.getValue();
}
获取值后还需通过BeanPropertyHandler类中的setValue将值设置到BeanWrapperImpl中的wrappedObject字段。
@Override
public void setValue(final @Nullable Object value) throws Exception {
final Method writeMethod = (this.pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) this.pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
this.pd.getWriteMethod());
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
return null;
});
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () ->
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value), acc);
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {
throw ex.getException();
}
}
else {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value);
}
}
最终将值设置到BeanWrapperImpl中。
AbstractPropertyBindingResult中的target是这样设置进去的
protected AbstractPropertyBindingResult createBeanPropertyBindingResult() {
// 这个的getTarget就是获取WebDataBinder中的target。将这个对象设置进AbstractPropertyBindingResult中
BeanPropertyBindingResult result = new BeanPropertyBindingResult(getTarget(),
getObjectName(), isAutoGrowNestedPaths(), getAutoGrowCollectionLimit());
if (this.conversionService != null) {
result.initConversion(this.conversionService);
}
if (this.messageCodesResolver != null) {
result.setMessageCodesResolver(this.messageCodesResolver);
}
return result;
}
而target对象最终通过如下的方式设置到BeanWrapperImpl中。
@Override
public final ConfigurablePropertyAccessor getPropertyAccessor() {
if (this.beanWrapper == null) {
this.beanWrapper = createBeanWrapper();
this.beanWrapper.setExtractOldValueForEditor(true);
this.beanWrapper.setAutoGrowNestedPaths(this.autoGrowNestedPaths);
this.beanWrapper.setAutoGrowCollectionLimit(this.autoGrowCollectionLimit);
}
return this.beanWrapper;
}
protected BeanWrapper createBeanWrapper() {
if (this.target == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot access properties on null bean instance '" + getObjectName() + "'");
}
// 在这里最终将BeanPropertyBindingResult中的target值设置到BeanWrapperImpl中。
return PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this.target);
}
至此后面如果设置BeanWrapperImpl中的wrappedObject字段其实就是直接设置WebDataBinder中的target值,因为它们都是同一个对象。
整个WebDataBinder的工作原理如下: